UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography Optional for UPSC > Trade Balance
Trade Balance | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Balance of Trade
- The term ‘trade’ refers to buying and selling of goods. However, when it is performed on an international scale, it is called imports and exports. Balance of Trade (BOT) mentions the import and exports made by a nation’s economy within a specific year. BOT only records tangible items.
- Balance of Trade or Trade balance is also called an International trade balance.
- Balance of trade (BOT) is the difference between the value of a country’s imports and exports for a given period and is the largest component of a country’s balance of payments (BOP).
(i) Balance of Payment is a combination of accounts that shows the commercial transactions concluded by a country within a specific period with other countries. These accounts reflect every monetary transaction, i.e. commodities, services, and incomes during that period.
(ii) The Balance of Payment (BOP) combines every private and public investment to find out the money inflow and outflow in an economy over a specific period. The ideal status of BOP should be zero, which indicates that the money coming into the country is equal to the money going out of the country. However, this situation is highly unlikely. Therefore, if it is negative, then it indicates deficit, and if positive, it means a surplus. - BOT portrays the variability of imports and exports made by a country during a period. In case a country achieves an equal status in terms of imports and exports, then this situation is regarded as Trade Equilibrium.
- However, if the former surpasses the latter, then it creates a Trade Deficit, which is not a favorable situation for a country. On the other hand, if the export value exceeds that of imports, then it creates a Trade Surplus, which puts an economy in a favorable situation.
- The balance of trade of a nation is a part of the current account. The current account also comprises other transactions like the income from the NIIP or the net international investment position and international aid. When a country’s current account is in surplus, its net international asset position rises accordingly.
- In 2012-13, India had a huge trade deficit, import exceeds export by around $ 195.6 billion.
- A trade deficit can be for two reasons;
- Not enough domestic production for consumption
(i) For instance, India may be producing a lot of milk but still not enough for the total milk demand in the country. As such, India may choose to import milk.
(ii) Crude oil, pulse, and edible oil production are not enough to meet the domestic demand, we need to import. - Costly domestic production is a result of consumers choosing foreign goods.
In the case of Steel, we have enough capacity for production but the cost of production is higher as compared to China, hence Indian consumers such as automobile companies are buying Chinese steel at a cheaper rate for the same quality.
- Not enough domestic production for consumption
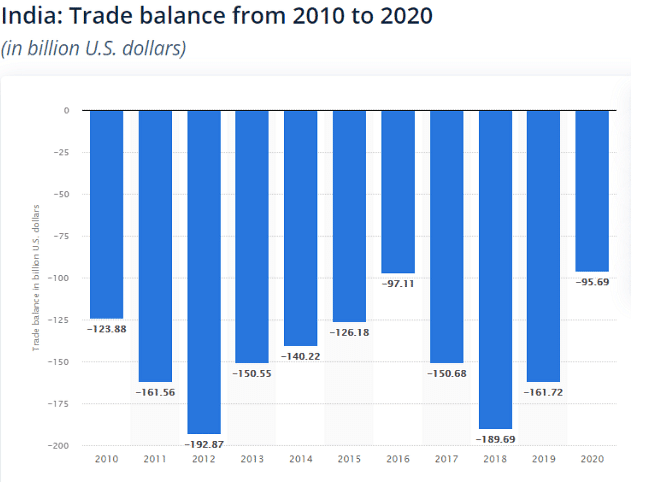
India’s Trade Surplus
- India had a trade surplus with nine of the 20-odd countries in the Indo-Pacific region, which covers countries from the western shores of the American continent to the eastern coast of Africa, in 2020, a study by the industry chamber Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) showed.
- India’s trade with select Indo-Pacific economies increased eight times over the last 19 years, reaching $262 billion in 2020 from $33 billion in 2001, with the US being the largest trade partner with a dominant share of 29% in 2020.
- The Indo-Pacific region comprises Australia, Bangladesh, Chile, Colombia, France, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, Kenya, South Korea, Maldives, Mauritius, Malaysia, Mexico, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam, the UAE, and the US.
- It consists of 44% of world surface area and accounts for 62% of global gross domestic product (GDP), with more than 50% of global trade traversing through its waters.
- As per the study, India had a trade surplus with eight countries – Kenya, Mauritius, France, Fiji, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Maldives, and the US – from 2016 to 2020.
- India’s imports from these economies accounted for 36% of its global imports in 2020.
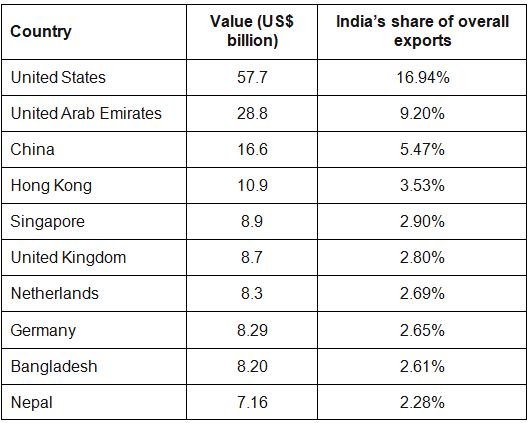
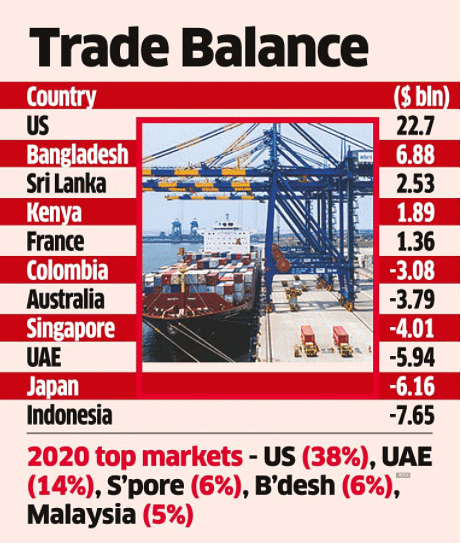
India’s Trade Deficit
- North-East Asia constituting of China, Japan, Korea RP, Hong Kong, Taiwan, etc. accounted for the trade of USD 124.95 billion in 2015-16 which was 19.42% of India’s total trade.
