Sustainable Development | Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
Historical Context - Sustainable Development

- The historical context of sustainable development is rooted in the debate between development and the environment. Traditionally, the economic growth model of development has been characterized by modern technology, industrialization, and urbanization. Western countries initially followed this model and prescribed it to less developed countries, believing that they would eventually catch up if they adopted the Western economic and social systems.
- However, the consequences of adopting the Western model of development were not entirely positive. Economic growth occurred, but it also widened the gap between developed and developing countries and increased economic disparities within societies. This realization led to a shift in development thinking, incorporating additional criteria such as distributive justice, equity, and overall quality of life improvements for the masses.
- Furthermore, the examination of the impact of the Western model of development on the global environment led to its critical reconsideration. The pursuit of industrialization and resource-exploitative technologies caused significant environmental degradation, threatening the existence of various living species. This environmental degradation is marked by the large-scale extraction of finite natural resources, loss of forests and biodiversity, depletion of the ozone layer, and various forms of pollution.
- The increasing awareness of environmental problems led to the emergence of environmentalism, which added an important dimension to the development discourse and caused a paradigm shift in our vision of development. This growing awareness highlighted the need for both development and environmental protection, eventually leading to the concept of sustainable development.
- Sustainable development, as defined in the report of the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) titled "Our Common Future" (1987), aims to reconcile the goals of development and environmental protection. It emphasizes the importance of ensuring that economic development and sound environmental management are complementary aspects of the same agenda, as without one, the other will inevitably fail. This concept has since become an essential aspect of global development discussions and policies.
Sustainable Development: Genesis and Evolution
The concept of "sustainable development" has evolved over time through various international events and publications. It first emerged in the 1981 document, "World Conservation Strategy: Living Resource Conservation for Sustainable Development," published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), and the UN Environment Programme (UNEP). The document defined sustainable development as considering social and ecological factors, along with economic ones, and taking into account both short-term and long-term consequences of various actions.- The United Nations set up the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) in 1983, which published the report "Our Common Future" in 1987. This report provided the first official definition of sustainable development and suggested an international strategy for addressing global environmental issues. It also brought about a paradigm shift in conventional thinking regarding the notion of "development."
- The 1991 document "Caring for the Earth: A Strategy for Sustainable Living" emphasized the importance of local people's participation in global nature conservation. In 1992, the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), known as the "Earth Summit," further developed the concept of sustainable development by establishing linkages between environment and development. The summit produced several key documents and conventions, including the Rio Declaration, which set out principles for environmental conservation and sustainable development.
- Since then, various international events have aimed to assess progress made by nations towards sustainable development, such as the World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) held in Johannesburg in 2002. The scope of sustainable development has broadened to include economic development, social development, and environmental protection.
- The concept of sustainable development has come a long way since its inception, evolving through various international events and publications to encompass a wide range of issues related to environment and development. The concept now focuses on balancing economic, social, and environmental factors, emphasizing the need for global cooperation and local participation to achieve a sustainable future for all.
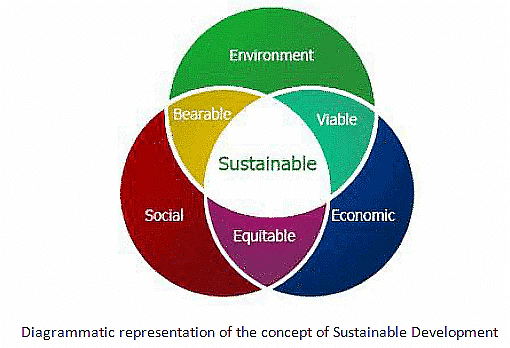
Concept of Sustainable Development as Defined in Our Common Future (1987)
The concept of sustainable development, as defined in the report Our Common Future (1987), refers to a development model that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This concept encompasses two key notions: (i) addressing the needs of the world's poor as a priority, and (ii) recognizing the limitations of technology and social organization in meeting the present and future needs of the environment.- It is crucial to understand the core issues addressed by this definition. Firstly, sustainable development emphasizes the importance of economic growth, not only for poverty reduction but also for meeting human needs and aspirations for a better life. Secondly, it acknowledges the limitations of the environment's capacity to meet the needs of present and future generations due to the pressures of societal demands and the use of modern technologies in extracting and utilizing limited natural resources.
- To achieve sustainable development, it is necessary to address various requirements, including meeting the basic needs of all individuals and providing equal opportunities for everyone to fulfill their aspirations. This involves promoting values that encourage responsible consumption within ecologically sustainable boundaries and ensuring that demographic developments are in harmony with the ecosystem's productive potential. Moreover, sustainable development necessitates the preservation of natural systems, such as the atmosphere, waters, soils, and living beings, ensuring equitable access to limited resources, and promoting technological advancements that mitigate environmental pressures.
