Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Sound
Sound Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 11
Introduction
- Sound helps us to communicate with one another and plays an important role in our life.
- Vibrating body produces sound.
- In this chapter, we will know about how sound is produced and how we hear them.
Vibration motion

- This refers to the to-and-fro or back-and-forth movement of an object.
- In humans, sound is produced by the vibration of the vocal cords.
- Sound cannot travel through a vacuum.
- Sound waves are classified as longitudinal waves.
- The frequency of oscillation is the number of vibrations per second.
- A larger amplitude of vibration results in a louder sound.
How Sound is Produced by Humans?
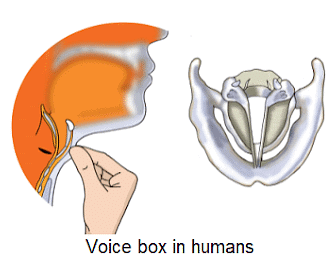
- Sound in humans is made by the voice box or larynx, which is at the top of the windpipe.
- When air from the lungs pushes through, the vocal cords vibrate and create sound.
- Sometimes, the sound made is so soft that it can't be heard.
- The muscles connected to the vocal cords can tighten or loosen them, changing the type of sound produced. Tight and thin cords create a different sound quality compared to loose and thick cords.
- Everyone has unique vocal cords. This is why the voices of men, women, and children sound different. Men's vocal cords are about 20 mm long, women's around 15 mm, and children's are much shorter.
Propagation of Sound

- Sound requires material medium for propagation.
- Sound can travel through solid, liquid or gas.
- Sound cannot travel through vacuum.
- No sound can be heard in outer spaces.
Frequency
- Frequency is measure of number of oscillations per second.
- It is measured in hertz(Hz).
Loudness of sound

- Loudness is measured in a unit called decibel (dB).
- The loudness relates to the square of the vibration's amplitude.
- If the amplitude doubles, the loudness increases four times.
- Pitch or shrillness is determined by frequency.
- Higher frequency means a higher pitch.
- Audible sound: Humans can hear sounds between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz.
Noise
- Unpleasant sound is called noise.
Noise pollution
- Presence of unwanted and excessive sound in the environment
- Noise pollution may cause many health related problems.
Measures to control noise pollution
- All noisy activities should take place away from residential areas.
- Industries that generate noise must be located away from these areas.
- Minimise the use of automobile horns.
- Keep the volume of TVs and music systems low.
- Plant trees along roads and near buildings to help absorb sounds, reducing the impact of noise pollution on residents.
- Install silencing devices in aircraft, vehicles, industrial machines, and household appliances.
Human Ear
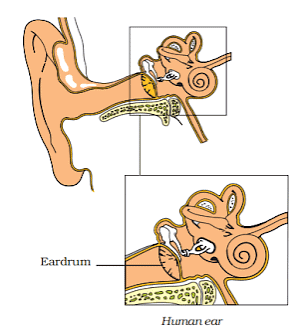
- The human ear is made up of three sections: outer, middle, and inner.
- The outer ear has a funnel-like shape.
- The eardrum plays a crucial role in hearing.
- It transmits vibrations to the inner ear.
- Sound needs a medium—like gas, liquid, or solid—to travel; it cannot move through a vacuum.
- When sound vibrations hit the eardrum, it vibrates, sending signals to the brain, enabling us to hear.
- A greater amplitude of vibration results in a louder sound.
- A higher frequency of vibration corresponds to a higher pitch, producing a shriller sound.
The document Sound Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 11 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
90 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Sound Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 11
| 1. क्या मानव ध्वनि का उत्पादन कैसे करते हैं? |  |
Ans. मानव ध्वनि का उत्पादन मुख्यतः वोकल कॉर्ड्स (गले की रज्जुओं) के माध्यम से होता है। जब हम बोलते हैं या गाते हैं, तो हमारे फेफड़े हवा को बाहर निकालते हैं, जिससे वोकल कॉर्ड्स कंपन करते हैं और ध्वनि उत्पन्न होती है।
| 2. क्या ध्वनि की तीव्रता और उच्चता एक समान होती है? |  |
Ans. नहीं, ध्वनि की तीव्रता और उच्चता अलग चीजें हैं। तीव्रता ध्वनि की शक्ति या जोर को दर्शाती है, जबकि उच्चता (पिच) ध्वनि की आवृत्ति पर निर्भर करती है। उच्च आवृत्ति वाली ध्वनियाँ उच्च पिच की होती हैं, जबकि निम्न आवृत्ति वाली ध्वनियाँ निम्न पिच की होती हैं।
| 3. मानव ध्वनि की आवृत्ति क्या होती है? |  |
Ans. मानव ध्वनि की आवृत्ति विभिन्न हो सकती है, लेकिन सामान्यतः यह 85 हर्ट्ज से लेकर 255 हर्ट्ज के बीच होती है। पुरुषों की आवाज़ें आमतौर पर निम्न आवृत्ति में होती हैं, जबकि महिलाओं की आवाज़ें उच्च आवृत्ति में होती हैं।
| 4. ध्वनि के उत्पादन में अन्य अंगों की भूमिका क्या होती है? |  |
Ans. ध्वनि के उत्पादन में केवल वोकल कॉर्ड्स का ही नहीं, बल्कि मुँह, जीभ, होंठ, और गले का भी योगदान होता है। ये सभी अंग ध्वनि को आकार देने और उसे स्पष्ट बनाने में मदद करते हैं।
| 5. क्या मानव ध्वनि को मापने के लिए कोई उपकरण होते हैं? |  |
Ans. हाँ, मानव ध्वनि को मापने के लिए साउंड मीटर जैसे उपकरणों का उपयोग किया जाता है। ये उपकरण ध्वनि की तीव्रता (डेसिबल में) और आवृत्ति (हर्ट्ज में) को मापने में सहायक होते हैं।
Related Searches
















