UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Banking in India | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
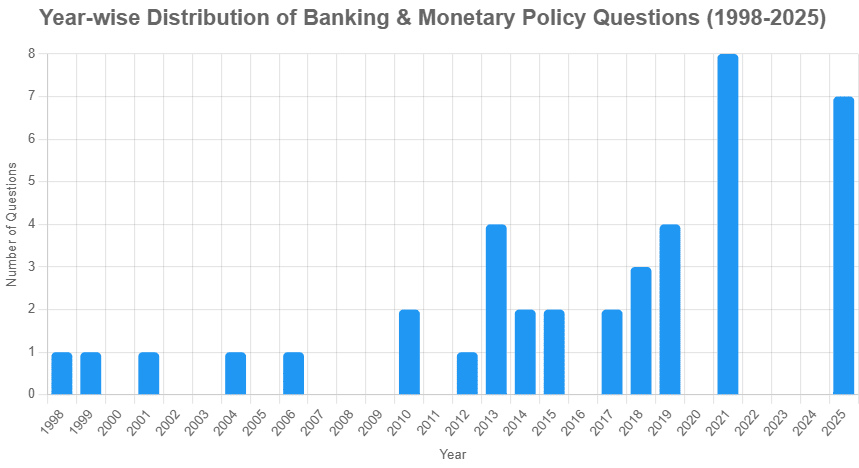
Between 1998 and 2025, 40 questions have been asked with varying difficulty level 12 easy (30%), 20 medium (50%), and 8 hard (20%), covering critical topics such as banking operations, monetary policy, and financial regulations in India.
Q.1. Which of the following are the sources of income for the Reserve Bank of India? (2025)
I. Buying and selling Government bonds
II. Buying and selling foreign currency
III. Pension fund management
IV. Lending to private companies
V. Printing and distributing currency notes
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) I and II only
(b) II, III and IV
(c) I, III, IV and V
(d), II and V
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) generates income primarily through its monetary and financial operations:
- I. Buying and selling Government bonds: Correct. The RBI earns interest on government securities it holds and profits from trading them in open market operations.
- II. Buying and selling foreign currency: Correct. The RBI earns income through foreign exchange transactions, including gains from currency appreciation or forex reserves management.
- III. Pension fund management: Incorrect. The RBI does not manage pension funds as a source of income; this is handled by entities like the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA).
- IV. Lending to private companies: Incorrect. The RBI does not directly lend to private companies; it provides liquidity to banks and financial institutions.
- V. Printing and distributing currency notes: Incorrect. Printing currency is a cost for the RBI, not a source of income, though it earns seigniorage (the difference between the face value of currency and its production cost) indirectly, but this is not the same as income from distribution.
Thus, only I and II are correct.
Q.2. Consider the following statements: (2025)
I. The Reserve Bank of India mandates all the listed companies in India to submit a Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR).
II. In India, a company submitting a BRSR makes disclosures in the report that are largely non-financial in nature.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Statement I: The RBI does not mandate the BRSR. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) mandates listed companies (top 1,000 by market capitalization) to submit a BRSR as part of their annual reporting to promote sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) disclosures. Thus, this statement is incorrect.
- Statement II: Correct. The BRSR includes disclosures on non-financial metrics such as environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices, focusing on sustainability and ethical operations.
Thus, only Statement II is correct.
Q.3. Consider the following statements: (2025)
I. India accounts for a very large portion of all equity option contracts traded globally thus exhibiting a great boom.
II. India's stock market has grown rapidly in the recent past even overtaking Hong Kong's at some point of time.
III. There is no regulatory body either to warn the small investors about the risks of options trading or to act on unregistered financial advisors in this regard.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and Il only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- Statement I: Correct. India has become a global leader in equity options trading, with the National Stock Exchange (NSE) accounting for a significant portion of global equity option contracts due to high trading volumes in index and stock options.
- Statement II: Correct. India’s stock market has grown rapidly, with its market capitalization surpassing Hong Kong’s in early 2024, driven by strong economic growth and investor interest.
- Statement III: Incorrect. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates the stock market and options trading, issuing warnings to investors about risks and taking action against unregistered financial advisors. SEBI’s investor education initiatives and regulations on advisory services contradict this statement.
Thus, only I and II are correct.
