UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Parliamentary System | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
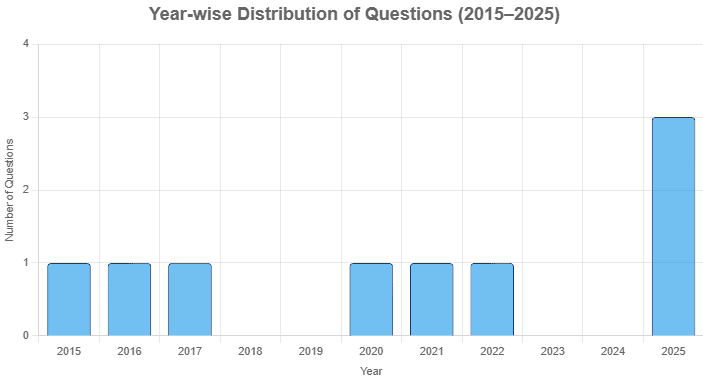
From 2015 to 2025, a collection of 11 questions on the Indian Constitution and parliamentary system from examination datasets provides insights into their temporal distribution and complexity. With a peak of three questions in 2025, and none in 2023–2024, the questions are categorized by topic—10 on the Indian Constitution and parliamentary system (90.9%) and 1 on constitutional conventions (9.1%)—and by difficulty level—3 easy (27.3%), 6 medium (54.5%), and 2 hard (18.2%).
Q.1. Consider the following statements: (2025)
I. On the dissolution of the House of the People, the Speaker shall not vacate his/her office until immediately before the first meeting of the House of the People after the dissolution.
II. According to the provisions of the Constitution of India, a Member of the House of the People on being elected as Speaker shall resign from his/her political party immediately.
III. The Speaker of the House of the People may be removed from his/her office by a resolution of the House of the People passed by a majority of all the then Members of the House, provided that no resolution shall be moved unless at least fourteen days’ notice has been given.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) I and III only
- Statement I- On the dissolution of the House of the People, the Speaker shall not vacate his/her office until immediately before the first meeting of the House of the People after the dissolution : Correct
According to Article 94 of the Constitution of India, the Speaker does not vacate office upon the dissolution of the Lok Sabha. The Speaker continues in office until the first meeting of the newly elected House of the People. - Statement II- According to the provisions of the Constitution of India, a Member of the House of the People on being elected as Speaker shall resign from his/her political party immediately: Incorrect.
There is no constitutional provision that mandates a Speaker to resign from his or her political party upon election. Although the Speaker is expected to act impartially, the Constitution does not require resignation from party membership. - Statement III- The Speaker of the House of the People may be removed from his/her office by a resolution of the House of the People passed by a majority of all the then Members of the House, provided that no resolution shall be moved unless at least fourteen days’ notice has been given: Correct.
As per Article 94 of the Constitution and the Rules of Procedure, the Speaker can be removed by a resolution passed by a majority of all the then members of the House (i.e., an effective majority), with a mandatory 14 days’ notice before the resolution is moved.
Q.2. Consider the following statements: (2025)
I. If any question arises as to whether a Member of the House of the People has become subject to disqualification under the 10th Schedule,the President’s decision in accordance with the opinion of the Council of Union Ministers shall be final.
II. There is no mention of the word ‘political party’ in the Constitution of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Neither I nor II
- Statement I- If any question arises as to whether a Member of the House of the People has become subject to disqualification under the 10th Schedule, the President’s decision in accordance with the opinion of the Council of Union Ministers shall be final: Incorrect.
As per the Tenth Schedule (Anti-Defection Law) of the Constitution of India, the decision on disqualification of a member rests with the Speaker (or the Chairman in case of the Rajya Sabha) of the House, not the President.
The President deals with disqualification under Articles 102 and 103, but not under the Tenth Schedule. - Statement II- There is no mention of the word ‘political party’ in the Constitution of India: Incorrect.
This is factually wrong. The term "political party" is explicitly mentioned in the Tenth Schedule of the Constitution, which was added by the 52nd Amendment Act, 1985.
Q.3. With reference to the Indian polity, consider the following statements:
I. An Ordinance can amend any Central Act.
II. An Ordinance can abridge a Fundamental Right.
III. An Ordinance can come into effect from a back date.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) I and III only
- Statement I: An Ordinance can amend any Central Act (Correct)
Under Article 123, the President can promulgate an Ordinance when Parliament is not in session, and such an ordinance has the same force and effect as an Act of Parliament. Therefore, it can amend or repeal any existing Central law, including any Act of Parliament. - Statement II: An Ordinance can abridge a Fundamental Right (Incorrect)
Although an Ordinance has the same effect as a law made by Parliament, no law, including an Ordinance, can violate Fundamental Rights as per Article 13(2) of the Constitution.
So, any Ordinance that abridges or takes away Fundamental Rights would be unconstitutional and invalid. - Statement III: An Ordinance can come into effect from a back date (Correct)
Yes, an Ordinance can be made retrospective—i.e., it can take effect from a back date. This power is similar to that of the Parliament, which can pass retrospective laws.
So, the President (or Governor) can give an Ordinance retrospective effect.
Note: No questions has been asked from this topic in the year 2024 and 2023
Q.4. With reference to Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha, consider the following statements: (2022)
1. As per the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, the election of Deputy Speaker shall be held on such date as the Speaker may fix.
