A Busy Month Class 4 Notes EVS Chapter 16
| Table of contents |

|
| Dove |

|
| Sparrow |

|
| Indian Robin |

|
| Crow |

|
| Barbet |

|
| TailorBird |

|
| Sunbird |

|
| Weaver |

|
| Why do Birds Make Nests Before Laying Eggs? |

|
| Bird Feet |

|
| Bird Beaks |

|
| Animal Teeth |

|
| Important Learnings |

|
This chapter teaches us about a special time in the lives of animals and birds. There's a specific month when female birds are getting ready to lay eggs, so they need to prepare. They make nests to keep their eggs safe, and each type of bird makes nests in its own unique way and lays eggs in different spots. Let us now look at different birds and understand the nest and laying types.
Dove
- The dove bird is small, long tailed pigeon, also called as the rock dove.
- This bird is called as bird of peace.
- Doves look like other birds with small heads, pointy beaks, round bodies, long wings, and tails.
- The dove builds its nest in the prickly thorns of a cactus or a mehendi bus.
Sparrow
 Sparrow
Sparrow
- Sparrows look cute and are gray and brown in color. They can fly fast, reaching speeds up to 38.5 kilometers per hour and sometimes even 50 kilometers per hour.
- Sparrows usually lay eggs in spring and summer when they're making nests.
- They can lay three to seven eggs, but typically it's around four to five eggs.
- The sparrow can be seen near our homes, making its nest in various places like on top of a cupboard, behind a mirror, or on a ledge.
Indian Robin
- The Indian robin is a type of bird found in many places across the Indian subcontinent, such as Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
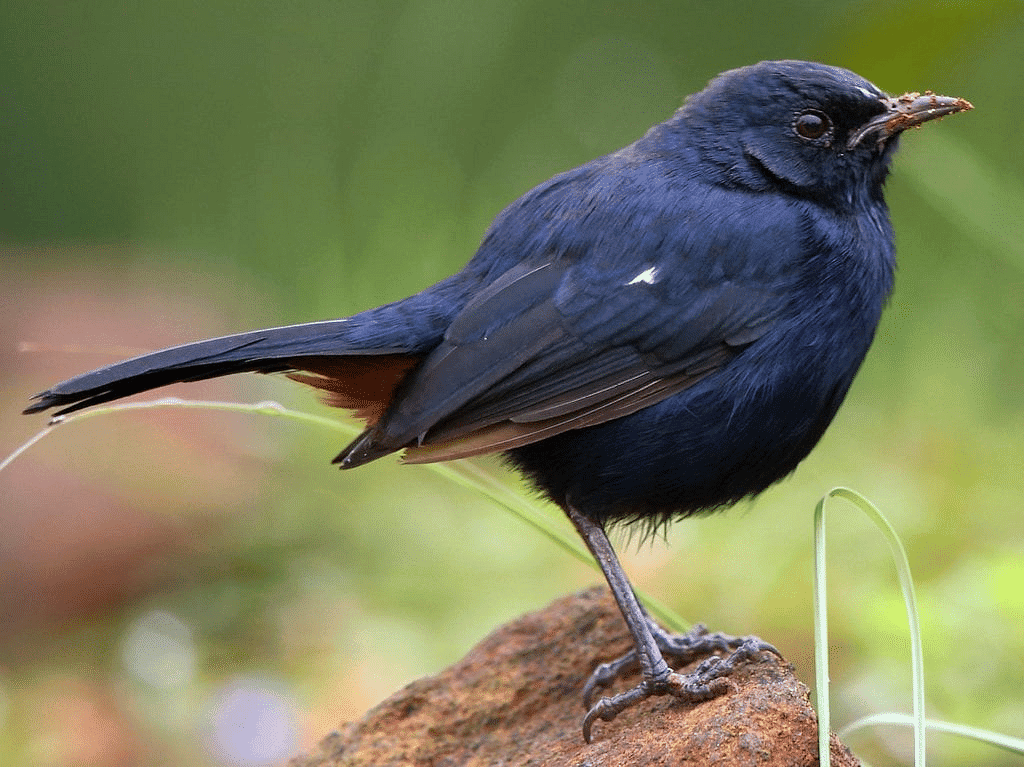 Indian Robin
Indian Robin
- When it's time to lay eggs, the Indian robin typically lays 2-3 eggs that are creamy-white in color.
- Lays eggs in spaces between roadside stones. Nests made of grass with soft twigs, roots, wool, hair, and cottonwool.
Crow
- Crows are shiny black birds found almost everywhere except southern South America.
- When it's time to breed, a crow typically lays about five eggs, one each day.
- Crows build their nests in the crook of a tree trunk or on a branch near the top of the tree.
- A crow's nest is built using various materials like wire and wood scraps.
Did you know that the Koel sings lovely songs? It's interesting because this bird doesn't make its own nest. Instead, it puts its eggs in a crow's nest. The Koel's eggs hatch together with the crow's eggs.
Barbet
- Barbets are chubby birds that come in different sizes, from small to large.
- They have a strong, pointy beak, short wings, a short tail, and a big head with bristles near their beak.