Q.4. Consider the following statements in respect of RTGS and NEFT: (2025)
I. In RTGS, the settlement time is instantaneous while in case of NEFT, it takes some time to settle payments.
II. In RTGS, the customer is charged for inward transactions while that is not the case for NEFT.
III. Operating hours for RTGS are restricted on certain days while this is not true for NEFT.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) I and II
(c) I and III
(d) III only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- Statement I: Correct. Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) processes transactions instantly, while National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) settles payments in batches, causing a delay.
- Statement II: Incorrect. The RBI does not charge customers for inward RTGS or NEFT transactions; charges, if any, are determined by banks, and inward NEFT transactions are typically free.
- Statement III: Incorrect. Both RTGS and NEFT operate 24/7 as of 2025, following RBI’s expansion of operating hours in recent years. There are no restrictions on specific days for either.
Thus, only Statement I is correct.
Q.5. Consider the following countries: (2025)
I. United Arab Emirates
II. France
III. Germany
IV. Singapore
V. Bangladesh
How many countries amongst the above are there other than India where international merchant payments are accepted under UPI?
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) All the five
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The countries where UPI international merchant payments are already accepted (excluding India) from your list are:
- United Arab Emirates
- France
- Singapore
Both Germany and Bangladesh are not currently supporting UPI-based merchant payments
Thus, only three countries are accepted under UPI.
Q.6. Consider the following statements: (2021)
- The Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is appointed by the Central Government.
- Certain provisions in the Constitution of India give the Central Government the right to issue directions to the RBI in public interest.
- The Governor of the RBI draws his power from the RBI Act.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Statement (1) is correct: RBI Governor and Deputy Governors are appointed by the Central Government.
- Statement (2) is incorrect: RBI ACt, 1934- The Central Government may from time to time give such directions to the Bank as it may, after consultation with the Governor of the Bank, consider necessary in the public interest.
- Statement (3) is correct: RBI Act- 1934 -S Governor and in his absence the Deputy Governor nominated by him in this behalf, shall also have powers of general superintendence and direction of the affairs and the business of the Bank, and may exercise all powers and do all acts and things which may be exercised or done by the Bank
Q.7. With reference to urban cooperative banks in India consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the state governments
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The recent Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act 2020 enables the RBI to get all the powers, including those hitherto exclusively with the registrar of cooperative societies. However, powers of registrar continue to be with him but the powers of RBI override those of registrar.
UCBs are permitted to raise equity share capital, preference shares and debt instruments.
The applicability of banking laws to cooperatives societies since March 1, 1966 ushered in ‘duality of control’ over UCBs between the Registrar of Cooperative Societies/Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies and the Reserve Bank of India.
Q.8. The money multiplier in an economy increases with which one of the following? (2021)
(a) Increase in the cash Reserve Ration in the banks
(b) Increase in the Statutory Liquidity Ratio in the banks
(c) Increase in the banking habit of the people
(d) Increase in the population of the country
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- The money created by the Federal Reserve is the monetary base, also known as high-powered money.
- Banks create money by making loans. A bank loans or invests its excess reserves to earn more interest. A one-dollar increase in the monetary base causes the money supply to increase by more than one dollar.
- The increase in the money supply is the money multiplier.
Q.9. With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Retail investors through demat account can invest in ‘Treasury Bills’ and ‘Government of India Debt Bonds’ in primary market.
- The ‘Negotiated Dealing System-Order Matching’ is a government securities trading platform of the Reserve Bank of India.
- The ‘Central Depository Services Ltd’. is jointly promoted by the Reserved Bank of India and the Bombay Stock Exchange.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
CDSL is promoted by BSE which later divested its stakes among nationalized bank
Q.10. In India, the central bank’s function as the ‘lender of last resort’ usually refers to which of the following? (2021)
- Lending to trade and industry bodies when they fail to borrow from other sources
- Providing liquidity to the banks having a temporary crisis
- Lending to governments to finance budgetary deficits
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
A lender of last resort (LoR) is an institution, usually a country’s central bank, that offers loans to banks or other eligible institutions that are experiencing financial difficulty or are considered highly risky or near collapse
Q.11. In India, the central bank’s function as the ‘lender of last resort’ usually refers to which of the following? (2021)
- Lending to trade and industry bodies when they fail to borrow from other sources
- Providing liquidity to the banks having a temporary crisis
- Lending to governments to finance budgetary deficits
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
A lender of last resort (LoR) is an institution, usually a country’s central bank, that offers loans to banks or other eligible institutions that are experiencing financial difficulty or are considered highly risky or near collapse.
Q.12. What is the importance of the term “Interest Coverage Ratio” of a firm in India? (2020-I)
- It helps in understanding the present risk of a firm that a bank is going to give a loan to.
