Science & Technology - 1 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
James Webb Telescope
After years of delays, the James Webb Space Telescope is set to go into orbit on December 18, 2021, ushering in the next age of astronomy.
James Webb Space Telescope
- JWST is a NASA–ESA–CSA space telescope that will take over as NASA's flagship astrophysics mission from the Hubble Space Telescope.
- It is the world's most powerful space telescope.
- It will enable a wide range of astronomical and cosmological investigations, including the observation of some of the universe's most distant events and objects.
- It will aid in the understanding of events such as the formation of the first galaxies and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets.
 Significance
Significance
- Some have termed JSWT the "telescope that ate astronomy."
- It is thought to peer back in time to the universe's Dark Ages.
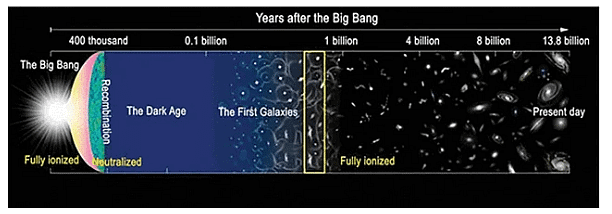
‘Dark Ages’ of The Universe
- Evidence suggests that the universe began 13.8 billion years ago with an event known as the Big Bang, which left it in an ultra-hot, ultra-dense condition.
- Following the Big Bang, the cosmos began expanding and cooling.
- The cosmos was a hundred trillion miles across one second after the Big Bang, with an average temperature of an astonishing 18 billion degrees Fahrenheit (10 billion C).
- The cosmos was 10 million light-years vast and the temperature had dropped to 5,500 degrees Fahrenheit around 400,000 years after the Big Bang (3,000 C).
- Space was filled with a smooth soup of high-energy particles, radiation, hydrogen, and helium throughout this epoch.
- There was no framework to speak of. The soup thinned out as the expanding cosmos grew wider and colder, and everything faded to darkness.
How Will JWST Study This
- The Dark Ages came to an end when gravity created the first stars and galaxies, which then began to radiate light.
- Astronomers want to learn more about this interesting and significant period of the cosmos but identifying first light is extremely difficult.
- The initial objects were tiny in comparison to today's big, luminous galaxies, and they're now tens of billions of light years away from Earth owing to the universe's ongoing expansion.
- In addition, the first stars were surrounded by gas left over from their birth, which behaved like fog and absorbed most of the light.
- It took hundreds of millions of years for radiation to clear the fog. By the time it reaches Earth, this early light is quite dim.
Physiology Nobel for Work on Temperature and Touch
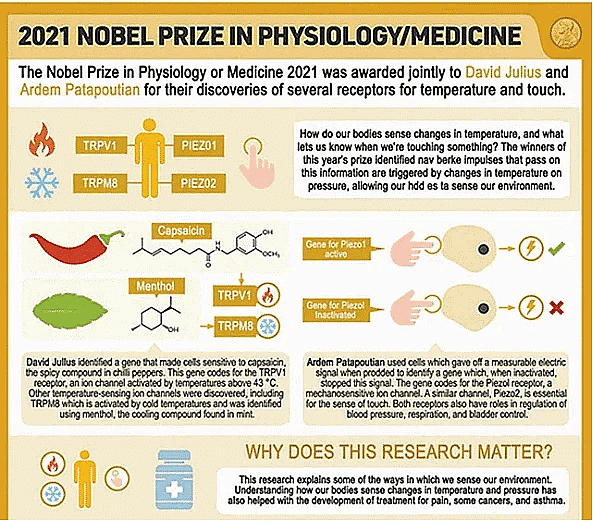
The Nobel Medicine Prize has been awarded to David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian of the United States for their findings on temperature and touch receptors.
What Did They Discover?
- In the late 1990s and early 2000s, David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian, discovered our bodies' touch detectors and the process by which they interact with the nervous system to recognise and respond to certain touches.
- They identified molecular sensors in the human body that are sensitive to heat and mechanical pressure and allow us to "feel" hot or cold, as well as the contact of a sharp item on our skin.
- Dr. Julius and his colleagues published a paper in Nature in 1997 that explained how capsaicin, a chemical compound found in chilli peppers, causes the burning sensation.
- They built a library of DNA fragments to decipher the related genes and eventually uncovered TRPV1, a novel capsaicin receptor.
- Many more temperature-sensing receptors have since been discovered because of this finding.
- They also discovered a novel receptor called TRPM8, which is triggered by cold. It's only found in a small number of pain- and temperature-sensing neurons.