 Barbet
Barbet
- Barbets make their homes by digging holes in trees. They mostly eat fruits but also snack on insects like winged termites.
- From September to December, they lay one to five eggs, one each day. Mom bird keeps the eggs warm for about 13 to 17 days until they hatch. When the chicks are born, they're blind and featherless. Both parents take turns feeding them insects until they grow up.
- Summer call is 'tuk, tuk, tuk'.
TailorBird
- Tailorbirds are named for how they make their nests.
 Tailorbird
Tailorbird
- They use plant fibres or spider silk to sew together the edges of a big leaf, creating a cradle for their nest.
- Tailorbirds lay 2 to 5 eggs that are light blue with brown spots.
- The female bird sits on the eggs for about 12 days until they hatch.
- Both parents work hard to find food and take care of their 2 to 5 chicks after they hatch.
Sunbird
 Sunbird
Sunbird
- Sunbird nests look like small purses and hang from thin branches with lots of spiderwebs.
- Builds hanging nests from branches with various materials like hair, grass, twigs, leaves, cottonwool, bark, cloth, and spider webs.
- Sunbirds are small birds that feed on nectar and their nests are usually 9 to 15 cm long.
- Female sunbirds lay up to four eggs, and only the females incubate them, except for spiderhunters.
- After about 15 to 17 days, the eggs of purple sunbirds hatch. The male sunbirds help take care of the baby birds.
Weaver
- Weaverbirds are small birds found in the Old World. They are known for their skillful nest-building using grass stems and plant fibers.
 Weaverbird
Weaverbird
- Male builds intricately woven nests. Female chooses the nest and lays eggs.
- The female weaverbird lays two to four white eggs, and she sits on them for about 14 to 17 days until they hatch. Sometimes, male weaverbirds help feed the chicks.
 Pigeon Nest
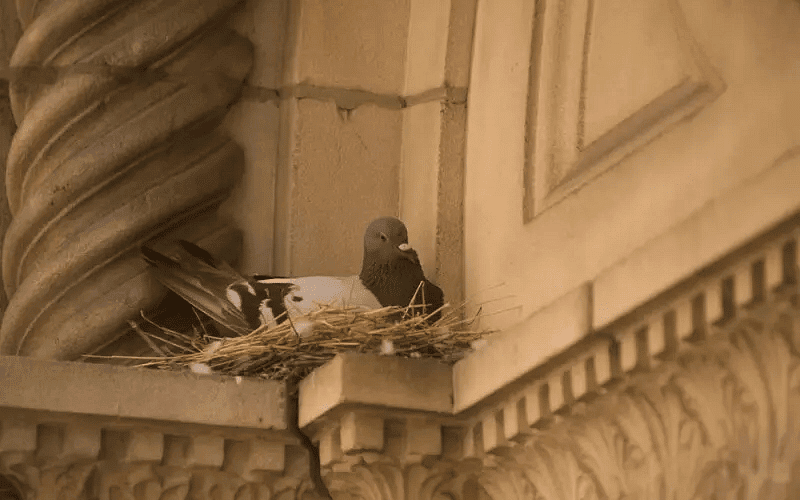
Pigeon Nest
Pigeon: Builds nests in old or deserted buildings.
Why do Birds Make Nests Before Laying Eggs?
- To keep their eggs safe, many birds hide their nests.
- Some birds choose places that are hard for predators to reach, or they build their nests in tricky ways that make it tough for predators to find them.
- Bird nests can also become homes for other animals. These animals might help or harm the birds, depending on what they do.
Bird Feet
Bird’s feet come in different sizes and shapes. A bird’s foot is designed to help it navigate its environment and find the food it needs.
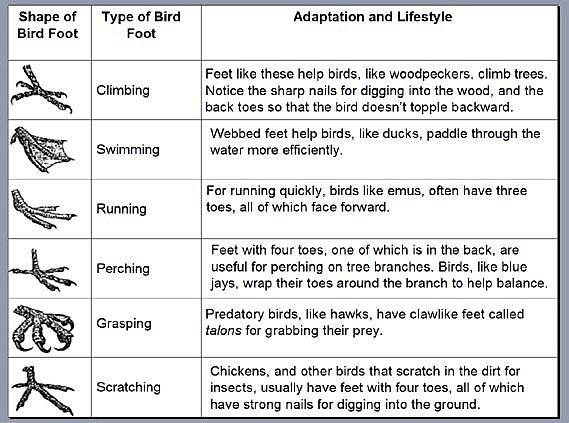 Bird Feet
Bird Feet
Bird Beaks
