Lab Manual: Cleaning Capacity of Soap in Hard and Soft Water - Class 10 PDF Download
Objective
To study the comparative cleansing capacity of a sample of soap in soft and hard water.Materials Required
Tap water (or well water), distilled water, calcium hydrogen carbonate or calcium sulphate, soap sample, test tubes, test tube stand, glass rod, measuring cylinder (50 ml) and a measuring scale.
Theory
Hardness of water is due to the presence of the salts of calcium and magnesium (hydrogen carbonates, chlorides and sulphates) in water. Hardness is of two types, i.e. temporary hardness and permanent hardness.Temporary hardness of water is due to the presence of calcium and magnesium bicarbonates in water and can be remove by boiling or by adding Na2CO3.
Permanent hardness of water is due to the presence of chloride and sulphates of calcium and magnesium and can be remove by using ion exchange.
When soap is added to hard water, it forms a scum by reacting with the salts of magnesium and calcium ions. This scum is insoluble and floats on the surface of water. Calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water produce curdy white precipitates of calcium and magnesium salts of fatty acids.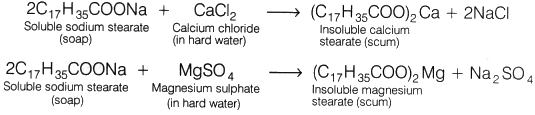 These scum creates hindrance to good washing because it adheres to fibres of the cloth as gummy mass. Therefore, the presence of calcium and magnesium salts in water precipitates the soap thereby reducing its cleansing power and hence, foaming capacity.
These scum creates hindrance to good washing because it adheres to fibres of the cloth as gummy mass. Therefore, the presence of calcium and magnesium salts in water precipitates the soap thereby reducing its cleansing power and hence, foaming capacity.
Note:
- When soap is shaken in soft water which does not contain Ca+2 and Mg+2 ions, lot of lather is formed which helps in cleaning clothes.
- When soap is shaken with hard water which contains Ca+2 and Mg+2 ions, very less lather is formed and cleaning of clothes does not take place.
Procedure
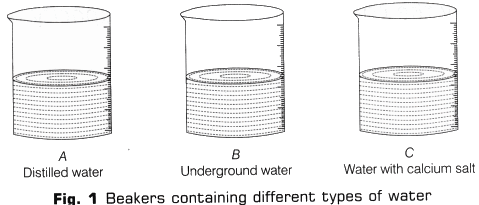
- Take three beakers and label them as A, B and C.
- Add 20 ml of distilled water in beaker A, 20 ml of underground water in beaker B and 20 ml of distilled water in beaker C (Fig. 1).
- Add 2g of calcium sulphate (or calcium hydrogen carbonate) to 20 ml of distilled water taken in C.
- Stir the contents of beaker C with the help of clean glass rod till calcium sulphate (or calcium hydrogen carbonate) dissolves in water.
- Add equal amount of weighed soap to all three beakers A, B and C.
- Stir the contents of these beakers with separate clean glass rods.
- Place three tubes in a test tube stand and label them as P, Q and R (Fig. 2).
- Pour 5 ml of the above prepared soap solution from the beakers in the corresponding test tubes.
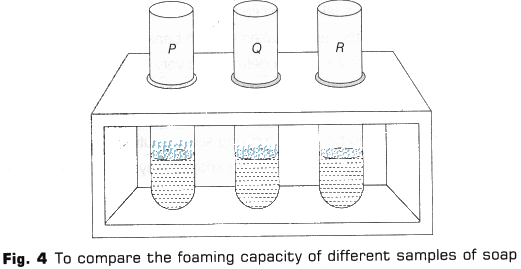
- Take test tube P and shake it ten times by placing thumb on its mouth (Fig. 3).
- On shaking the test tube, foam or lather will be formed. Measure the length of foam produced immediately with the help of a measuring scale.
- Similarly, repeat steps 9 and 10 with the remaining two samples(Fig. 4).
Observations
- Mass of sample of soap taken in each beaker = _______
- Volume of distilled water and underground water added in each beaker = _______ mL
- Volume of soap sample taken in each test tube = _______ mL
- Number of times each test tube shaken = _______
Calculations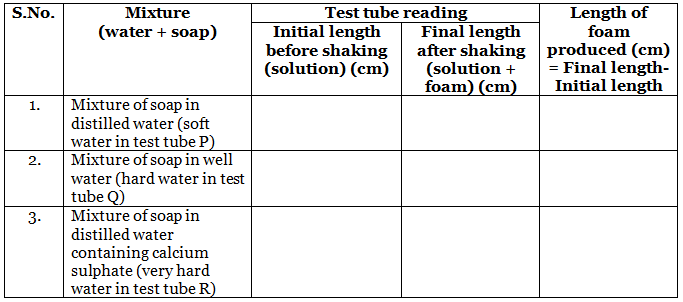
Result
- Soap solution in test tube P produces the maximum length of foam. Thus, distilled water (soft water) has the most cleansing capability.
- Soap solution in test tube 0 produces smaller length of foam as compare to test tube P. Thus, underground water has less cleansing capability than soft water.
- Soap solution in test tube R produces minimum length of foam. Thus, distilled water with calcium hydrogen carbonate has least cleansing capability.
Precautions
- Use similar soap for each water sample.
- Stir the mixture carefully while dissolving soap in water for avoiding spilling of soap solution.
- The quantity of soap sample taken in all solutions should be same.
- The amount of distilled water sample taken in each beaker should be same.
- The mass of the soap sample must be determined very carefully using a physical balance.
- Shake every test tube for equal number of times in a similar manner in order to avoid any disparity.
- Measure the length of the foam produced immediately after its production.
- Use wire gauze for warming beaker containing soap solution if needed.
- For the experiment of cleansing capacity of a soap, always use cloth washing soap and not bathing soap or the synthetic detergent.