2. There is a mandatory provision that the election of a candidate, as Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha shall be from either the principal opposition party or the ruling party.
3. The Deputy Speaker has the same power as of the Speaker when presiding over the sitting of the House and no appeal lies against his rulings.
4. The well-established parliamentary practice regarding the appointment of Deputy Speaker is that the motion is moved by the Speaker and duly seconded by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 2 and 4 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- Statement 1: The Speaker determines the date for electing the Deputy Speaker. In contrast, the President sets the date for the election of the Speaker.
- Statement 2: It is incorrect to say that a candidate for Deputy Speaker must come from either the principal opposition party or the ruling party. It is merely a tradition in India to offer the Deputy Speaker position to someone from the opposition party.
- Statement 3: If the Speaker is not present, the Deputy Speaker takes charge of the Lok Sabha sessions and manages the activities in the house. The Deputy Speaker has the same authority as the Speaker while leading the house.
- Statement 4: The Deputy Speaker is also chosen by the Lok Sabha from among its members immediately after the Speaker is elected. There is no rule or usual practice requiring the Speaker to propose the motion for the Deputy Speaker's election, nor is it seconded by the Prime Minister.
Q.5. We adopted parliamentary democracy based on the British model, but how does our model differ from that model? (2021)
1. As regards legislation, the British Parliament is supreme or sovereign but in India, the power of the Parliament to legislate is limited.
2. In India, matters related to the Amendment of an Act of the Parliament are referred to the Constitution Bench by the Supreme Court.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Statement 1 is correct. Parliamentary sovereignty is a principle of the UK constitution. It makes Parliament the supreme legal authority in the UK, which can create or end any law. Generally, the courts cannot overrule its legislation and no Parliament can pass laws that future Parliaments cannot change.
Indian Parliament is not a sovereign body like the British Parliament. The Indian Parliament may, in exercise of its constituent power, amend by way of addition, variation or repeal any provision of the Constitution in accordance with the procedure laid down for the purpose. However, the Parliament cannot amend those provisions which form the ‘basic structure’ of the Constitution. This was ruled by the Supreme Court in the Kesavananda Bharati case (1973). - Statement 2 is correct. In India, matters related to the constitutionality of an amendment of an act of the Parliament are referred to the Constitution Bench by the Supreme Court. A Constitution Bench is a bench of the Supreme Court having five or more judges on it. These benches are not a routine phenomenon. A vast majority of cases before the Supreme Court are heard and decided by a bench of two judges (called a Division Bench), and sometimes of three. Constitution Benches are set up when the case involves a substantial question of law pertaining to the interpretation of the Constitution (Article 145(3) of the Constitution, which mandates that such matters be heard by a bench of not less than five judges).
Presently, Constitution Benches are set up on an ad hoc basis as and when the need arises. The idea behind a Constitution Bench is clear: it is constituted in rare cases to decide important questions of fact or legal and/or constitutional interpretation.
Q.6. A parliamentary system of government is one in which (2020)
(a) All political parties in the parliament are represented in the government
(b) The government is responsible to the parliament and can be remove by it
(c) The government is elected by the people and can be removed by them
(d) The government is chosen by the parliament but cannot be removed by it before completion of a fixed term
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Article 75: The ministers are collectively responsible to the Parliament in general and to the Lok Sabha in particular. The principle of collective responsibility implies that the Lok Sabha can remove the ministry (i.e., council of ministers headed by the prime minister) from office by passing a vote of no confidence.
Note: No questions has been asked from this topic in the year 2019 and 2018.
Q.7. The main advantage of the parliamentary form of government is that (2017)
(a) the executive and legislature work independently
(b) it provides continuity of policy and is more efficient
(c) the executive remains responsible to the legislature
(d) the head of the government cannot be changed without election
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Parliamentary system is also known as Cabinet Government. It provides for collective responsibility of the executive to the legislature.
Q.8. The Parliament of India acquires the power to legislate on any item in the State List in the national interest if a resolution to that effect is passed by the (2016)
(a) Lok Sabha by a simple majority of its total membership
(b) Lok Sabha by a majority of not less than two-thirds of its total membership
(c) Rajya Sabha by a simple majority of its total membership
(d) Rajya Sabha by a majority of not less than two-thirds of its members present and voting
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
If the Rajya Sabha declares that it is necessary in the national interest that Parliament should make laws on a matter in the State List, then the Parliament becomes competent to make laws on that matter. Such a resolution must be passed by the Rajya Sabha by a majority of not less than two-third of its members present and voting.
Q.9. There is a Parliamentary System of Government in India because the (2015)
(a) Lok Sabha is elected directly by the people
(b) Parliament can amend the Constitution
(c) Rajya Sabha cannot be dissolved
(d) Council of Ministers is responsible to the Lok Sabha
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The executive in a Parliamentary system is responsible 1to the legislature for all its actions. The ministers are answerable to the parliament and responsible to the Lok Sabha. The Council of Ministers remains in office as long as they enjoy the support and confidence of the Lok Sabha.
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Parliamentary System - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the parliamentary system of government? |  |
| 2. How does the parliamentary system differ from the presidential system? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of a parliamentary system? |  |
| 4. What role does the Prime Minister play in a parliamentary system? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the concept of a vote of no confidence in a parliamentary system? |  |
















