Grade 11 Exam > Grade 11 Notes > Biology for Grade 11 > Glossary: Biological Classification
Glossary: Biological Classification | Biology for Grade 11 PDF Download
Domain: A domain is the highest rank of organisms. The three domains of life are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
Kingdom: The Kingdom happens to be the highest classification after domain into which living organisms are grouped. At present, there are five known kingdoms till now.
In Linnaeus' time a Two Kingdom system of classification with Plantae and Animalia kingdoms was developed that included all plants and animals respectively.
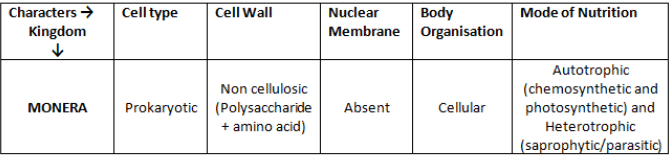
Kingdom Monera
Bacteria are the sole members of the Kingdom Monera. They are the most abundant micro-organisms.
- Archaebacteria: These bacteria are special since they live in some of the most harsh habitats. Archaebacteria differ from other bacteria in having a different cell wall structure and this feature is responsible for their survival in extreme conditions.
- Eubacteria: There are thousands of different eubacteria or ‘true bacteria’. They are characterised by the presence of a rigid cell wall, and if motile, a flagellum.
- Cyanobacteria: The cyanobacteria (also referred to as blue-green algae) have chlorophyll a similar to green plants and are photosynthetic autotrophs.
- Heterocysts: Some of the organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts, e.g., Nostoc and Anabaena
- Chemosynthetic autotrophic: Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria oxidise various inorganic substances such as nitrates, nitrites and ammonia and use the released energy for their ATP production. They play a great role in recycling nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous, iron and sulphur.
- Heterotrophic Bacteria: Heterotrophic bacteria are most abundant in nature. The majority are important decomposers. They are helpful in making curd from milk, production of antibiotics, fixing nitrogen in legume roots, etc. Some are pathogens causing damage to human beings, crops, farm animals and pets.
- Mycoplasma: The Mycoplasma are organisms that completely lack a cell wall. They are the smallest living cells known and can survive without oxygen.
Kingdom Protista
All single-celled eukaryotes are placed under Protista, but the boundaries of this kingdom are not well defined that whether its a plant or photosynthetic protistan.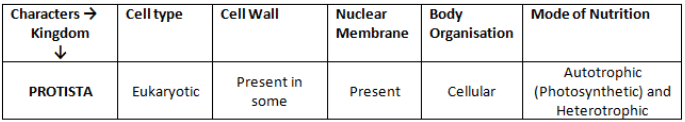
- Diatomaceous earth: Diatoms have left behind large amount of cell wall deposits in their habitat; this accumulation over billions of years is referred to as ‘diatomaceous earth’.
- Pellicle: Instead of a cell wall in Euglenoids, they have a protein rich layer called pellicle which makes their body flexible.
- Plasmodium: Under suitable conditions, slime moulds form an aggregation called plasmodium which may grow and spread over several feet.
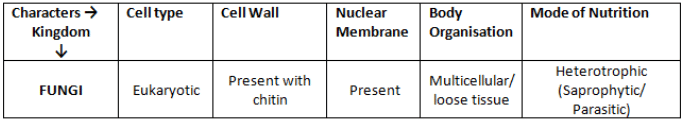
Kingdom Fungi
- Hyphae: fungi are filamentous. Their bodies consist of long, slender thread-like structures called hyphae.
- Mycelium: The network of hyphae is known as mycelium.
- Coenocytic hyphae: Some hyphae are continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm – these are called coenocytic hyphae.
- Saprophytes: Most fungi are heterotrophic and absorb soluble organic matter from dead substrates and hence are called saprophytes.
- Parasites: Fungi that depend on living plants and animals are called parasites.
- Plasmogamy: Fusion of protoplasms between two motile or non-motile gametes called plasmogamy.
