Life Processes Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 5
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What are Life Processes? |

|
| Nutrition |

|
| Autotrophic Nutrition |

|
| Heterotrophic Nutrition |

|
| How do Amoeba Obtain their Nutrition? |

|
| Nutrition in Human Beings |

|
Introduction
Differentiating between living and non-living entities can sometimes be challenging, but certain characteristics can help us make this separation. While the visible movement, such as breathing or growth, is often associated with living beings, it is not always a definitive indicator. Even a motionless plant or an animal that breathes without visible movement can still be considered alive. Organisms are organized structures that require constant maintenance and repair to sustain. As these structures are composed of molecules, the continuous movement of molecules is necessary for the maintenance processes in living organisms. Life Processes
Life Processes
What are Life Processes?
Life processes are one of the most important parts of living beings which collective help us to sustain. These simple points capture the basic ideas that explain what life processes are in living things.
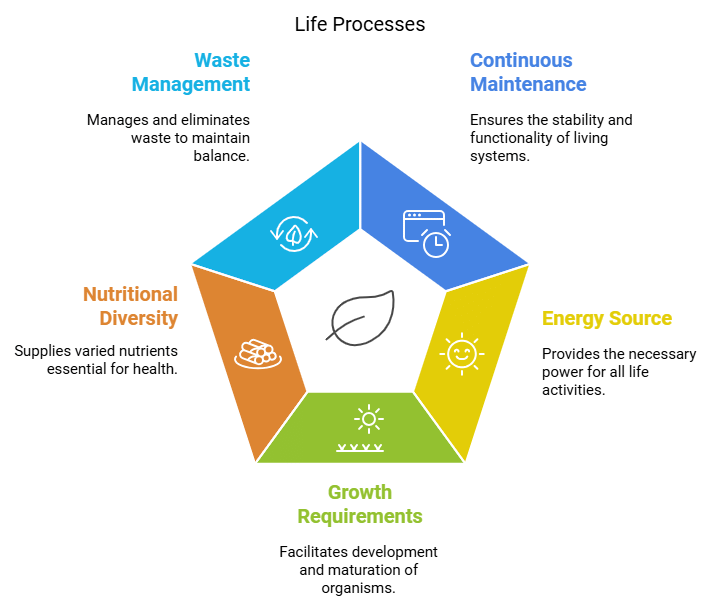
- Continuous Maintenance: Even when at rest, living organisms require ongoing maintenance processes to prevent damage and breakdown.
- Energy Source: Energy for maintenance comes from external sources called food. The process of transferring energy from food to the body is called nutrition.
- Growth Requirements: For growth, additional raw materials are needed from the environment, often carbon-based substances.
- Nutritional Diversity: Different organisms use various nutritional processes based on the complexity of carbon sources.
- Energy Transformation: External energy sources vary, so they are broken down or transformed into a uniform energy source for sustaining cellular functions and growth.
- Chemical Reactions: Chemical reactions inside the body are necessary for breaking down molecules. Oxidising-reducing reactions are common, often involving oxygen, known as respiration.
- Multi-cellular Challenges: As organisms grow larger and more complex, specialized tissues handle food and oxygen uptake. This complexity requires a transportation system to distribute these essentials.
- Waste Management: Energy-generating reactions produce waste by-products. Specialized tissues for waste elimination require a transportation system to remove waste from cells.
Nutrition
The process by which an organism takes food and utilizes it, is called nutrition.
Organisms need the energy to perform various activities. The energy is supplied by the nutrients. They need various raw materials for growth and repair. These raw materials are provided by nutrients. Carbohydrates, proteins and fats are the main nutrients and are called macronutrients. Minerals and vitamins are required in small amounts and hence are called micronutrients.
How do living things get their food?
- All organisms have a general requirement for energy and materials. This requirement is fulfilled in different ways.
- Some organisms, called autotrophs, use simple food materials obtained from inorganic sources like carbon dioxide and water. Autotrophs include green plants and some bacteria.
