Internal Security - 2 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
BrahMos Export to Philippines
Why in News?
Recently, Philippines has signed a deal with BrahMos Aerospace Private Ltd. for the supply of a shore-based anti-ship variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile. This is the first export order for the missile, a joint product of India and Russia.
- The Philippines wants to induct this missile amid tensions with China over the disputed islands in the South China Sea.
- Several countries have shown interest in acquiring the BrahMos missile. For example, discussions are in advanced stages with Indonesia and Thailand.
What are the features of BrahMos Missile?
- BrahMos is a joint venture between the Defence Research and Development Organisation of India (DRDO) and the NPOM of Russia.
- BrahMos is named on the rivers Brahmaputra and Moskva.
- It is a two-stage (solid propellant engine in the first stage and liquid ramjet in second) missile.
- It is a multiplatform missile i.e it can be launched from land, air, and sea and multi capability missile with pinpoint accuracy that works in both day and night irrespective of the weather conditions.
- It operates on the “Fire and Forgets” principle i.e it does not require further guidance after launch.
- Brahmos is one of the fastest cruise missiles currently operationally deployed with speed of Mach 2.8, which is nearly 3 times more than the speed of sound.
- Recently, an Advance Version of BrahMos (extended range sea-to-sea variant) was test fired.
- Following India’s entry into the MTCR (Missile Technology Control Regime) club in June 2016, the range is planned to be extended to 450 km and to 600km at a later stage.
- The BrahMos missile was initially developed with a range capped at 290 km.
What is Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR)?
- It is an informal and voluntary partnership among 35 countries to prevent the proliferation of missile and unmanned aerial vehicle technology capable of carrying greater than 500 kg payload for more than 300 km.
- The members are thus prohibited from supplying such missiles and UAV systems that are controlled by the MTCR to non-members.
- The decisions are taken by consensus of all the members.
- This is a non–treaty association of member countries with certain guidelines about the information sharing, national control laws and export policies for missile systems and a rule-based regulation mechanism to limit the transfer of such critical technologies of these missile systems.
- It was established in April 1987 by G-7 countries –USA, UK, France, Germany, Canada, Italy, and Japan.
What is the Status of India’s Defence Exports?
- Defence exports are a pillar of the government’s drive to attain self-sufficiency in defence production.
- Over 30 Indian defence companies have exported arms and equipment to countries like Italy, Maldives, Sri Lanka, Russia, France, Nepal, Mauritius, Sri Lanka, Israel, Egypt, UAE, Bhutan, Ethiopia, Saudi Arabia, Philippines, Poland, Spain and Chile.
- The exports include personal protective items, defence electronics systems, engineering mechanical equipment, offshore patrol vessels, advanced light helicopters, avionics suits, radio systems and radar systems.
- However, India’s defense exports are still not upto the expected lines.
- The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) ranked India at number 23 in the list of major arms exporters for 2015-2019.
- India still accounts for only 0.17% of global arms exports.
- Reason for dismal performance in India’s Defense exports is that, India’s Ministry of Defense so far has no dedicated agency to drive exports.
- Exports are left to individual corporations, like BrahMos or the defence public shipyards and undertakings.
- In this context, the KPMG report titled ‘Defence Exports: Untapped Potential recommends the first step of setting up of an exclusive “defence export help desk”.
- On the basis of inputs from the help-desk, the report says, Indian companies could work with government machinery to realise exports.
- If India is successful in providing big-ticket military systems to countries in the neighbourhood, it won’t just be a boost for defence exports but will also be a strategic step to counter China’s influence as it provides defence products in Asia, including Pakistan, Bangladesh and Myanmar.
India Accidentally Fires Missile Into Pakistan
India admitted the supersonic missile that landed in Pakistan was accidentally fired from one of its bases.
What Had Happened
- As per Pakistan, a high-speed flying object originating from the northern Indian city of Sirsa (Haryana) had crashed in eastern Pakistan.
- The object, flying at 40,000 feet and three times the speed of sound, had flown 124 km (77 miles) in Pakistani airspace.
- The missile was unarmed and had crashed near the country’s eastern city of Mian Channu, about 500 km from capital Islamabad.
Missile Used
- Neither country has spelt this out; Pakistan has only called it a “supersonic” missile.
- Some experts have speculated that it was a test of one of India’s top missiles, BrahMos, jointly developed with Russia.
(i) BrahMos has a top speed of Mach 3, a range of around 290 km, and a cruising altitude of 15 km (around 50,000 feet).
(ii) BrahMos can be fired from anywhere, is nuclear-capable, and can carry warheads of 200-300 kg. - Other experts have wondered if the missile was a variant of the nuclear-capable Prithvi. However, India never tests Prithvi around this region, and only does so from Balasore.