- They discovered a single gene, PIEZO2, that when silenced rendered the cells immune to probing. Piezo1 is the name given to this novel mechanosensitive ion channel.
How Do They Work?
- The capacity of humans to perceive heat, cold, and pressure is like the operation of many detectors that we are familiar with. When anything hot or cold encounters the body, heat
- sensors allow certain molecules, such as calcium ions, to flow through the nerve cell membrane.
- It's like a gate that only opens when a certain request is made. The chemical's entrance into the cell generates a slight change in electrical potential, which the nervous system detects.
- There are several distinct types of receptors that are sensitive to different temperature ranges.
- Greater channels open up to facilitate the flow of ions when there is more heat, and the brain can perceive higher temperatures.
Therapeutic Implications
- Physiological breakthroughs have frequently improved our ability to battle illnesses and disorders. This one is no exception.
- There are receptors in our bodies that cause us to sense pain. The participant felt less pain if these receptors could be suppressed or rendered less effective.
- A variety of diseases and ailments cause chronic pain. Previously, the sensation of pain was a mystery.
- However, as we learn more about these receptors, it's likely that we'll be able to control them in such a manner that pain is reduced.
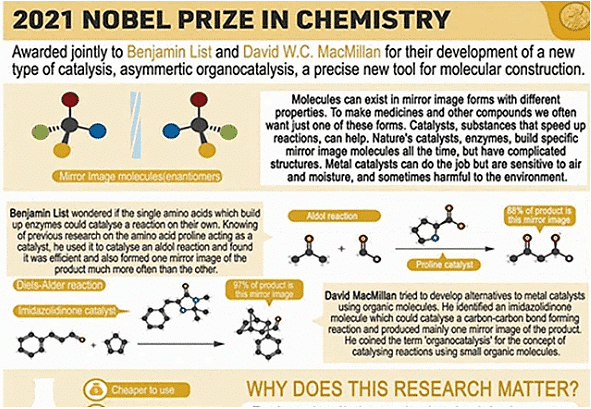
Chemistry Nobel to Duo for Developing Organo-Catalysis
For their work on inventing an organo-catalyst, German scientist Benjamin List of the Max Planck Institute and Scotland-born scientist David WC MacMillan of Princeton University have been awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
What are Catalysts?
- Other chemicals that do not change but assist speed up the reaction are commonly used to help two or more compounds react to produce new molecules.
- These catalysts have been around since the middle of the nineteenth century and are currently employed in almost every chemical process.
- Only two types of compounds were known to operate as efficient catalysts until approximately the year 2000: metals, primarily heavier metals, and enzymes, naturally occurring heavy molecules that aid all life sustaining biochemical processes.
- Both catalysts have their drawbacks.
Issues With Conventional Catalysts
- Heavy metals are costly, difficult to mine, and harmful to persons and the environment.
- Despite the best methods, residues persisted in the final product, posing a challenge in circumstances when extremely pure chemicals were required, such as in the creation of pharmaceuticals.
- Metals also required a dry, oxygen-free atmosphere, which was difficult to provide on a large scale.
- Enzymes, on the other hand, perform best when the chemical reaction is carried out in water.
- However, that is not an ideal setting for many chemical processes.
 Organo-Catalysis
Organo-Catalysis
- Organic molecules are generally found in nature and are made up of carbon atoms with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, or phosphorus as minor components.
- Proteins, which are lengthy sequences of amino acids (carbon molecules containing nitrogen and oxygen) that support life, are organic.
- Enzymes are organic substances because they are proteins.
- List and MacMillan began studying individual amino acids in enzymes and discovered gold.
What is Asymmetric Catalysis?
- Substances with same chemical composition and molecular formula can have vastly different characteristics. They're referred to as isomers.
- Isomers that differ in the orientation of individual atoms in three-dimensional space are one sort of isomer.
- Two molecules might be identical if they weren't mirror reflections of each other, as our hands are.
- Scientists commonly refer to these molecules as left handed or right-handed for ease of understanding.
- When molecules interact with other molecules, this small change can have huge repercussions because it permits them to connect in various places.
- In most chemical reactions, the final result is a combination of left-handed and right-handed molecules.
- By employing a natural chemical like an amino acid as a catalyst, List and MacMillan realised that they could only get one unique mirror image of the end-product.
Organo-Catalysis
- Organic molecules are generally found in nature and are made up of carbon atoms with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, or phosphorus as minor components.