- It helps in evaluating the emerging risk of a firm that a bank is going to give a loan to.
- The higher a borrowing firm’s level of Interest Coverage Ratio, the worse is its ability to service its debt.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- NCERT class 12 Accountancy book also confirms, “A higher Interest coverage ratio ensures safety of interest on debts.”
- Third statement is wrong. Statement 1 is correct, By looking at the interest coverage ratio we can identify the present risk of a firm (That it is not generating good revenue). There is only “A” option where statement#1 is present.
Q.13. Which of the following is not included in the assets of a commercial bank in India? (2019-I)
(a) Advances
(b) Deposits
(c) Investments
(d) Money at call and short notice
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
NCERT Macroeconomics Class12, page 40: observe the table 3.1: Deposits are plotted on the liability side of a commercial bank’s balance sheet.
Q.14. The Chairman of public sector banks are selected by the (2019-I)
(a) Banks Board Bureau
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) Union Ministry of Finance
(d) Management of concerned bank
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Bank Board Bureau (BBB) was setup in 2016, BBB selects top officials (MD, CEO, Chairman and full-time Directors) for PSBs, LIC and other public sector financial institutions.
Q.15. The Reserve Bank of India’s recent directives relating to ‘Storage of Payment System Data’, popularly known as data diktat command the payment system providers that: (2019-I)
- They shall ensure that entire data relating to payment systems operated by them are stored in a system only in India.
- They shall ensure that the systems are owned and operated by public sector enterprises.
- They shall submit the consolidated system audit report to the comptroller and Auditor General of India by the end of the calendar year.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
As per RBI’s directive, payment system providers are required to store the data in India only. Other features are not required by RBI.
Q.16. Which one of the following is not the most likely measure the Government/RBI takes to stop the slide of Indian rupee? (2019-I)
(a) Curbing imports of non-essential goods and promoting exports
(b) Encouraging indian borrowers to issue rupee denominated Masala bonds
(c) Easing conditions relating to external commercial borrowing
(d) Following an expansionary monetary policy
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
To control rupee weakening,
A: will help by reducing the Current account deficit.
B: will help by reducing the demand of dollars in loan-repayment.
C: will help by increasing the inflow of dollars and other currencies.
D: will backfire, because rupee currency supply will increase without corresponding increase in the supply of dollars and as a result: dollar will strengthen, Indian Rupee will weaken further. So D is the answer.
Q.17. With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements: (2018-I)
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- BHIM App was launched in 2016, it allows money transfer to UPI-enabled bank accounts so #1 is right.
- The BHIM apps has three levels of authentication. For one, the app binds with a device's ID and mobile number, second a user needs to sync whichever bank account (UPI or non-UPI enabled) in order to the conduct transaction. Third, when a user sets up the app they are asked to create a pin which is needed to log into the app. Hence #2 is wrong.
Q.18. Which one of the following links all the ATMs in India ? (2018-I)
(a) Indian banks' Association
(b) National Securities Depository Limited
(c) National Payments Corporation of India
(d) Reserve Bank of India
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Till 2009, RBI's Institute for Development and Research in Banking Technology (IDRBT) provided the linkages to ATM network in India but afterwards, it was taken over by NPCi's National Financial Switch (NFS).
Q.19. Consider the following statements: (2018-I)
- Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is the amount that banks have to maintain in the form of their own funds to offset any loss that banks incur if the account-holders fail to repay dues.
- CAR is decided by each individual bank.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
CAR is decided by the benchmarks set by BASEL-III Committee on Banking supervision and implemented by the central bank of individual country. So, #2 is right, whereas #1 is correct.
Q.20. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017-I)
- It decides the RBI's benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
MPC has 6 members, not 12; and it's headed by RBI governor and not Finance Minister. So statement 2 and 3 are wrong, hence by elimination, we reach answer (A) only 1 correct.
Q.21. What is the purpose of setting up of Small Finance Banks (SFBs) in India? (2017-I)
- To supply credit to small business units
- To supply credit to small and marginal farmers
- To encourage young entrepreneurs to set up business particularly in rural areas.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
While directly or indirectly all three will be encouraged because of Small Finance banks. But when RBI invited applications, the specific purpose were 1 and 2 only.