- Exports to NEA countries were USD 30.84 billion (11.76% of India’s exports) and imports from NEA countries were USD 94.11 billion (24.7% of India’s imports).
- India’s trade deficit with NEA countries in 2015-16 stood at USD 63.28 billion which is 53.3% of India’s total trade deficit (USD 118.72 billion).
- China accounts for 56.6% of NEA’s total trade, while Hong Kong, Japan, and Korea contribute 14.5%, 11.6 %, and 13.3 % respectively. Taiwan, Mongolia, Macau & DPR Korea make up the balance 4%.
- While China constitutes 10.99 % of India’s total trade, it accounts for over 44.38 % of our trade deficit.
- Apart from trade, the NEA countries together are amongst the most dominant economic players in the world at present with total exports of USD 4233 billion & imports of USD 3548.7 billion, and USD 7781.6 billion of total trade.
- China, Korea, Taiwan, and Hong Kong are leading economies with high growth rates; they could be significant investment partners for India. Engagement with NEA is also integral to India’s ‘Act East Policy’ which seeks to expand India’s economic engagement beyond the traditional spheres of North America and Europe.
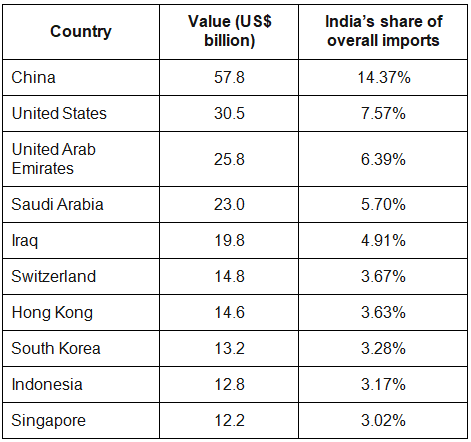
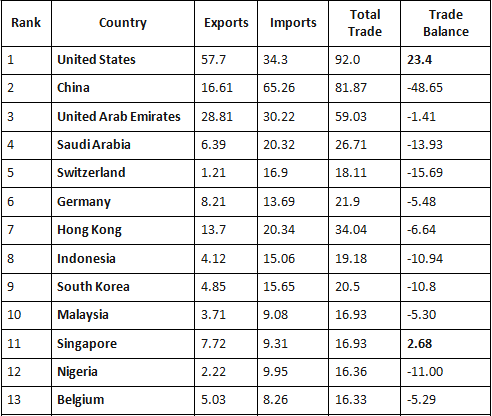
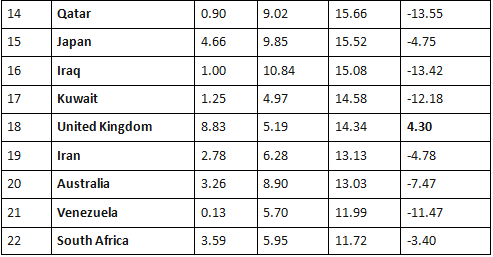
Largest trading partners with India
India’s largest trade partners with their total trade (sum of imports and exports) in billions of US dollars for the financial year 2019–20 were as follows:
The document Trade Balance | Geography Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Geography Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Trade Balance - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the meaning of balance of trade? |  |
Ans. The balance of trade refers to the difference between the value of a country's exports and the value of its imports. If the value of exports is higher than the value of imports, it is known as a trade surplus, and if the value of imports is higher, it is known as a trade deficit.
| 2. How is the balance of trade calculated? |  |
Ans. The balance of trade is calculated by subtracting the value of imports from the value of exports. The formula is:
Balance of Trade = Value of Exports - Value of Imports
This calculation provides an indication of a country's trade position and whether it has a surplus or deficit.
| 3. What factors can affect the balance of trade? |  |
Ans. Several factors can affect the balance of trade. Some of the key factors include:
1. Exchange rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the competitiveness of exports and imports, affecting the balance of trade.
2. Economic conditions: The overall economic health of a country can influence its export and import levels, thereby affecting the balance of trade.
3. Trade policies: Government policies such as tariffs, quotas, and subsidies can impact the balance of trade by influencing the cost and availability of imports and exports.
4. Consumer preferences: Changes in consumer preferences for certain products or brands can affect the demand for imports and exports, impacting the balance of trade.
5. Global economic conditions: Economic conditions in other countries can also affect a country's balance of trade, as it can impact the demand for exports and imports.
| 4. Why is the balance of trade important for a country? |  |
Ans. The balance of trade is important for a country as it provides insights into its economic competitiveness and trade relationships with other nations. A trade surplus indicates that a country is exporting more than it is importing, which can lead to increased domestic production, job creation, and economic growth. On the other hand, a trade deficit suggests that a country is importing more than it is exporting, which can lead to a reliance on foreign goods, increased borrowing, and potential economic vulnerabilities.
| 5. How does the balance of trade impact the currency value? |  |
Ans. The balance of trade can impact the currency value of a country. If a country has a trade surplus, indicating that it is exporting more than it is importing, it leads to an increase in demand for its currency. This increased demand can strengthen the currency's value. Conversely, a trade deficit, where a country is importing more than it is exporting, can lead to a decrease in demand for its currency, potentially weakening its value. The balance of trade, therefore, plays a role in determining the relative strength or weakness of a country's currency.
Related Searches
