- Proteins, which are lengthy sequences of amino acids (carbon molecules containing nitrogen and oxygen) that support life, are organic.
- Enzymes are organic substances because they are proteins.
- List and MacMillan began studying individual amino acids in enzymes and discovered gold.
What is Asymmetric Catalysis?
- Substances with same chemical composition and molecular formula can have vastly different characteristics. They're referred to as isomers.
- Isomers that differ in the orientation of individual atoms in three-dimensional space are one sort of isomer.
- Two molecules might be identical if they weren't mirror reflections of each other, as our hands are.
- Scientists commonly refer to these molecules as left handed or right-handed for ease of understanding.
- When molecules interact with other molecules, this small change can have huge repercussions because it permits them to connect in various places.
- In most chemical reactions, the final result is a combination of left-handed and right-handed molecules.
- By employing a natural chemical like an amino acid as a catalyst, List and MacMillan realised that they could only get one unique mirror image of the end-product.
Antimicrobial Resistance
During World Antimicrobial Awareness Week, the Ministry of Animal Husbandry and Dairying held a session on the National Action Plan to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). The theme of WAAW this year was "Spread awareness, and resistance." During WAAW, the AMR tripartite organisations (World Health Organization, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, and World Organization for Animal Health) launched an international colour campaign, dubbed "Go Blue," to raise awareness of AMR.
About Antimicrobial Resistance
- Any microorganism (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites etc.) may develop resistance to antimicrobial medications (such as antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, antimalarials, and anthelmintic) used to treat infections.
- Consequently, traditional therapies are rendered ineffective, illnesses persist, and the risk of spreading infection to others increases.
- Antimicrobial-resistant microorganisms are frequently referred to as "superbugs."
- AMR has been named one of the top ten global health hazards by the WHO.
Reasons For Spread of AMR
- Contamination in the vicinity of pharmaceutical production plants, when untreated waste releases enormous volumes of active antimicrobials into the environment.
- Overuse and abuse of pharmaceuticals in people, animals, and agriculture, as well as limited access to clean water, sanitation, and hygiene.
Concerns About AMR
- Healthcare costs will rise: AMR is currently responsible for up to 7,00,000 deaths each year. It also raises the expense of healthcare by requiring longer hospital stays, more testing, and the use of more costly medications.
- Incurable infections: AMR is undermining a century of medical progress; infections that were once treated and curable with our treatments have become (or are on the verge of becoming) incurable (as medicines are not working against infections).
- Infections and surgeries are growing more dangerous: Even ordinary infections are becoming more dangerous. Surgeries are growing more dangerous, and the root of the problem is human behaviour that misused or overused antimicrobials.
- Insufficient financial incentives for new antibiotics: In the previous three decades, no new classes of antibiotics have made it to market, owing to a lack of incentives for their research and manufacturing.
- Antibiotic apocalypse: Without immediate action, we are on the verge of an antibiotic apocalypse — a world without antibiotics, in which germs become entirely resistant to treatment, and in which routine diseases and small injuries may kill once again.
AMR in india
- With a huge population, growing wages that promote the purchase of antibiotics, a high burden of infectious illnesses, and simple over-the-counter access to antibiotics, India is a key breeding ground for resistance genes (such genes help bacteria in surviving on being exposed to antibiotics).
- New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1 (NDM-1) is a multi-drug resistance determinant that originated in India and has since spread around the world.
- Multidrug-resistant typhoid, which originated in South Asia, has also spread to Africa, Europe, and other regions of Asia.
- In India, microbes resistant to first-line antibiotics cause about 56,000 neonatal fatalities each year owing to sepsis.
Measures Taken For AMR
- The Surveillance Network has been reinforced by the establishment of laboratories in State Medical College as part of the National Programme on AMR Containment.
- The National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) focuses on a One Health strategy with the goal of incorporating many stakeholder ministries/ departments.
- The AMR Surveillance and Research Network (AMRSN) was established in 2013 with the goal of gathering data and identifying trends and patterns in drug resistant illnesses throughout the nation.
- Antibiotic Stewardship Program: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has launched an antibiotic stewardship programme (AMSP) as a pilot initiative throughout India to prevent antibiotic abuse and overuse in hospital wards and intensive care units.
- Integrated One Health Surveillance Network for AMR: Assessing Indian Veterinary Laboratories' readiness to participate in an integrated AMR surveillance network.
- India has launched several initiatives, such as Mission Indradhanush, to address poor vaccine coverage, increased micro-planning, and added monitoring and accountability measures.