- Other organisms, called heterotrophs, utilize complex substances. These complex substances need to be broken down into simpler ones before they can be used for the upkeep and growth of the body. To achieve this, organisms use enzymes, which are bio-catalysts. Therefore, the survival of heterotrophic organisms depends directly or indirectly on autotrophs. Heterotrophic organisms include animals and fungi.
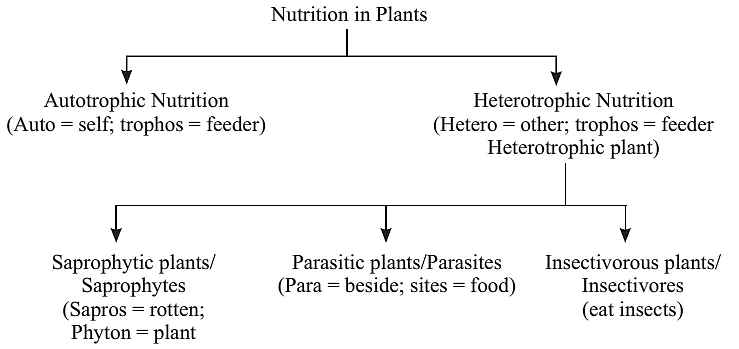 Categorization
Categorization
Autotrophic Nutrition
The mode of nutrition in which an organism prepares its own food is called autotrophic nutrition. Green plants and blue-green algae follow the autotrophic mode of nutrition.
The term “autotrophic” is formed by the combination of two terms, “auto” meaning self, and “trophic” meaning nutrition. The literal meaning of this term is self-nutrition.
What is Photosynthesis?
Autotrophic nutrition is fulfilled by the process by which autotrophs intake CO2 and H2O and convert these into carbohydrates in the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight, which is called photosynthesis.
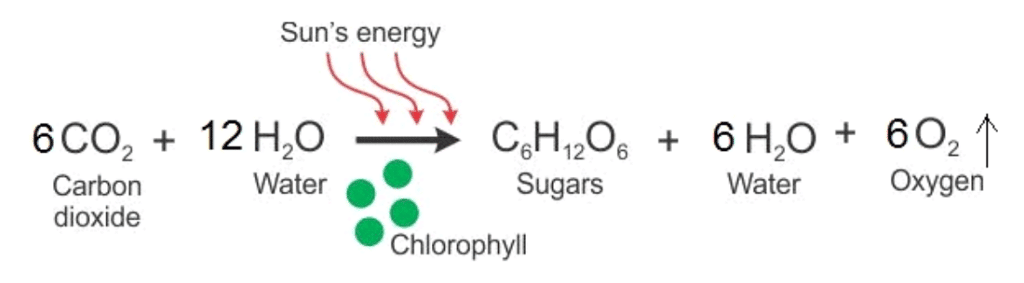 Photosynthesis Equation
Photosynthesis Equation
Main Events of Photosynthesis
- Chlorophyll absorbs light energy.
- The absorbed light energy is converted into chemical energy.
- Water molecules are split into hydrogen and oxygen during this conversion process.
- Carbon dioxide is reduced to form carbohydrates.
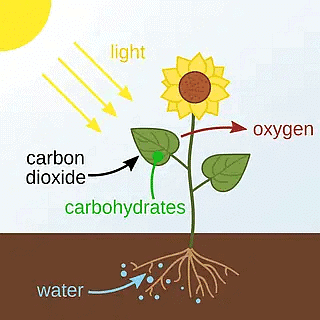 Process of Photosynthesis
Process of Photosynthesis
Site of Photosynthesis: Chloroplast in the leaf. Chloroplast contains chlorophyll (green pigment)
Stomata
Stomata are tiny pores in the epidermis of leaf or stem through which gaseous exchange and transpiration occur.
Functions of stomata
- Exchange of gases, O2 and CO2.
