Bank Exams Exam > Bank Exams Notes > IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation > BASEL Norms
BASEL Norms | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
Basel is a city in Switzerland which is also the headquarters of Bureau of International Settlement (BIS).- BIS fosters co-operation among central banks with a common goal of financial stability and common standards of banking regulations.
- The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) established on 17 May 1930, is the world's oldest international financial organisation. There are two representative offices in the Hong Kong and in Mexico City. In total BIS has 60 member countries from all over the world and covers approx 95% of the world GDP.
Objective
- The set of the agreement by the BCBS (BASEL COMMITTEE ON BANKING SUPERVISION), which mainly focuses on risks to banks and the financial system are called Basel accord.
- The purpose of the accord is to ensure that financial institutions have enough capital on account to meet the obligations and absorb unexpected losses.
- India has accepted Basel accords for the banking system.
- BASEL ACCORD has given us three BASEL NORMS which are BASEL 1,2 and 3.
Tier 1 - The Tier- I Capital is the core capital
- Paid up Capital, Statutory Reserves, Other disclosed free reserves, Capital Reserves which represent surplus arising out of the sale proceeds of the assets, other intangible assets belong from the category of Tier1 capital.
Tier 2 - Tier-II capital can be said to be subordinate capitals.
- Undisclosed reserves, Revaluation Reserves, General Provisions and loss reserves , Hybrid debt capital instruments such as bonds, Long term unsecured loans, Debt Capital Instruments etc belong from the category of Tier 2 capital.
Risk Weighted Assets
- RWA means assets with different risk profiles; it means that we all know that is much larger risk in personal loans in comparison to the housing loan, so with different types of loans the risk percentage on these loans also varies.
BASEL - I
- In 1988, The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) introduced capital measurement system called Basel capital accord, also called as Basel 1.
- It focused almost entirely on credit risk, It defined capital and structure of risk weights for banks.
- The minimum capital requirement was fixed at 8% of risk-weighted assets (RWA).
- India adopted Basel 1 guidelines in 1999.
BASEL - II
In 2004, Basel II guidelines were published by BCBS, which were considered to be the refined and reformed versions of Basel I accord.
The guidelines were based on three parameters which are as follows:
- Banks should maintain a minimum capital adequacy requirement of 8% of risk assets.
- Banks were needed to develop and use better risk management techniques in monitoring and managing all the three types of risks that is credit and increased disclosure requirements.
- The three types of risk are- operational risk, market risk, capital risk.
- Banks need to mandatory disclose their risk exposure, etc to the central bank.
- Basel II norms in India and overseas are yet to be fully implemented.
The three pillars of BASEL-3 can be understood from the following figure
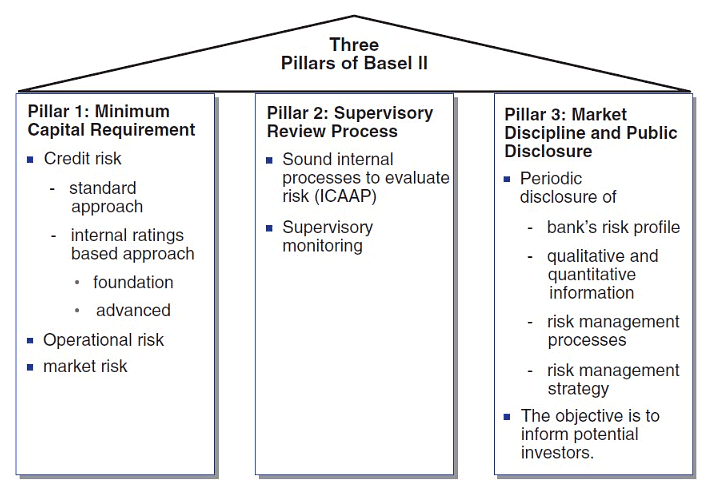
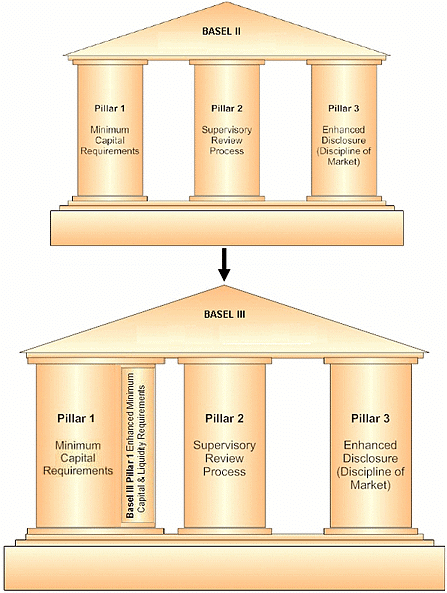
Basel III
- In 2010, Basel III guidelines were released. These guidelines were introduced in response to the financial crisis of 2008.