- AMR is one of the top ten goals for the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare's (MoHFW) joint effort with the World Health Organization (WHO).
Way Forward
- Detecting and preventing the sale of counterfeit medications, especially in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- Measurement of bioavailability at pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, enforcement of antibiotic regulations through prescription databases, and pharmacy auditing are all things that are done on a regular basis.
- The study of the time course of medication absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion is known as pharmacokinetics.
- GST (Goods and Services Tax) tracking/matching of e-prescriptions is used to keep track of medicine sales.
- Use of modern technology such as imaging and bioinformatics, as well as geographic information systems, to move away from a syndromic approach to diagnostic therapy.
- Observance of the WASH strategy, antibiotic-free animal feed and antibiotics supplied to animals that are not the same as those ingested by people (e.g., marked by different colour schemes).
5g Leap for Tomorrow
The fifth-generation mobile network, or 5G, is the next level of mobile network that will shape the Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industrial Revolution 4.0, quality of service delivery, innovation, etc. by facilitating smarter and developing societies. Commercial 5G networks began to be deployed in 2020 and are expected to reach 12% of world mobile connections (1.1 billion) and generate revenues up to U.S.$1.3 trillion by 2025 for operators. The technology that 5G uses will improve data transfer speed at unexpected higher levels — almost 100 times more — and reduce latency times helping mission-critical services. Thus, 5G is essential but India needs to look if it is ready for the deployment of the technology.
Potential
- 5G has the transformative potential to provide a range of benefits to the Indian economy, which when enhanced with artificial intelligence provides a new dimension to connected and autonomous systems.
- Socio-economic Benefits: This may allow citizens and communities to get socio-economic benefits and comforts delivered by a well-advanced, more data intensive, digital economy, educate and empower citizens and businesses & transform existing cities into smart and innovative cities.
Benefits of 5G
- Encompass enhanced outdoor and indoor broadband
- Internet of things
- Smart cities
- Smart agriculture
- Energy monitoring
- Remote monitoring
- Smart grids
- Telehealth
- Industrial automation
- Remote patient monitoring
- Industrial automation
- There is great potential for India to move to an advanced digital revolution.
Issues Associated With 5g
- India as a Late Adopter: India is late in adopting 5G technology, hence, will get insignificant revenue from the service.
- Lesser Government Subsidies: A low likelihood of government subsidies is expected, given high reserve prices set by the government for spectrum auctions amid ongoing fiscal deficits. This will increase the cost of access to 5G by end consumers.
- Digital Divide: 5G will not bridge the digital divide among the rural and urban areas in the short term, rather increase it as the business case of 5G even in urban areas is limited. Therefore, it will not be easily available in rural areas too.
- 5G, A Niche Service: 5G will be a niche service unlike 3G and 4G which were pervasive services. It will get intensified over a comparatively longer period. The rollout of 5G technology will be different from the one seen in 4g; it will be introduced in specific sectors and areas.
- Inadequate Accessibility of Previous Technology: The consumers are still grappling with basic network issues like call drops and interrupted data services. There are still areas where 4G networks have not stabilised causing frequent disruptions in internet services. It is important to meet the quality-of-service parameters of existing 4G networks before embarking on a new 5G platform.
- Enabling Critical Infrastructures: 5G will require a fundamental change to the core architecture of the communication system. The major flaw of data transfer using 5G is that it can't carry data over longer distances. Hence, even 5G technology needs to be augmented to enable infrastructure.
- Financial Liability on Consumers: For transition from 4G to 5G technology, one must upgrade to the latest cellular technology, thereby creating financial liability on consumers.
Way Forward
- Analysis of Existing Infrastructure and Capacity: Priority for India will be in identifying end users and population to be covered, analysis of the existing network and operators, identification of cities for 5G roll out, working out an investment model, and minimisation of the digital risk and pricing based on the externalities and usage of various sectors.
- Cost Benefit Analysis: The deployment of 5G in India needs to be carefully planned after a cost benefit analysis by independent experts which will create a level-playing field through market mechanisms such as facilitating, simulating, auctioning, ensuring competition, functioning markets, etc.
- Sector-friendly Steps: As the deployment of 5G network is expensive, both the Central and State governments may need to consider measures which stimulate fibre investment, attract investment through public private partnerships (PPPs) and facilitate investment funds on a nominal interest basis. Allowing 100% foreign direct investment in the telecom sector under the automatic route along with other policy reforms augurs well for the sector to attract investment. Implementation of 5G requires huge investment and the relief package is a welcome step.