- Additionally, sustainable development involves the prudent use of non-renewable resources, conservation of plant and animal species, and minimizing adverse impacts on air, water, and other natural elements to maintain the ecosystem's overall integrity. In essence, sustainable development is a process that aligns the exploitation of resources, investment direction, technological development, and institutional change with the goal of enhancing both current and future potential to meet human needs and aspirations.
Criticisms of the Concept of Sustainable Development
Sustainable development, as defined by the Brundtland Commission, has been subject to various criticisms from scholars who argue that the concept is not only logically contradictory and semantically ambivalent, but also vague and ambiguous in its definition. These criticisms also highlight the difficulties in operationalizing the concept and question the underlying assumptions and political motives.1. Sustainable Development: Logical Contradiction and Semantic Ambivalence
- Some scholars, like Ramesh Deewan, argue that the concept of sustainable development represents a contradiction in terms. They believe that development and sustainability are not only incompatible but also contradictory. In other words, any form of development - economic growth, growth with equity, improvement in the quality of life, or modernization - inevitably leads to increased consumption and exploitation of natural resources.
- Wolfgang Sachs suggests that linking sustainability to development creates semantic ambivalence. He argues that the focus of sustainability has shifted from nature to development, making development the primary concern and nature the critical factor to be monitored. This shift results in the meaning of sustainability changing from the conservation of nature to the conservation of development.
2. Definition of Sustainable Development: Vague and Ambiguous
- Scholars like Sukhamoy Chakravorty argue that the phrase "sustainable development" is imprecise and therefore can mean anything to anyone. This ambiguity allows individuals with different viewpoints, philosophical positions, goals, and strategies to use the same moral vocabulary of social justice and economic rhetoric of sustainable development. As a result, the term is used to justify various actions and criticize those with differing opinions.
- V. Ratna Reddy (1995) points out the difficulty in balancing the interests of present and future generations, as the concept of needs differs across environments, cultures, and generations. C. R. (2002) Reddy adds that despite the creation of a United Nations machinery around "sustainable development," the world is still waiting for a clear definition of the concept.
- K. R. Nayar (1994) views the concept of sustainable development as a political tool that is often anti-south, anti-poor, and anti-ecological. He contends that the concept has emerged from countries that practice unsustainable resource use and that it often focuses on affluence rather than basic needs.
Conclusion
The concept of sustainable development has evolved significantly over time, incorporating economic, social, and environmental aspects while emphasizing the need for global cooperation and local participation. However, the concept has faced various criticisms, including logical contradictions, semantic ambivalence, and ambiguity in its definition. Despite these challenges, sustainable development remains an essential part of global development discussions and policies, seeking to balance the needs of present and future generations while addressing environmental limitations and promoting equitable growth.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Sustainable Development
What is the historical context of sustainable development?
The historical context of sustainable development is rooted in the debate between development and the environment. As the negative consequences of the Western model of development became more evident, such as widening economic disparities and environmental degradation, the need for a new approach to development emerged, leading to the concept of sustainable development.
How has the concept of sustainable development evolved over time?
The concept of sustainable development has evolved through various international events and publications. Key milestones include the 1981 document "World Conservation Strategy," the 1987 report "Our Common Future," the 1991 document "Caring for the Earth," and the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in Rio de Janeiro. The concept has broadened to include economic development, social development, and environmental protection.
How is sustainable development defined in Our Common Future (1987)?
Sustainable development is defined as a development model that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The concept emphasizes the importance of economic growth while recognizing the limitations of the environment's capacity to meet the needs of present and future generations.
What are some key requirements for achieving sustainable development?
Key requirements for achieving sustainable development include meeting the basic needs of all individuals, providing equal opportunities for everyone, promoting responsible consumption within ecologically sustainable boundaries, preserving natural systems, ensuring equitable access to limited resources, and promoting technological advancements that mitigate environmental pressures.
What are some criticisms of the concept of sustainable development?
Criticisms of sustainable development include the argument that it is a logical contradiction and semantically ambivalent, as development and sustainability can be seen as incompatible. Critics also argue that the definition is vague and ambiguous, allowing people with different viewpoints to use the term for their own purposes. Additionally, some argue that the concept is a political tool that is often anti-south, anti-poor, and anti-ecological.
|
120 videos|428 docs
|





















