Introduction of Computer | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
In today's digital age, understanding how computers work is more important than ever, especially for SSC exams. Whether you are entering data, creating reports, or analyzing information, having a solid grasp of computer functions and components can make these tasks easier and more efficient. Think of it as learning the language of technology—once you know the basics, you'll feel more confident and capable in any job role you pursue. Plus, computer literacy is an important skill tested in many competitive exams, making it essential for success in your career. Embrace this knowledge, and you'll find that navigating the digital world becomes second nature!

What is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic device that takes data from the user, processes this data by performing calculations and operations, and then produces the desired output. The word "computer" comes from the Latin word "computare," which means "to compute."
Basic Functions of a Computer System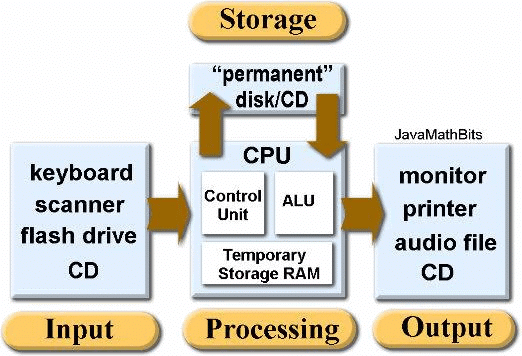
A computer performs four basic functions:
Input: This is the information or data that is entered into the computer. For example, typing on a keyboard or clicking with a mouse. The data is sent to the Central Processing Unit (CPU).
Processing: This is the series of actions the computer takes to convert the input data into meaningful information. This can include calculations, comparisons, or decision-making processes.
Output: This function makes the processed data available to the user. For example, displaying text on a screen or printing a document.
Storage: This involves storing data and programs permanently. For example, saving a file on a hard drive so it can be accessed later.
History of Computer Evolution
 Abacus (Invented around 2700–2300 BCE, in Mesopotamia and China)
Abacus (Invented around 2700–2300 BCE, in Mesopotamia and China)
- Characteristics: The abacus is known as the first mechanical calculating device. It uses a set of beads to represent units, with a horizontal rod indicating the ones, tens, hundreds, etc.
- Applications: The abacus was primarily used for addition and subtraction operations, and it also allowed for the calculation of square roots.
Napier's Bones (Invented by John Napier in 1617)
- Characteristics: This device has a three-dimensional structure that holds numbers from 0 to 9. It represents the graphical structure of calculation results.
- Applications: Napier's Bones were used to perform multiplication on numbers. The technology used for this device is called Rabdologia, and operations were performed on embedded rods.
Pascaline (Invented by Blaise Pascal in 1642)
- Characteristics: Pascaline is considered the first mechanical adding machine. It has a rectangular box structure with eight discs representing the number of units.
- Applications: The Pascaline was used to perform addition and subtraction of two numbers and was designed using mechanical gears and wheels.
Card of Holes for Weaving Pattern (Invented by Joseph Jacquard in 1801)
- Characteristics: This was the first mechanical loom that used a punched card for the sequence of operations and mainly weaved a silk-based pattern.
- Applications: The invention simplified the process of textiles.
Analytical Engine (Invented by Charles Babbage, 1834-71)
- Characteristics: To program the machine, it used punched cards for input and control. It is considered the first design of a general-purpose programmable computer.
- Applications: The analytical engine was generally used for basic arithmetic operations and could represent numbers using signs and magnitude.
Tabulating Machine (Invented by Herman Hollerith in 1880)
- Characteristics: This machine used punched cards with round holes and read one card at a time. It is the first electromechanical machine.
- Applications: It was designed to process data for the census in 1890.
MARK-I (Invented by Howard Aiken in 1944)
- Characteristics: The MARK-I consisted of interlocking panels of small glass, counters, switches, and control circuits, with data entered manually.
- Applications: Mainly used during World War II for war efforts, with magnetic drums used for storage.