- Tax issues: The Government needs to address information asymmetry and negative externalities through laws and regulations/taxes and subsidies.
- The deployment of 5G technology will also need the right of access to government infrastructure such as traffic lights, lamp posts, etc. where wireless operators can deploy electronic small cell apparatus.
- At the same time, reasonable fees may be charged by State and local governments to operators for affordable deployment of 5G equipment.
- Further, removing the tax burden for deploying fibre networks reduces associated costs, thereby promoting investment as was done by the Singapore government, could help in the smooth deployment of fibre in India.
- Bridging the Rural-urban Gap: 5G can be deployed at different band spectrums and at the low band spectrum, the range is much longer which is helpful for the rural areas.
- Government’s Assistance: The government has complete control over the inputs. One of the key inputs of 5G is the band spectrum.
- By managing the design of the spectrum, the government can control the price to be paid by the people.
- The government shall support the telecom companies to roll out networks which are sustainable and affordable for the public.
- Tackling the Spectrum Pricing Issue: The government in recent times, has had two failed auctions. The current high reserve price needs to be reduced to conduct a successful auction. The pricing will have to be worked out keeping in mind the financial stress in the sector and affordability of services.
- Enabling the Manufacturing Sector in India: As 5G starts taking shape in India, it is important to strengthen its domestic telecommunication manufacturing market so that it is not only the users of 5G in India, but also the manufacturers and providers of these technologies who will be able to make a mark in the global arena
- Viable Technology from Consumers’ Perspective: For widespread 5G deployment, it needs to become financially viable otherwise rural integration will remain a pipe dream. 5G technology must be viable to the telecom operators too.
Conclusion
As India has already witnessed digital revolution even in its remotest areas due to cost-effective 4G technology, the use of 5G can play a vital role in enhancing this sector and facilitating India’s goal to emerge as a manufacturing and innovation hub. The negative implication of 5G is furthering the ‘digital divide’. Therefore, Government policies should also focus on affordable coverage too.
Electric Vehicles
India has 9 of the 10 most polluted cities in the world. Vehicular pollution is one of the primary factors behind the worsening air quality of Indian cities. In this context, India is encouraging electric vehicles. In this context, India must prepare itself with better charging infrastructure, battery making factories and smart incentives for car companies and consumers to go electric.
Electric Vehicles (EVS)
- An EV operates on an electric motor instead of an internal combustion engine and has a battery instead of a fuel tank.
- EVs have low running costs as they have fewer moving parts and are also environmentally friendly.
- Fuel cost for an EV is approximately 80 paisa per kilometre which is very low compared to petrol, diesel or gas-based transportation.
Current Situation
- According to International Energy Agency (IEA), Electric Vehicle has
- Global growth rate ~ 75%.
- Global sale ~ 5.2 million (2018)
- Market share
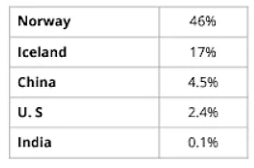
Annual sale
- China ~ 2.4 million (IEA)
- India ~ 75, 000 (Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers) [60,000 vehicles are sold every day in India.
Benefits of Electric Vehicle
- Import bill reduction ~ $60 billion in diesel and petrol. (Niti Aayog)
- Environment sustainability of Vehicular emission is a major source of urban pollution.
- on Lower GHG emissions
- Energy intensity reduction on
- EV ~ 60% conversion of the grid energy
- ICE vehicles ~ 20% conversion of petrol energy
- Indigenization of technology
- Manufacturing hub
- Support to the power sector
Reasons For Underdeveloped EVS Market
- Absence of robust government policy – for a long time.
- High rate of GST on EVs (now reduced to 5% from 12%)
- Low participation of OEM
- Lack of enabling infrastructure like public charging stations (only 250 in India)
- High charging time o Fast charger ~30-45 mins o Slow charge ~ 8hrs
- Short range for a single battery charge
- India does not have any known reserves of lithium and cobalt, which makes it dependent on imports of lithium-ion batteries from Japan and China.
- Lack of stable fiscal policy support to the EV ecosystem.
- Underdeveloped ecosystem in India electronics
Government Initiative
- As a member of Clean Energy Ministerial, India aims to achieve a 30 % EVs by 2030.
- The Union Budget 2019-20 has a vision of an era of electric mobility.
- National Electric Mobility Mission Plan – Target of 7 million sales EV by 2020.
- National Mission on Transformative mobility and Battery Storage – Production localization of batteries.