Q.22. 'Basel III Accord' or simply 'Basel III', often seen in the news, seeks to (2015-I)
(a) develop national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity
(b) improve banking sector's ability to deal with financial and economic stress and improve risk management
(c) reduce the greenhouse gas emissions but places a heavier burden on developed countries
(d) transfer technology from developed Countries to poor countries to enable them to replace the use of chlorofluorocarbons in refrigeration with harmless chemicals
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Basel III is a comprehensive set of reform measures which was developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision and to strengthen the regulation, supervision and risk management of the banking sector. These measures aim to:
Improve the banking sector's ability to absorb shocks arising from financial and economic stress, whatever the source; improve risk management and governance; strengthen banks' transparency and disclosures.
Q.23. With reference to Indian economy, consider the following (2015-I)
- Bank rate
- Open market operations
- Public debt
- Public revenue
Which of the above is/are component/ components of Monetary Policy?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 1, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The RBI implements the monetary policy through open market operations, bank rate policy, reserve system, credit control policy, moral persuasion and through many other instruments
Q.24. When the Reserve Bank of India reduces the Statutory Liquidity Ratio by 50 basis points, which of the following is likely to happen? (2015-I)
(a) India's GDP growth rate increases drastically
(b) Foreign Institutional Investors may bring more capital into our country
(c) Scheduled Commercial Banks may cut their lending rates
(d) It may drastically reduce the liquidity to the banking system
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
When the Reserve Bank of India reduces the Statutory Liquidity Ratio by 50 basis points; the Scheduled Commercial Banks may cut their lending rates.
Q.25. In the context of Indian economy, which of the following is/ are the purpose/purposes of ‘Statutory Reserve Requirements’? (2014 - I)
- To enable the Central Bank to control the amount of advances the banks can create
- To make the people’s deposits with banks safe and liquid
- To prevent the commercial banks from making excessive profits
- To force the banks to have sufficient vault cash to meet their day-to-day requirements
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
1 is definitely correct as CRR. SLR is used to control money supply and credit off take. 2 may or may not be correct, to make people's deposit safe, capital adequacy ratio is the norm. 3 is definitely wrong as to control excess profit, margins would have to be reduced, not CRR, SLR.
Q.26. The terms ‘Marginal Standing Facility Rate’ and ‘Net Demand and Time Liabilities’, sometimes appearing in news, are used in relation to (2014 - I)
(a) banking operations
(b) communication networking
(c) military strategies
(d) supply and demand of agricultural products
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Marginal Standing Facility rate is the rate at which banks borrow funds overnight from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) against approved government securities. Net Demand and time liability is the sum of demand and time liability of Banks with public and other banks wherein assets with other banks is subtracted to get net liability of other bank.
Q.27. Priority Sector Lending by banks in India constitutes the lending to (2013 - I)
(a) agriculture
(b) micro and small enterprises
(c) weaker sections
(d) All of the above
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Priority sector lending constitutes the lending to– agriculture, micro and small enterprises, micro credit, education, housing and weaker sections.
Q.28. In the context of Indian economy, ‘Open Market Operations’ refers to (2013 - I)
(a) borrowing by scheduled banks from the RBI
(b) lending by commercial banks to industry and trade
(c) purchase and sale of government securities by the RBI
(d) None of the above
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
It is an activity by a central bank(RBI) to buy or sell government securities. The aim of open market operations is to manipulate the short term interest rate and the supply of base money in an economy, and indirectly control the total money supply.
Q.29. The Reserve Bank of India regulates the commercial banks in matters of (2013 - I)
- liquidity of assets
- branch expansion
- merger of banks
- winding-up of banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The Reserve Bank of India is the main monetary authority of the country and beside that, in its capacity as the central bank, acts as the bank of the national and state governments.
Q.30. An increase in the Bank Rate generally indicates that the (2013 - I)
(a) market rate of interest is likely to fall
(b) Central Bank is no longer making loans to commercial banks
(c) Central Bank is following an easy money policy
(d) Central Bank is following a tight money policy
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
A tight monetary policy is a course of action undertaken by Central bank to constrict spending in an economy, or to curb inflation when it is rising too fast. The increased bank rate increases the cost of borrowing and effectively reduces its attractiveness.
Q.31. Consider the following liquid assets: (2013 - I)
- Demand deposits with the banks
- Time deposits with the banks
- Saving deposits with the banks
- Currency
The correct sequence of these assets in the decreasing order of liquidity is
(a) 1-4-3-2
(b) 4-3-2-1
(c) 2-3-1-4
(d) 4-1-3-2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Currency/cash is the most liquid, then the demand deposits (current accounts), then the saving deposits with bank and finally the least liquid is the time deposits with the bank (fixed deposits).