ENIAC (Invented by JP Eckert and JW Mauchly in 1950)
- Characteristics: ENIAC is a combination of twenty accumulators that can trigger different operations.
- Applications: It was the first general-purpose electronic digital computer used for weather prediction, atomic energy calculations, and other scientific uses.
EDSAC (Invented by Maurice Wilkes, 1946–49)
- Characteristics: EDSAC was the first computer to provide storage capacity, capable of storing instructions and data in memory, and could also calculate squares and a list of prime numbers.
- Applications: The first computer program was run on this machine, using mercury delay lines for memory and vacuum tubes for logic.
UNIVAC (Invented by Eckert and JW Mauchly in 1951)
- Characteristics: UNIVAC was the first commercially available computer in the US, delivered in 1951.
- Applications: It used magnetic tapes as input and output.
IBM-650 Computer (Invented by IBM Company in 1954)
- Characteristics: This computer provided input/output units converting alphabetical and special characters to a two-digit decimal code.
- Applications: It was used for payroll processing, oil refinery design, and market research analysis.
History of Computers Generation
- The word 'computer' originally meant a person who does calculations, used since the 16th century.
- In the past, women were often hired as human computers to perform various calculations.
- By the late 19th century, the term began to refer to machines that could do calculations.
- Today, the word 'computer' usually describes programmable digital devices that operate on electricity.

Generations of Computer
Let us now discuss the development in Computer Technology over the different generations.
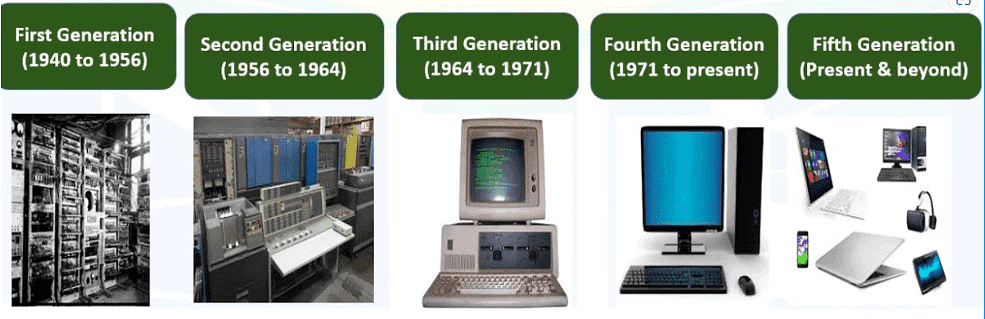
First Generation
- The era between 1940 and 1956 marks the initial phase of computer development.
- First-generation computers were built using vacuum tubes or thermionic valves.
- These computers utilized punched cards and paper tape for input, while output was in printed form.
- They operated on a binary-coded language, represented by 0s and 1s. Examples include ENIAC and EDVAC.
Second Generation
- The time period from 1956 to 1963 is generally known as the era of Second Generation Computers.
- Transistor technology was used to create the second generation computers.
- Second generation computers were smaller than the first generation ones.
- Computers in the second generation took less time for calculations compared to the first generation.
Third Generation
- The time period from 1963 to 1971 is often known as the Third Generation of computers.
- Third generation computers were created using Integrated Circuit (IC) technology.
- Compared to second generation computers, third generation computers were smaller in size.
- When compared to second generation computers, third generation computers were faster in processing data.
- Third generation computers consumed less power and produced less heat.
- The maintenance expenses for third generation computers were lower.
- The computer systems in third generation computers were more user-friendly for business purposes.
Fourth Generation
- The era from 1972 to 2010 is often seen as the fourth phase of computers.
- Fourth phase computers were made using microprocessor technology.
- With the fourth phase, computers became quite small and easy to carry around.
- These fourth phase machines produced very little heat.
- They were faster and more reliable in terms of accuracy.
- The cost of making them reduced significantly compared to earlier versions.
- They became accessible to the general public.
Fifth Generation
- The era from 2010 until now and moving forward is commonly known as the fifth generation of computers.