- Karyogamy: Fusion of two nuclei called karyogamy.
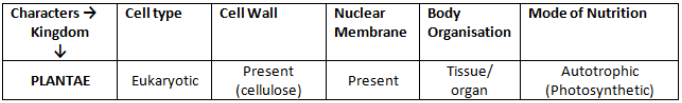
Kingdom Plantae
- Conidiophores: The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores.
- Ascospores: Ascomycetes sexual spores are called ascospores which are produced endogenously in sac like asci (singular ascus).
- Ascocarps: These asci are arranged in different types of fruiting bodies called ascocarps.
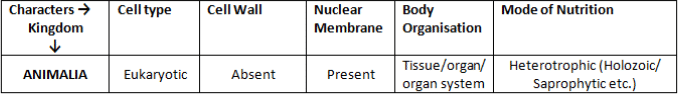
Kingdom Animalia
- Imperfect Fungi: Deutromycetes are commonly known as imperfect fungi because only the asexual or vegetative phases of these fungi are known.
- Conidia: The deuteromycetes reproduce only by asexual spores known as conidia.
Viruses, Viroids and Lichens
- Virus: A virus is a nucleoprotein and the genetic material is infectious. In general, viruses that infect plants have single stranded RNA and viruses that infect animals have either single or double stranded RNA or double stranded DNA.
- Capsomere: The protein coat called capsid made of small subunits called capsomeres, protects the nucleic acid.
- Viroids: Infectious agent that was smaller than viruses and caused potato spindle tuber disease. It was found to be a free RNA; it lacked the protein coat that is found in viruses.
- Prions: It Consists of abnormally folded protein. The agent was similar in size to viruses. These agents were called prions.
- Lichens: Lichens are symbiotic associations i.e. mutually useful associations, between algae and fungi. The algal component is known as phycobiont and fungal component as mycobiont, which are autotrophic and heterotrophic, respectively.
The document Glossary: Biological Classification | Biology for Grade 11 is a part of the Grade 11 Course Biology for Grade 11.
All you need of Grade 11 at this link: Grade 11
|
219 videos|306 docs|270 tests
|
FAQs on Glossary: Biological Classification - Biology for Grade 11
| 1. What is biological classification? |  |
Ans. Biological classification is the process of categorizing and organizing organisms into different groups based on their characteristics, similarities, and evolutionary relationships. It helps in understanding the diversity of life on Earth and provides a systematic way to study and classify different species.
| 2. Why is biological classification important? |  |
Ans. Biological classification is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in identifying and naming new species, ensuring a standardized and universal way of referring to organisms. Secondly, it aids in understanding the evolutionary relationships between different species and their ancestors. Additionally, it enables scientists to study the distribution and diversity of organisms across different ecosystems and geographical regions.
| 3. What are the different levels of biological classification? |  |
Ans. Biological classification is hierarchical and consists of various levels. The broadest level is the kingdom, which is further divided into phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. These levels represent increasing levels of similarity and shared characteristics among organisms. For example, humans belong to the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, class Mammalia, order Primates, family Hominidae, genus Homo, and species sapiens.
| 4. How is biological classification done? |  |
Ans. Biological classification is done based on the similarities and differences in the physical characteristics, genetic makeup, and evolutionary relationships of organisms. Scientists use various techniques, such as morphological observations, DNA sequencing, and comparative anatomy, to determine the classification of an organism. These methods help in identifying shared characteristics and grouping organisms accordingly.
| 5. What is the importance of scientific names in biological classification? |  |
Ans. Scientific names play a crucial role in biological classification as they provide a universal and standardized way of referring to organisms. Each species is given a unique scientific name consisting of two parts: the genus and the species epithet. This binomial nomenclature system, developed by Carl Linnaeus, ensures that every organism has a distinct and globally recognized name. Scientific names eliminate confusion caused by common names, which can vary across different languages and regions.
Related Searches