- A bird's beak is mainly used for finding and eating food. It helps them tear, crush, pick, and break food items.
- Birds also use their beaks to clean their feathers and keep them in good shape.
- They use their beaks like we use our hands, for tasks like building nests and feeding their babies.
- By looking at a bird's beak, we can learn about its habits, where it lives, and what it eats.
 Types of Bird Beaks
Types of Bird Beaks
Animal Teeth
Animals have different types of teeth suited for their diets and lifestyles.
 Types of Animal Teeth
Types of Animal Teeth
1. Cows:
- Short front teeth for snipping grass.
- Large, flat side teeth for chewing grass.
2. Cats:
- Sharp teeth for tearing and cutting meat.
3. Snakes:
- Sharp, curved teeth.
- Don't chew prey, swallow food whole.
- Snakes have sharp teeth for catching and holding onto prey, but they don't chew their food; instead, they swallow it whole.
4. Squirrels:
- Front teeth keep growing throughout life.
- Gnaw on things to prevent teeth from becoming too long.
Humans have different types of teeth for biting, tearing, and chewing food.
- Front Teeth (Incisors): Used for biting into food.
- Back Teeth (Molars): Used for chewing and grinding food.
- Canines: Pointed teeth used for tearing food.
- Premolars: Flat teeth used for crushing and grinding food.
Important Learnings
- Birds Build Nests: Different birds build nests in different ways. Some use grass, twigs, and leaves to make cozy homes for their babies.
- Bird Parenting: Parent birds take care of their babies by feeding them insects and other food. They work hard to keep their babies safe and comfortable.
- Bird Diversity: Birds come in many shapes, sizes, and colors. Each bird has its own unique way of building nests and raising its young ones.
- Respect for Nature: Understanding the challenges birds face, like finding food and protecting their nests from predators, helps us appreciate and respect nature. It shows us how tough life can be for them and why it's important to care for our environment.
- Understanding Teeth: We can also learn about the diversity of animal teeth and how they're adapted for different purposes, like chewing grass or tearing meat. It's fascinating to see how animals have evolved to meet their specific dietary needs.
|
49 videos|217 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on A Busy Month Class 4 Notes EVS Chapter 16
| 1. Why do birds build nests? |  |
| 2. What materials do birds use to make their nests? |  |
| 3. How long does it take for birds to build a nest? |  |
| 4. Do all birds make nests in the same way? |  |
| 5. When do birds typically lay their eggs? |  |