- Earlier, computer generations were distinguished mainly by their hardware, but the fifth generation introduced a focus on software as well.
- Fifth generation computers were known for their substantial capabilities and extensive memory storage.
- Tasks performed on these computers were swift, and they could handle multiple operations at once.
- Noteworthy technologies of the fifth generation encompass Artificial Intelligence, Quantum Computing, Nanotechnology, Parallel Processing, and more.
Brief History of Computers
The naive understanding of computation had to be overcome to realize the true power of computing. Inventors had to see that computers were more than just calculators; they had to tackle many challenges in designing and building these machines. The history of computers is a story of solving these difficulties.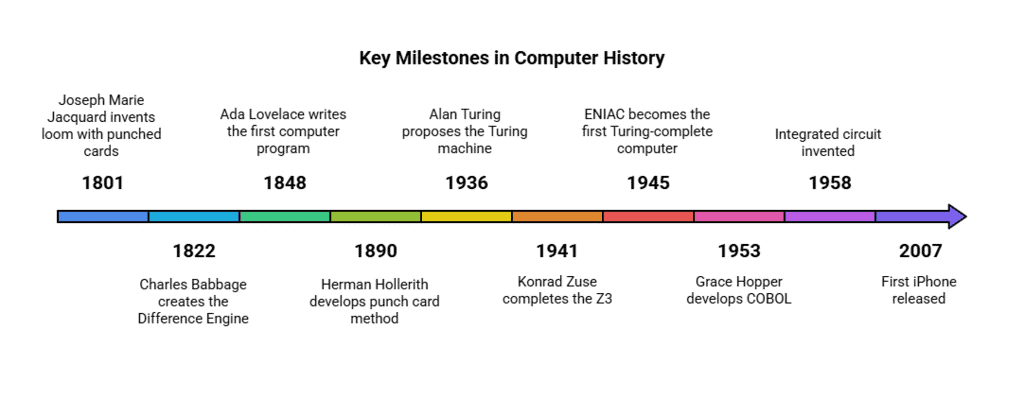
19th Century
- 1801 – Joseph Marie Jacquard invented a loom using punched cards to weave designs automatically.
- 1822 – Charles Babbage created the Difference Engine, a steam-powered calculator, but it could not be built due to technology limitations.
- 1848 – Ada Lovelace wrote the first computer program for Babbage's machine.
- 1890 – Herman Hollerith developed the punch card method for the 1880 U.S. census, leading to IBM.
Early 20th Century
- 1930 – Vannevar Bush built the first mechanical analogue computer called the Differential Analyzer.
- 1936 – Alan Turing proposed the Turing machine, a universal computing model.
- 1941 – Konrad Zuse completed the Z3, the first digital computer, which was later destroyed in WWII.
- 1945 – John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert created ENIAC, the first Turing-complete computer.
- 1951 – UNIVAC I became the first general-purpose electronic computer in the U.S.
Late 20th Century
- 1954 – IBM created FORTRAN, a programming language for scientific computation.
- 1958 – The integrated circuit was invented, marking a key development in electronics.
- 1959 – Grace Hopper contributed to the development of COBOL, one of the first high-level programming languages.
- 1964 – Douglas Engelbart introduced a prototype with a mouse and GUI.
- 1975 – The first personal computers were introduced to the market.
- 1981 – IBM launched its first personal computer.
- 1990 – Tim Berners-Lee created HTML and the WorldWideWeb.
21st Century
- 2000 – The first USB flash drive was introduced.
- 2001 – Apple launched Mac OS X.
- 2007 – The first iPhone was released, revolutionizing mobile computing.
- 2011 – Google introduced the Chromebook.
- 2016 – The first reprogrammable quantum computer was built.
