What is an Adverb? | English Grammar Class 5 PDF Download
What is an adverb?
Adverbs are words that give us more information about a verb. They tell us how, when, where, how often, or why an action happens.
For example: In the sentence "The fox is very clever," the word "very" is an adverb that describes the extent of the cleverness. Similarly, in "The tortoise walked slowly," "slowly" explains how the tortoise walked.
Kinds of Adverbs
1. Adverb of Manner: Adverb of Manner tells us how an action has been performed; as:
- The master treated the servant cruelly.
- The thief crept into the house quietly.
2. Adverb of Place: Adverb of Place tells us where the action has taken place; as:
- God is present everywhere.
- The ring was found nowhere.
3. Adverb of Time: Adverb of Time tells us when the action has taken place; as:
- I wake up early.
- He has not come home yet.
4. Adverb of Frequency: Adverb of Frequency shows how often an action has been done; as:
- He never tells a lie.
- She rarely speaks to strangers.
5. Adverb of Degree: Adverb of Degree shows how much and what extent a thing is done; as:
- Your logic is not entirely wrong.
- I am extremely sorry for the inconvenience you are facing.
6. Adverb of Reasons: Adverb of Reasons show why an action is performed.
- He ran fast in order to catch the train.
- I could not go because I was ill.
- The school was closed on account of Holi.
Comparison of Adverbs
Some adverbs, like adjectives, have three degrees of comparison: Positive, Comparative and Superlative.
1. If the adverb is of one syllable, we form the Comparative by adding “er”, and the Superlative by adding “est” to the Positive; as:
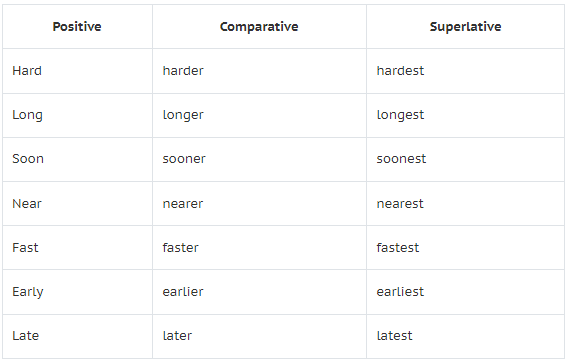
For example:
- I stay near our school. (Positive)
- You stay nearer to our school. (Comparative)
- He stays nearest to our school. (Superlative)
Adverbs ending in ly form the Comparatives by adding more and the superlatives by adding most; as:
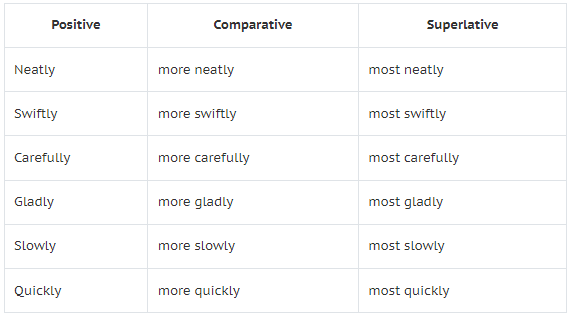
For example:
- Ravi played the guitar skillfully. (Positive)
- Rajan played the guitar more skillfully. (Comparative)
- Raju played the guitar most skillfully of all. (Superlative)
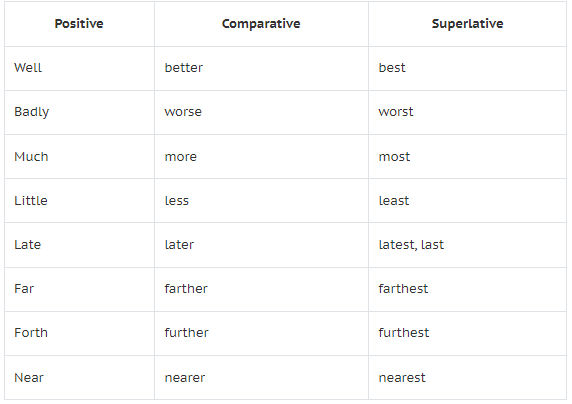
A few Adverbs are compared irregularly:
For example:
- Usha sings well. (Positive)
- Asha sings better. (Comparative)
- Lata sings the best. (Superlative)
Some adverbs cannot be compared include: Thus, now, then, here, there, once, seldom, often, twice, very, almost, half, every day, consequently, tomorrow.
Note:
- In general, adverbs of time, adverbs of place, adverbs of frequency, and adverbs of degree cannot be compared.
- Adverbs of manner are mostly compared.
|
37 videos|289 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on What is an Adverb? - English Grammar Class 5
| 1. What is an adverb and how is it used in a sentence? |  |
| 2. Can you provide examples of different types of adverbs? |  |
| 3. How do adverbs differ from adjectives? |  |
| 4. Are there any common mistakes to avoid when using adverbs? |  |
| 5. How can I identify adverbs in a sentence? |  |

