- In 2008, Lehman Brothers collapsed in September 2008, the need for a fundamental strengthening of the Basel II framework had become apparent.
- Basel III norms aim at making most banking activities such as their trading book activities more capital-intensive.
- The guidelines aim to promote a more resilient banking system by focusing on four vital banking parameters viz. capital, leverage, funding and liquidity.
- Presently, the Indian banking system follows Basel III norms. Additionally, the RBI has extended Basel III capital framework to All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs) from April 2024.
- The Reserve Bank of India has fully implemented Basel III capital regulations, with continuous refinements based on evolving risk factors
Important Points Regarding Implementation of Basel III
- The Government of India has been infusing capital into Public Sector Banks (PSBs) to strengthen their financial position and ensure compliance with Basel III norms
- The government has announced a capital infusion of Rs 55,250 crore in ten public sector banks, including Punjab National Bank (Rs 16,000 crore), Union Bank (Rs 11,700 crore), Bank of Baroda (Rs 7,000 crore), and Canara Bank (Rs 6,500 crore), to enhance their capital and meet global risk norms
- This capital infusion is part of the government's ongoing efforts to strengthen PSBs, with significant allocations made in recent budgets to support these bank
- The Indian government has infused significant capital into PSBs over the years. However, in 2025, the focus has shifted to strategic stake sales in public sector banks to ensure compliance with the 25% public shareholding mandat
- The Finance Minister has highlighted the need for capital infusion in public sector banks but has also introduced alternative strategies, such as stake sales, to enhance their financial health and governance.
The document BASEL Norms | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams is a part of the Bank Exams Course IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation.
All you need of Bank Exams at this link: Bank Exams
|
670 videos|994 docs|322 tests
|
FAQs on BASEL Norms - IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the BASEL norms in banking? |  |
Ans.The BASEL norms, established by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, are a set of international banking regulations aimed at enhancing the stability and resilience of the financial system. They focus on capital adequacy, stress testing, and market liquidity risk. The key agreements are BASEL I, II, and III, with each iteration introducing more stringent capital requirements and risk management practices.
| 2. How do BASEL norms affect banks' capital requirements? |  |
Ans.BASEL norms require banks to maintain a minimum level of capital to cover risks associated with their operations. Under BASEL III, banks must hold a common equity tier 1 (CET1) capital ratio of at least 4.5% of risk-weighted assets, along with additional capital buffers. This ensures banks have enough capital to absorb losses and continue operations during financial stress.
| 3. What is the significance of capital adequacy ratios in BASEL norms? |  |
Ans.Capital adequacy ratios (CAR) are crucial in BASEL norms as they measure a bank's available capital relative to its risk-weighted assets. This ratio is essential for ensuring that banks can absorb a reasonable amount of loss and comply with statutory capital requirements. Higher CAR indicates a stronger financial position, reducing the likelihood of bank failure.
| 4. How do BASEL norms impact risk management practices in banks? |  |
Ans.BASEL norms promote improved risk management practices within banks by requiring them to identify, assess, and manage various risks, including credit, market, operational, and liquidity risks. Banks must implement robust risk management frameworks and conduct regular stress testing to ensure they can withstand adverse economic conditions, thereby enhancing their overall stability.
| 5. What challenges do banks face in complying with BASEL norms? |  |
Ans.Banks face several challenges in complying with BASEL norms, including the need for significant investments in technology and systems to track and manage risk exposures. Additionally, the complexity of regulations can lead to difficulties in interpretation and implementation. Balancing compliance costs with profitability while maintaining sufficient capital levels can also pose a significant challenge for financial institutions.
Related Searches
