Classification of Computer
Computers can be classified into 3 Categories as follows: 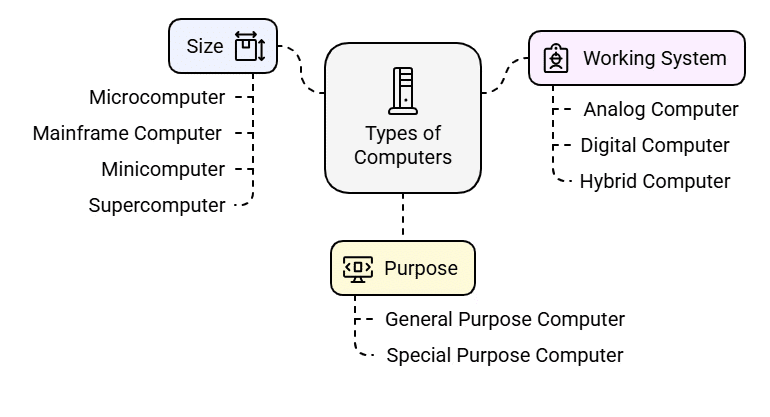
Types of Computers Based on Size
1. Microcomputer
Microcomputers are the least powerful but the most widely used and fastest growing type of computers. They are also known as portable computers. They consist of three basic categories of physical equipment: the system unit, input/output devices, and memory.
Types of Microcomputers:
- Desktop Computer or Personal Computer (PC): These are small, relatively inexpensive computers based on microprocessor technology (Integrated Circuit). They are used for various personal and business applications.
- Notebook: Also known as laptops or ultrabooks, these are portable and lightweight, designed to fit into briefcases. They include a rechargeable battery, making them usable anywhere. Laptops were developed by Alan Kay.
- Handheld Computers or Palmtops: These are very small computers designed to fit into the palm of your hand. They are practical for certain functions such as phone books and calendars and use a pen for input instead of a keyboard.
- Tablet Computer: Tablets have the key features of notebooks but accept input from a pen instead of a keyboard or mouse.
- Smartphones: These are cellular phones that function both as a phone and a small PC. They may use a pen or have a small keyboard and can connect to the internet wirelessly. Examples include Apple, Blackberry, and Nokia smartphones.
2. Mainframe Computer
Mainframe computers have large internal memory storage and a comprehensive range of software. They serve as the backbone for the entire business world, allowing many people to work simultaneously. Mainframe computers include IBM-370, IBM-S/390, and UNIVAC-1110.
3. Minicomputer
Minicomputers are smaller, faster, and cost less than mainframe computers. Initially designed for specific tasks like engineering and Computer-Aided Design (CAD) calculations, they are now used as central servers. Examples include IBM-17, DEC PDP-11, and HP-9000.
4. Supercomputer
Supercomputers are the fastest and most expensive machines with high processing speeds compared to other computers. Their speed is measured in FLOPS (Floating Point Operations Per Second). They are used for complex tasks like weather forecasting, scientific simulations, and cryptography.
Types of Computers Based on Working System
1. Analog Computer
Analog computers are job-oriented, performing arithmetic and logical operations by manipulating and processing data. They use continuous variables for mathematical operations and include devices like speedometers and seismographs.
2. Digital Computer
Digital computers work by calculating binary digits. They perform mathematical problems and produce desired graphics and sounds. Examples include desktop PCs.
3. Hybrid Computer
Hybrid computers combine the features of analog and digital computers. They are used in specialized applications like hospitals for ECG and DIALYSIS machines.
Types of Computers Based on Purpose
1. General Purpose Computer
General-purpose computers are designed to solve various problems by changing the program or instructions. They are used for tasks like small database calculations and accounting.
2. Special Purpose Computer
Special-purpose computers are designed to solve a single, dedicated type of problem. Examples include automatic aircraft landing systems and multimedia computers.