- FAME phase-II – Rs 10,000 crore outlay.
- Incentives o Income tax rebate on interest on EV loans.
- GST rate cut - 5% to 12%
- ‘Service status’ – to charging of batteries, to operate without licence.
- Solar powered public charging stations are being rolled out by Discoms like BHEL.
- Smart cities would also boost electric vehicles.
Way Forward
- Establishing strong linkage between sustainable development and Electric mobility.
- Framework to phase out ICE vehicles by 2030.
- R&D in battery technology.
- Acquiring lithium fields in Bolivia, Australia, and Chile
- Incentives: waiver of road tax and registration fees etc for EVs.
- Promotion of charging infrastructures (solar)
- Awareness of adverse impact of air pollution.
Shale Oil
Cairn Oil & Gas has formed a joint venture with Halliburton, located in the United States, to begin shale exploration in the Lower Barmer Hill formation in Western Rajasthan. In collaboration with Halliburton, the corporation wants to boost the recoverable reserves of its offshore holdings by ten times manufacturing.
About Shale Oil
- Shale oil is an unconventional oil generated by pyrolysis, hydrogenation, or thermal dissolution from oil shale rock fragments.
- The organic substance inside the rock (kerogen) is converted into synthetic oil and gas via these procedures.
- The refined products may be utilised in the same ways as crude oil-derived goods can.
Shale Distribution in World
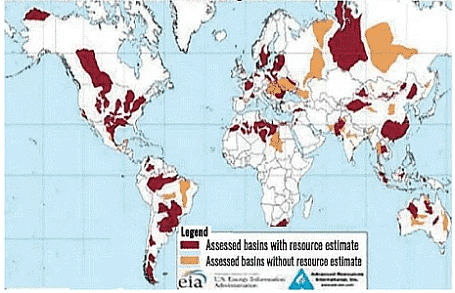 Shale Distribution in India
Shale Distribution in India
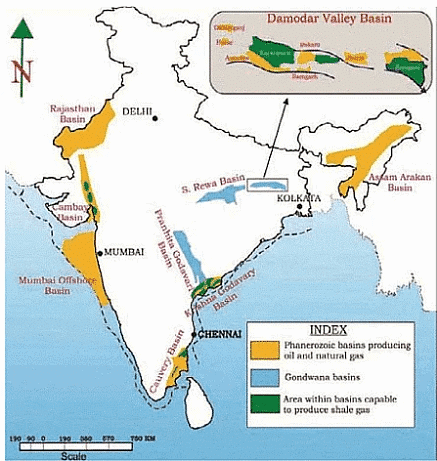
- According to the US EIA 2015 study, India possesses 96 trillion cubic feet of theoretically recoverable shale gas.
- The Cambay, Krishna – Godavari, Cauvery, Damodar Valley, Upper Assam, Pranhita – Godavari, Rajasthan, and Vindhya Basin have been recognised as having recoverable deposits.
Difference Between Shale Oil and Conventional Crude
- The primary distinction between shale oil and conventional crude is that the former, sometimes known as 'tight oil,' is discovered in smaller quantities and at greater depths than conventional crude deposits.
- Hydraulic fracking is a procedure that involves creating fissures in oil and gas-rich shale to liberate hydrocarbons.
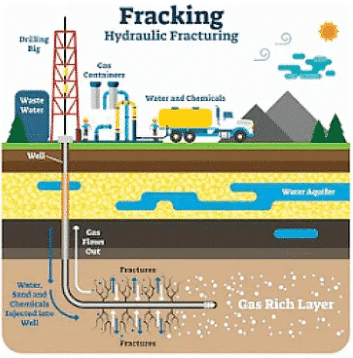
About Fracking
- Drilling deep into the soil before directing a high-pressure water combination at the rock to liberate the gas within is known as fracking.
- Water, sand, and chemicals are pumped under high pressure into the rock, allowing the gas to flow out to the well's head.
- The operation may be carried either vertically or horizontally to the rock layer, which can be utilised to construct new paths for gas escape or to expand existing channels.
- The high-pressure combination fractures the rock, which is known as hydraulic fracturing.
Shale Production in The World
- Russia and the United States are two of the world's top shale oil producers.
- With a boom in shale oil output in the United States, the nation has gone from being a net importer of petroleum to becoming a net exporter in 2019.
- In India, there is currently no large-scale commercial production of shale oil and gas.
- Environmental concerns: large water needs for fracking and the possibility for ground water pollution.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|






