- Loses a large amount of water (water vapour) during transpiration.
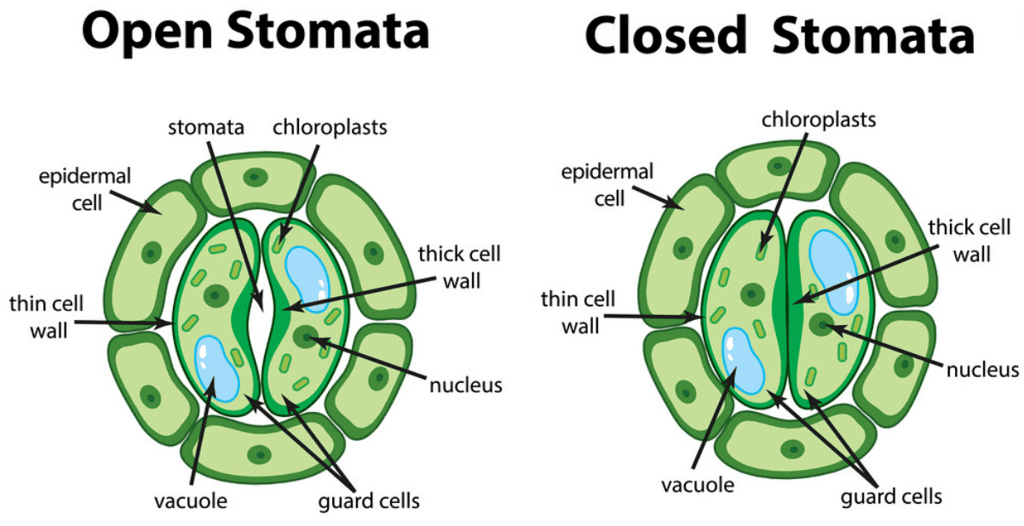 Stomata
Stomata
Opening and closing of stomatal pores
- The opening and closing of stomatal pores are controlled by the turgidity of guard cells.
- When guard cells uptake water from surrounding cells, they swell to become a turgid body, which enlarges the pore in between (Stomatal Opening).
- While, when water is released, they become flaccid shrinking to close the pore (Stomatal Closing).
How do other raw materials for photosynthesis become available to the plant?
Autotrophs not only require energy but also other raw materials for building their bodies.
- Water used in photosynthesis is obtained by terrestrial plants from the soil through their roots.
- Nitrogen, phosphorus, iron, and magnesium are other materials that autotrophs need, which are also obtained from the soil.
- Nitrogen is an essential element for the synthesis of proteins. It is mostly absorbed from the soil in the form of nitrates.
- Alternatively, autotrophs can also obtain nitrogen in the form of organic compounds that have been prepared by bacteria from atmospheric nitrogen.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
Heterotrophic nutrition refers to the mode of nutrition where an organism obtains food from other living organisms. 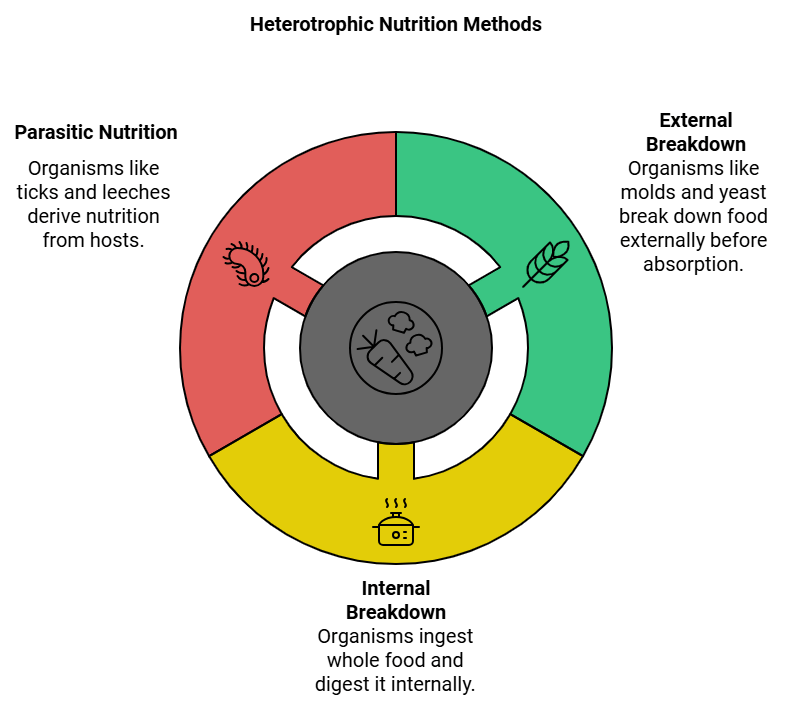
- Different organisms have different ways of obtaining food, depending on whether the food source is stationary or mobile.