Q.32. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as a bankers’ bank. This would imply which of the following? (2012 - I)
- Other banks retain their deposits with the RBI.
- 2. The RBI lends funds to the commercial banks in times of need.
- 3. The RBI advises the commercial banks on monetary matters.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
All the statements are correct.
Q.33. In India, the interest rate on savings accounts in all the nationalized commercial banks is fixed by (2010)
(a) Union Ministry of Finance
(b) Union Finance Commission
(c) Indian Banks’ Association
(d) None of the above.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
It is fixed by Reserve Bank of India. In 2011, RBI permitted the commercial banks to fix interest rate on saving account independently.
Q.34. When the Reserve Bank of India announces an increase of the Cash Reserve Rate, what does it mean? (2010)
(a) The commercial banks will have less money to lend
(b) The Reserve Bank of India will have less money to lend
(c) The Union Government will have less money to lend
(d) The commercial banks will have more money to lend
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
CRR or the Cash Reserve Ratio is that ratio of the total deposits held by a bank which it has to keep with the central bank of country.
Q.35. With reference to the institution of Banking Ombudsman in, India, which one of the statements is not correct? (2010)
(a) The Banking Ombudsman is appointed by the Reserve Bank of India.
(b) The Banking Ombudsman can, consider complaints from Non Resident Indians having accounts in India.
(c) The orders passed by the Banking Ombudsman are final and binding on the parties concerned.
(d) The service provided by the Banking Ombudsman is free of any fee.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Banking ombudsman Scheme is an expeditious and inexpensive forum for bank customers for resolution of complaints relating to certain services rendered by banks. Any person aggrieved by the decision of the Banking Ombudsman can approach the Appellate Authority. The Appellate Authority is vested with a Deputy Governor of the RBI.
Q.36. Which one of the following Indian banks is not a nationalized bank? (2006)
(a) Corporation Bank
(b) Dena Bank
(c) Federal Bank
(d) Vijaya Bank
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Federal Bank is a major Indian commercial bank in the private sector, headquartered at Kochi, Kerala.
Q.37. Consider the following statements: (2004)
- Reserve Bank of India was nationalized on 26 January, 1950
- The borrowing programme of the Government of India is handled by the Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
RBI was established in 1935 and was nationalized on 1 January, 1949. RBI handles the borrowing programme of the central and State Governments.
Q.38. Consider the following statements regarding Reserve Bank of India: (2001)
- It is a banker to the Central Government
- It formulates and administers monetary policy
- It acts as an agent of the Government in respect of India
- It handles the borrowing programme of Government of India
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(d) 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Functions of RBI: sole authority to issue currency; government’s bank; banker’s bank; guardian of money market; lender of the last resort; sole reservoir of Foreign exchange reserves; controller of credit; clearing house for settling inter bank transactions. It follows an independent monetary policy
Q.39. The banks are required to maintain a certain ratio between their cash in hand and total assets. This is called: (1998)
(a) SBR (Statutory Bank Ratio)
(b) SLR (Statutory Liquid Ratio)
(c) CBR (Central Liquid Reserve)
(d) CLR (Central Liquid Reserve)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
SLR or the Statutory Liquidity Ratio is that portion of total deposits which a commercial bank has to maintain with itself at any given point of time in the form of liquid assets like cash in hand, current balances with other banks and first class securities which can be turned into cash (gold, cash or other approve securities). This ratio at present is 25%. Some assets have to be in liquid form to take care of financial emergencies which every bank has to face. It regulates the credit growth in India.
Q.40. The Employment Assurance Scheme envisages financial assistance to rural areas for guaranteeing employment to at least: (1999)
(a) 50 percent of the men and women seeking jobs in rural areas
(b) 50 percent of the men seeking jobs in rural areas
(c) one man and one woman in a rural family living below the poverty line
(d) one person in a rural landless household living below the poverty line
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Employment Assurance scheme was launched on 2nd October, 1993. It is open to all adult rural poor who are in need of wage employment. A maximum of two adults per family would be provided wage employment, when there is demand during lean agricultural season, subject to availability of funds.
|
108 videos|431 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Previous Year Questions (Prelims): Banking in India - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in the banking sector? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of banks in India? |  |
| 3. How does the banking system in India support economic growth? |  |
| 4. What are Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and their significance? |  |
| 5. What are the major challenges faced by the banking sector in India? |  |

