Protocol for Missile Tests
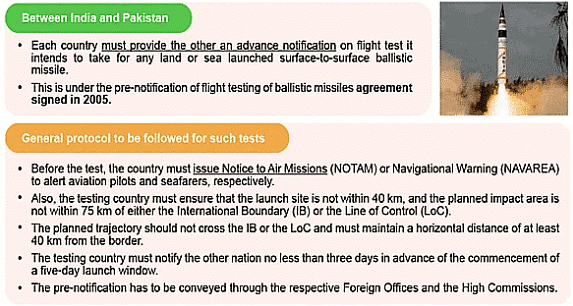 Extremely Alarming Incident
Extremely Alarming Incident
- This event is being widely seen as an extremely alarming incident that could have triggered a conflagration between the two nuclear-armed neighbours. The two nuclear-armed neighbours have fought wars in the past and they do not trust each other.
- It has also raised questions about safety mechanisms and the technical prowess of very dangerous weapon.
- The missile has several in-built locks and such accidental firing raises questions about safety protocols.
- Security analysts wondered if the incident meant that India had missiles in ready-to-launch positions and pointed at Pakistan. Hence, it will further raise suspicions about the intentions of India.
- The flight path of missile endangered many passenger flights both in Indian and Pakistani airspace as well as human life and property on ground.
53rd Raising Day Celebrations of CISF
- The Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) celebrated its 53rd Raising Day in Ghaziabad.
- While speaking at this occasion, Union Home Minister Amit Shah pitched for a hybrid security model.
- Hybrid Security Model Pitched By Home Minister
- In this model, the CISF would train and certify private security agencies.
- These private agencies can, then, take over the task of efficiently guarding various kinds of industrial and manufacturing units in the country.
- Under this model of security, the CISF will prepare the strategy and both private and the CISF personnel would work in synergy.
- The proposed hybrid security model will give space to the private security agencies.
- About Central Industrial Security Force (CISF)
- CISF is one of the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) established under an Act of Parliament, “Central Industrial Security Force Act, 1968.
- CISF was established in 1969 to provide integrated security cover to certain sensitive public sector undertakings with a strength of only three battalions.The force has since grown into a premier multi-skilled organization with a present strength of 1,63,590 personnel.
- Eventually, it was made an armed force of the Republic of India by another Act of Parliament passed in June 1983. It works under the administrative control of Ministry of Home Affairs and its headquarter is located at New Delhi.
- It secured the private manufacturing production units as India rode on to become a $2.5 trillion-strong economy. CISF has to play an important role in country's journey from a $2.5 trillion economy to becoming a $5 trillion economy
Operations

 Need To Remain Prepared For The Future Challenges
Need To Remain Prepared For The Future Challenges
- CISF been asked to prepare a 25-year road map so that it can emerge as a result-oriented security agency by the time India enters the 100th year of its independence.
- In the past, there has been increase in the drone threats to industrial units along sea ports and the land border.
- Hence, the CISF needs to effectively collaborate with agencies like DRDO and the BSF to prepare an effective counter-technology against this menace.
- The CISF needs to explore ways so that the representation of women personnel in the force could be enhanced from the present 6% to 20%.
Colombo Security Conclave
The fifth meeting of national security advisers of the Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) was held in the Maldives.
India was represented by NSA Doval.
Key Highlights of the meeting
1. Participating Members
The conclave was attended by the Maldives, India and Sri Lanka, and the newest member of the Conclave, Mauritius.
- At this meeting, Mauritius was included as the fourth member.
- Delegations from Bangladesh and Seychelles participated as Observers.
2. Road Map For Cooperation Adopted
- The meeting adopted a road map for cooperation and collaboration in areas such as maritime security, counterterrorism and drug trafficking.
- The roadmap will facilitate robust mechanisms for coordinated responses, capacity building and strengthening information flow.
3. Five Broad Areas Of Cooperation Identified
Conclave identified 5 broad areas of cooperation to strengthen regional security. These are:
 4. Commitment To Achieve Regional Peace And Security
4. Commitment To Achieve Regional Peace And Security
As maritime neighbours, facing similar threats, the Conclave reaffirmed their commitment to engage in consistent joint efforts to achieving regional peace and security.
5. India’s Stand At The Conclave
- NSA Doval said the conclave should institutionalise its cooperation with a road map.
- It should also form joint working groups to tackle drug trafficking and cybersecurity challenges.
- Members of the grouping remain vulnerable to trafficking, organised crime and maritime terrorism, particularly in the light of the developments in Afghanistan.
- He called for strengthening cooperation amongst maritime neighbours to address shared security challenges, and as first responders.
- India also proposed a meeting of the Heads of respective Coast Guards this year.
 Significance
Significance
- This India-driven mini-lateral grouping is being seen as India’s outreach to the Indian Ocean to underline regional co-operation and shared security objectives.
- CSC hopes to restrict China’s influence in an area of strategic importance, and to reduce the Chinese footprint in the member countries.
- Country’s national security is deeply intertwined with the collective security aspirations in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Geographical proximity of the member countries allows them to be first responders for each other in crisis situations. E.g., Indian Coast Guard helped douse the MT New Diamond and X-press Pearl ship fires in Sri Lankan waters
In this context, CSC is being described as the region’s 911 (the number "911" is the universal emergency number in the United States).