- Some organisms externally break down the food material and then absorb it, like bread molds, yeast, and mushrooms.
- Other organisms take in whole material and break it down internally.
- The ability to take in and break down food depends on the organism's body design and functioning.
- Some organisms derive nutrition from plants or a wide variety of other organisms, such as cuscuta, ticks, lice, leeches, and tapeworms.
How do Amoeba Obtain their Nutrition?
Amoeba is a unicellular animal. Digestion happens in five steps, viz. ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion.
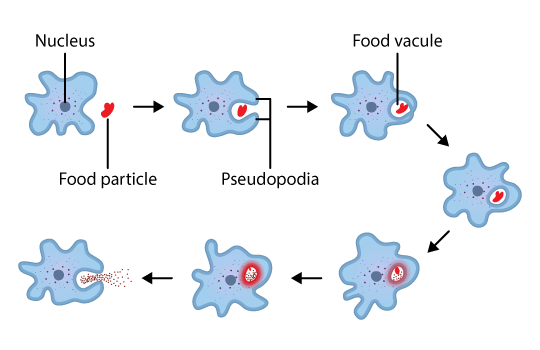 Nutrition in Amoeba
Nutrition in Amoeba
- The cell membrane of amoeba keeps on protruding into pseudopodia.
- Amoeba surrounds a food particle with its pseudopodia and forms a food vacuole.
- The food vacuole contains food particles and water.
- Digestive enzymes are secreted in the food vacuole and digestion takes place.
- After digestion, the food is absorbed from the food vacuole.
- Finally, the food vacuole moves near the cell membrane and undigested food is expelled out.
Nutrition in Human Beings
Human beings possess a sophisticated digestive system, consisting of both an alimentary canal and several accessory glands. The alimentary canal is a long, hollow tube that is divided into various parts, including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Meanwhile, the accessory glands, namely the salivary gland, liver, and pancreas, are located outside the alimentary canal and play essential roles in the digestive process.
Structure of the Human Digestive System
The human digestive system comprises of the alimentary canal and associated digestive glands.
