UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Science & Technology for UPSC CSE > NCERT Summary: Synthetic Fibres & Plastics
Synthetic Fibres & Plastics Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary
Introduction
- Fabrics are made from fibres obtained from natural or artificial sources.
- They are also used for making a large variety of household articles.
Synthetic fibres (or man-made fibres)
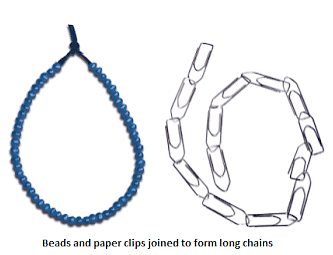
- They are chains of small units joined together (each small unit is a chemical substance).
- These small units combine to form a large single unit called a polymer.
Types of polymers
Addition polymers
- Monomers combine together to form a giant molecule known as the polymer. No molecule is eliminated during formation of addition polymers.
- Exmples of addition polymer are polythene, polyvinyl chloride etc.
Condensation polymers
- Several small units of monomers combine with each other, along with elimination of simple molecule like water to form polymer unit.
- Examples of condensation polymer are nylon-66, terylene etc.
Polyester
- Fabric made from polyester does not get wrinkled easily.
- Common polyester includes terylene and PET
- PET is used for making utensils, films, wires, bottles, etc. Terylene is used for making dress materials.
Acrylic
- It is relatively cheaper than wool.
- Sweaters, shawls and blankets are made from acrylic.
Characteristics of synthetic fibres
- They dry up quickly, are durable, less expensive, readily available, and easy to maintain.
- However, fabric made of synthetic fibre melts on catching fire and sticks to the body of person wearing it.
- So, synthetic clothes should not be worn while working in kitchen or laboratory.
Plastics
- They are polymer-like synthetic fibres.
- Arrangement of small units is linear or cross-linked.
- Can be recycled, reused, coloured, melted, rolled into sheets, or made into wires.
Thermoplastics
- These are the plastics that get deformed easily on heating and can be bent easily. Examples: polythene and PVC
Thermosetting plastics
- These are the plastics, which when moulded once, cannot be softened by heating. Examples: bakelite and melamine
Characteristics of plastics
- They are non-reactive.
- They are light, strong, and durable.
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Use of plastics
- They are used to store various kinds of materials such as food items, chemicals etc.
- It is widely used in various industries and for making a variety of household articles.
- They are extensively used in health care industry for making syringes, threads for stitching wounds, doctor’s gloves, and other medical instruments.
- Fire resistant plastics are used as a coating on the suits of the firemen.
Biodegradable substances
- These are the materials that decompose through natural processes such as by the action of bacteria.
Examples: paper, peels of vegetables, wood and fruits, etc.
Non-biodegradable substances
- These are the materials that are not easily decomposed by natural processes. Examples: plastic bags, metals, etc.
- Plastics are not environment friendly as they cause environment pollution.
- To minimize the environmental hazards, the 4R principle must be used.
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Recover.
The document Synthetic Fibres & Plastics Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary is a part of the UPSC Course Science & Technology for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Synthetic Fibres & Plastics Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary
| 1. What are synthetic fibres and plastics? |  |
Ans. Synthetic fibres are man-made fibres that are created through chemical processes. Plastics, on the other hand, are synthetic materials made from polymers that can be molded into various shapes.
| 2. What are the advantages of synthetic fibres over natural fibres? |  |
Ans. Synthetic fibres have several advantages over natural fibres. They are more durable, have higher strength, and are resistant to wrinkles and shrinkage. They also dry quickly and are less expensive to produce.
| 3. How are synthetic fibres and plastics produced? |  |
Ans. Synthetic fibres are produced by the polymerization of chemical compounds derived from petroleum. Plastics are produced by the polymerization of monomers, which are small molecular units, through a process called polymerization.
| 4. What are the different types of synthetic fibres and plastics? |  |
Ans. There are several types of synthetic fibres, including polyester, nylon, acrylic, and rayon. Plastics can be categorized into various types based on their properties, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polystyrene.
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of synthetic fibres and plastics? |  |
Ans. Synthetic fibres and plastics have significant environmental impacts. They are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. Their production also involves the use of fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions and climate change. Additionally, improper disposal of synthetic fibres and plastics can lead to pollution of water bodies and harm wildlife.
Related Searches
