Weapons of Mass Destruction (Amendment) Bill 2022
The Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Amendment Bill, 2022 has been unanimously passed in Lok Sabha.
Background
- The Bill was introduced in Lok Sabha in the first week of April 2022 and amends the Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Act, 2005.
- The 2005 Act prohibits unlawful activities (such as manufacturing, transport, or transfer) related to weapons of mass destruction, and their means of delivery.
Need For The Amendment
- To Focus On The Financial Ban On Activities Supporting WMDs
- There was an urgent need to have provision to ban financing for Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
- The existing legislation was silent on this aspect.
- It also prohibits making available funds, financial assets or economic resources for any prohibited activity in relation to WMD and their delivery systems.
- To Provide More Teeth To Government To Act Against Financiers Of Such Activities.
- The present bill empowers the Government to freeze, seize or attach funds or other financial assets or economic resources for preventing such financing. It will strengthen India’s national security.
- To Fulfil India's International Obligations adhering to:
- The recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and
- United Nations Security Council's targeted financial sanctions against financing of WMDs.
- This legislation will strengthen India's credentials and image.

International Legislations Covering The Use Of WMDs
The use of chemical, biological, and nuclear weapons is regulated by a number of international treaties and agreements. Among them are:
- Geneva Protocol, 1925 – It banned the use of chemical and biological weapons; and
- Biological Weapons Convention, 1972, and
- Chemical Weapons Convention, 1992.
- Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), 1968 and the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT), 1996- Use and proliferation of nuclear weapons is regulated
India’s Stand On International Legislations
- India has signed and ratified both the
(i) Biological Weapons Convention, 1972 and
(ii) Chemical Weapons Convention, 1992. - However, it has not signed the treaties regulating the use and proliferation of nuclear weapons (which includes NPT and CTBT).
SC Clears FCRA Changes
The Supreme Court has upheld amendments in Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act. These amendments had introduced restrictions in the handling of foreign contributions by organizations in India. It held that receiving foreign donations cannot be an absolute or vested right and can be regulated by the Parliament.
Background
- In 2020, the government had brought amendments in Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010. The amendment bill received Presidential assent in September 2020 & thus became an Act.
- It was brought with the declared objective to restrict misuse and diversion of foreign funds, and to infuse more accountability in the functioning of NGOs.
- The amendments were challenged as arbitrary and stringent.
Key Highlights Of The Judgment
- Medicine vs Intoxicant Metaphor
- Foreign Contributions serves as a medicine so long as it is utilized moderately and discreetly. However, free and uncontrolled flow of foreign contribution can act as an intoxicant impacting the sovereignty and integrity of the nation
- Amendments Necessary To Strengthen The Compliance Mechanism
- The verdict noted that many NGOs, which received the funds, did not utilise the foreign funds for the purposes for which they were registered.
- It further noted that there had been cases of successive transfers and creation of a layered trail of money. This makes it difficult to trace the flow and final utilisation.
- Increase In Inflow Of Foreign Contribution
- The court noticed that the inflow of foreign contribution had almost doubled between the years 2010 and 2019.
- It further said that many of the registered associations had failed to comply with basic statutory 130 formalities. This resulted in cancellation of certificates of registration of more than 19,000 organisations.
- Read Down Section 12A Of The Amended Act
- The apex court read down Section 12A which made it mandatory for all office-bearers of NGOs to provide Aadhaar number.
- The verdict held that producing Indian Passport for the purpose of their identification would be enough.
- A Country Can Even Completely Prohibit Acceptance Of Foreign Donations
- The court said a country can even completely prohibit acceptance of foreign donations.
- This can be done on the ground that it undermines the constitutional morality of the nation
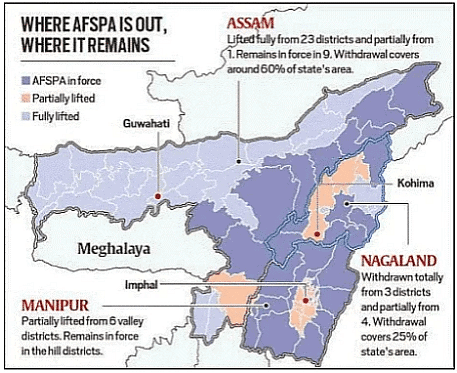
AFSPA From Parts Of Northeast Is Withdrawn
- The Centre has significantly reduced the footprint of the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA), 1958 in the Northeast.
- It has been withdrawn entirely from 23 districts in Assam; and partially from seven districts in Nagaland, six districts in Manipur, and one district in Assam.
After Being In Force For Many Years, Why Has AFSPA Been Withdrawn Now?
- Over the last two decades, various parts of the Northeast have seen a reduction in insurgencies.
- A number of major groups were already in talks with the Indian government, and these talks received traction during the current regime.
- In Nagaland, the killing of 14 villagers in Oting, Mon, is seen as having a telling impact on reviving the demand to repeal AFSPA.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|