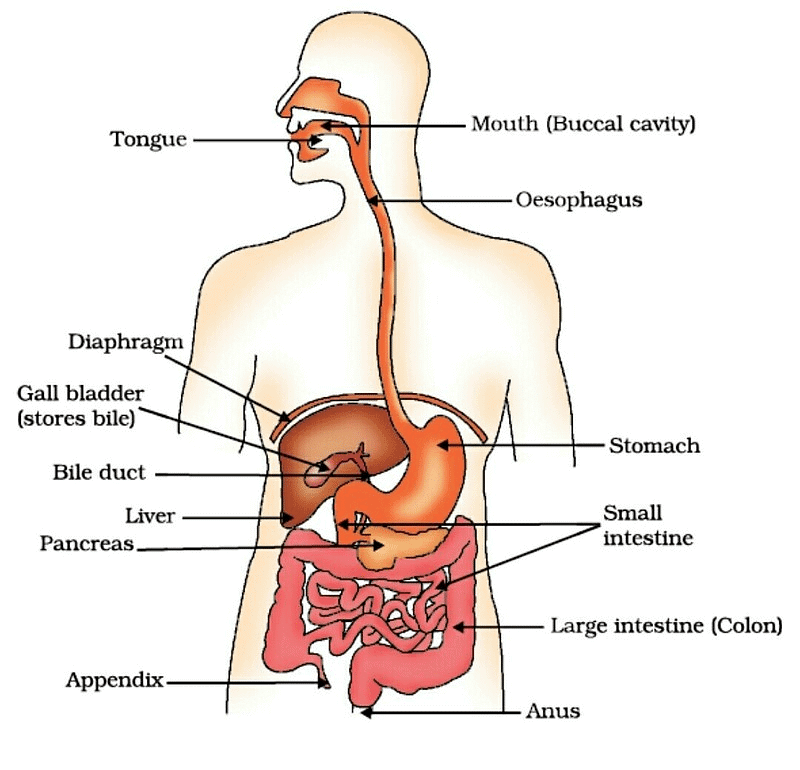 Structure of digestive system
Structure of digestive system
Alimentary Canal
It comprises of mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
1. Mouth or Buccal Cavity
- The mouth has teeth and tongue. Salivary glands are also present in the mouth which help by secreting saliva.
- The tongue has gustatory receptors which perceive the sense of taste.
- The tongue helps in turning over the food so that saliva can be properly mixed in it.
- Teeth help in breaking down the food into smaller particles so that, swallowing of food becomes easier.
- There are four types of teeth in human beings. The incisor teeth are used for cutting the food. The canine teeth are used for tearing the food and for cracking hard substances. The premolars are used for the coarse grinding of food. The molars are used for fine grinding of food.
2. Oesophagus
- Food is taken from the mouth to the stomach by peristaltic movement.
- Rhythmic contraction of muscles of the lining of the alimentary canal to push the food forward is called Peristaltic movement.

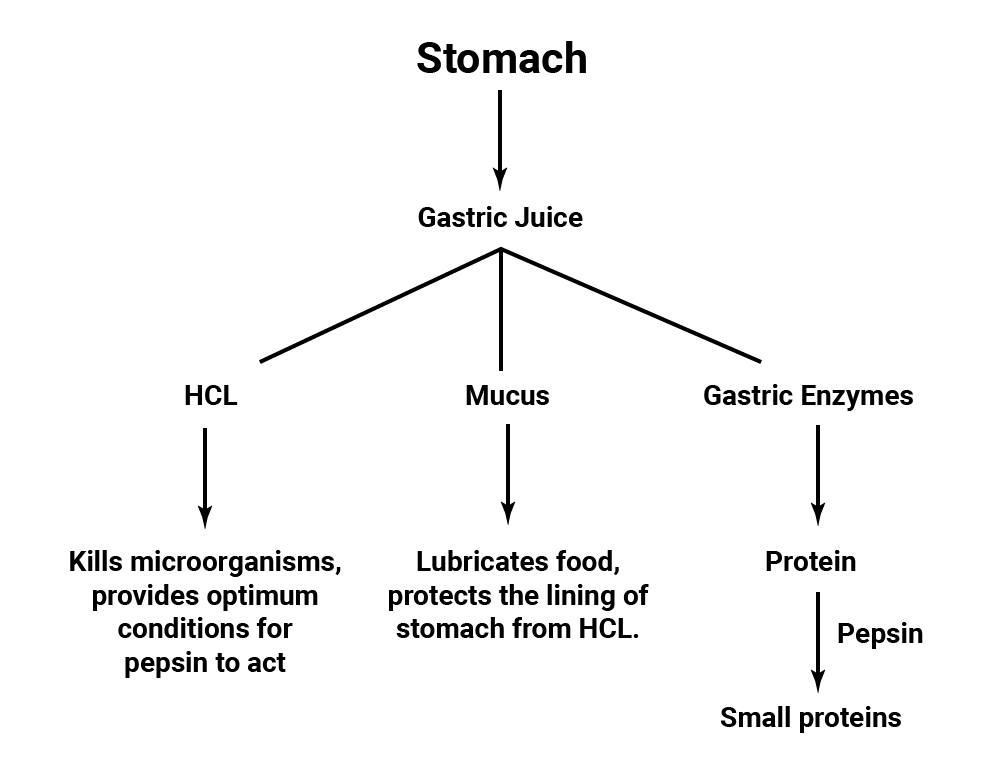
3. Stomach
- Stomach is a bag-like organ. Highly muscular walls of the stomach help in churning the food.
