Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Light
Light Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 13
Introduction
- Incident Ray: The ray of light directed towards the mirror is known as the incident ray.
- Reflected Ray: The ray of light that bounces back after hitting the mirror is called the reflected ray.
- Normal: This is the line that is perpendicular to the reflecting surface at the point where the light hits.
- A plane mirror reflects light following the laws of reflection.
Laws of Reflection
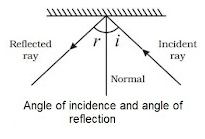
(i) ∠i (Angle of incidence) = ∠r (Angle of reflection)
The angle of incident is equal to the angle of reflection
(ii) The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
- The laws of reflection are valid in regular as well as irregular or diffused reflections.
Types of Reflections
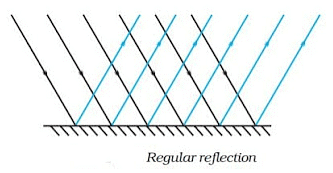
There are two types of reflection:
(i) Regular Reflections: Reflection from a smooth surface like that of a mirror is called regular reflection.
- Smooth or polished surfaces gives regular reflection.
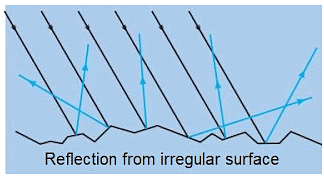
(ii) Irregular Reflections: When all the parallel rays reflected from a plane surface are not parallel, the reflection is known as diffused or irregular reflection.
- Uneven of unpolished surfaces gives irregular reflection.
Image formation by a plane mirror
- A plane mirror produces just one image of an object.
- Lateral inversion: Left part of the candle appears on the right and its right part appears on the left. This is known as lateral inversion.
- Objects that give their own light are known as luminous objects
- Objects that are visible because of reflected light are known as illuminated objects.
Multiple Reflections
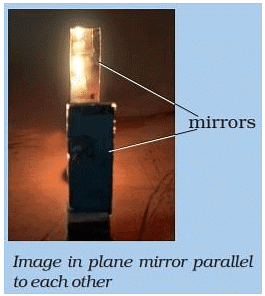
- Two mirrors kept parallel to each other forms multiple images of each other.
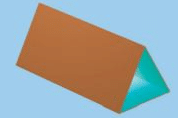
- Kaleidoscope works on the principle of multiple reflections.
- Periscope is an optical device used to see objects that are not along the line of sight.
Dispersion
- Sunlight consists of several colours.
- Splitting of white light into different colours is called dispersion.
Number of image formed in multiple reflection = (360°/angle between two plane mirror) - 1
Human Eye
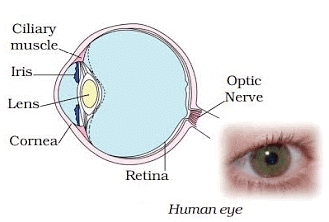
- The image is formed on the retina.
- The iris regulates the size of the pupil.
- The pupil controls how much light enters the eye.
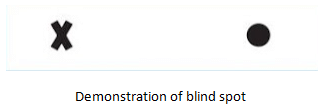
Blind Spot
- The meeting point of the optic nerve and the retina is called the blind spot.
- There are no sensory cells in this area, so vision is not possible.
- If a cross or a round mark disappears, it indicates a point on the retina that cannot send signals to the brain when light hits it.
- Cone cells react to bright light, whereas rod cells react to dim light.
Protection of Human Eye
To protect your eyes, the following points should be remembered:
- Avoid reading in dim light.
- Wash your eyes at least four times a day with clean, cold water.
- Rinse your eyes promptly if dust or small insects get in.
- Visit an eye specialist regularly, as poor vision can lead to stress, eyestrain, and headaches.
- When reading, keep a distance of at least 25 cm between your eyes and the book.
- Do not rub your eyes. If redness continues, see an eye specialist immediately.
- Stay out of direct sunlight, as too much light can damage your retina.
- A lack of vitamin A in your diet can cause various eye issues, with night blindness being one of the most common. Good sources include raw carrots, broccoli, and green vegetables.
- Some people are blind from birth, while others may lose their sight due to illness.
- Those with visual impairments often learn to identify things by touch and sound.
- The Braille system is beneficial for visually impaired individuals.
- Many Indian languages can be read using the Braille system.
The document Light Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 13 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Light Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 13
| 1. Light क्या है और यह कैसे कार्य करता है? |  |
Ans. Light एक प्रकार की ऊर्जा है जो कि विद्युत चुम्बकीय तरंगों के रूप में यात्रा करती है। यह हमारे दृष्टि के लिए आवश्यक है और वस्तुओं को देखने में मदद करती है। जब प्रकाश किसी वस्तु पर गिरता है, तो वह या तो अवशोषित होता है, परावर्तित होता है या पार होता है।
| 2. प्रकाश की गति क्या होती है और यह क्यों महत्वपूर्ण है? |  |
Ans. प्रकाश की गति लगभग 299,792 किलोमीटर प्रति सेकंड (या 3 x 10^8 मीटर प्रति सेकंड) होती है। यह सबसे तेज गति है जो ब्रह्मांड में संभव है। प्रकाश की गति का ज्ञान कई वैज्ञानिक सिद्धांतों, जैसे कि सापेक्षता के सिद्धांत, के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
| 3. प्रकाश के किस प्रकार के गुण होते हैं? |  |
Ans. प्रकाश के कई गुण होते हैं, जिनमें परावर्तन (reflection), अपवर्तन (refraction), अवशोषण (absorption) और विवर्तन (diffraction) शामिल हैं। ये गुण प्रकाश के विभिन्न व्यवहारों को समझने में मदद करते हैं और विज्ञान के विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में महत्वपूर्ण हैं।
| 4. प्रकाश का रंग क्या होता है और इसे कैसे समझा जा सकता है? |  |
Ans. प्रकाश का रंग उसके तरंग दैर्ध्य पर निर्भर करता है। विभिन्न तरंग दैर्ध्य विभिन्न रंग उत्पन्न करते हैं। जब सफेद प्रकाश को प्रिज्म के माध्यम से गुजारा जाता है, तो यह विभिन्न रंगों में बंट जाता है, जैसे लाल, नारंगी, पीला, हरा, नीला, इंडिगो और बैंगनी।
| 5. प्रकाश का उपयोग किन विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में किया जाता है? |  |
Ans. प्रकाश का उपयोग कई क्षेत्रों में किया जाता है, जैसे कि चिकित्सा (एक्स-रे, लेज़र), संचार (फाइबर ऑप्टिक्स), विज्ञान (प्रकाशिकी), और मनोरंजन (फिल्म और रंगीन रोशनी)। ये सभी क्षेत्रों में प्रकाश की विशेषताओं का लाभ उठाया जाता है।
Related Searches





