- The walls of the stomach secrete hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid kills the germs which may be present in food.
- Moreover, it makes the medium inside the stomach as acidic. The acidic medium is necessary for gastric enzymes to work.
- The enzyme pepsin, secreted in the stomach, does partial digestion of protein.
- The mucus, secreted by the walls of the stomach saves the inner lining of the stomach from getting damaged from hydrochloric acid.
4. Small Intestine
- The highly coiled, tube-like structure known as the small intestine is longer than the large intestine, although its lumen is smaller in comparison.
5. Large Intestine
- Large intestine is smaller than the small intestine.
- Undigested food goes into the large intestine.
- Some water and salt are absorbed by the walls of the large intestine. After that, the undigested food goes to the rectum, from where it is expelled out through the anus.
- Large Intestine absorb excess of water. The remaining material is expelled from the body through the anus as egestion.
Associated Glands
The main associated glands are the Salivary gland, Gastric Glands, Liver and Pancreas.
1. Salivary glands
- Saliva makes the food slippery which makes it easy to swallow the food.
- Saliva also contains the enzyme salivary amylase or ptyalin. Salivary amylase digests starch and converts it into sucrose, (maltose).
2. Liver
- Liver is the largest organ in the human body.
- The liver manufactures bile, which gets stored in the gall bladder.
- From the gall bladder, bile is released as and when required.
 Liver
Liver
3. Pancreas
- Pancreas is situated below the stomach.
- It secretes pancreatic juice which contains many digestive enzymes.
- The duodenum receives both bile and pancreatic juice through a common duct called the hepatopancreatic duct.
- Bile plays a crucial role in breaking down fats into smaller particles, a process known as emulsification.
- Following this, the enzyme lipase acts on the emulsified fats, breaking them down into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Moreover, the enzymes trypsin and chymotrypsin are responsible for digesting proteins into amino acids, while complex carbohydrates are broken down into glucose.
- The duodenum is the primary site for these digestive processes, where the major part of digestion occurs.
No digestion occurs in the jejunum: Inside the ileum, the inner wall has numerous finger-like structures known as villi. These villi serve two important functions: first, they increase the surface area of the ileum, allowing for efficient nutrient absorption. Second, they help reduce the lumen of the ileum, which allows food to stay inside for a longer time, facilitating better absorption. The digested food is then absorbed through these villi.
Excretion in Human Beings
Excretion is the process by which the body removes harmful metabolic wastes, primarily produced during cellular activities. In humans, the main excretory organs are the kidneys, which filter nitrogenous wastes like urea from the blood and expel them in the form of urine. The excretory system also includes ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, which help in transporting and storing urine before its removal. Along with kidneys, organs like the lungs (which remove carbon dioxide), skin (which releases sweat), and liver (which detoxifies harmful substances) also assist in excretion.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Life Processes Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 5
| 1. What are the main life processes essential for survival? |  |
| 2. What is nutrition and why is it important for living organisms? |  |
| 3. What are the different modes of nutrition in organisms? |  |
| 4. How do plants perform photosynthesis? |  |
| 5. What are some common nutritional deficiencies in humans? |  |





