Features of Computers
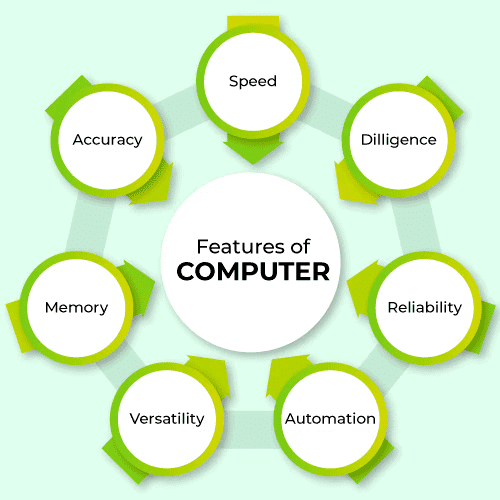
1. Speed: Computers can process data very quickly, handling millions of instructions per second. This high processing speed allows for efficient performance of complex tasks in a short amount of time.
2. Accuracy: Computers provide a high degree of accuracy. They execute instructions without errors, provided the input and instructions are correct. This makes them reliable for tasks requiring precision.
3. Storage Capacity: Computers can store a vast amount of data. The storage capacity depends on the size of the hard disk or other storage media. This feature allows users to save large volumes of information for future use.
4. Versatility: Computers can perform different types of tasks simultaneously. This versatility allows them to handle various applications and processes at the same time, making them useful in multitasking environments.
5. Plug and Play: Computers have the ability to automatically configure new hardware and software components. This feature simplifies the process of adding new devices or software, making it user-friendly.
6. Diligence: Unlike humans, computers do not suffer from fatigue, lack of concentration, or monotony. They can work continuously for long periods without making errors, ensuring consistent performance.
7. Secrecy: Computers enhance the security of information by implementing login systems with password protection. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and leakage of sensitive information. Examples include ATM counters and email systems.
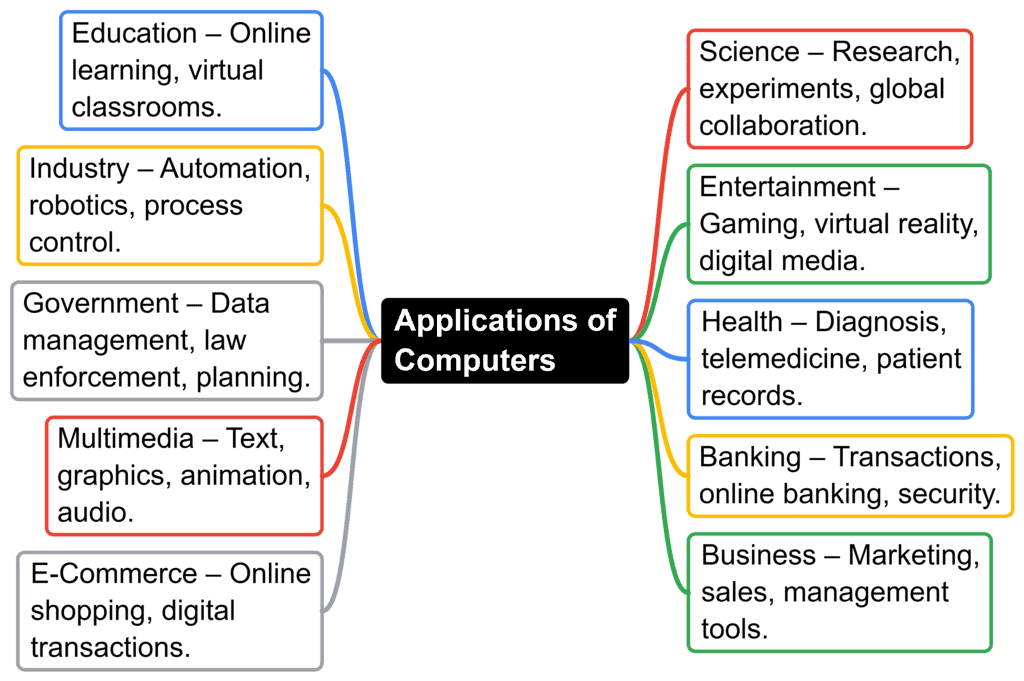
Applications of Computers
Nowadays, computers are used in almost every aspect of professional and personal life. Here are some key areas where computers play a vital role:
Advantages of Computer
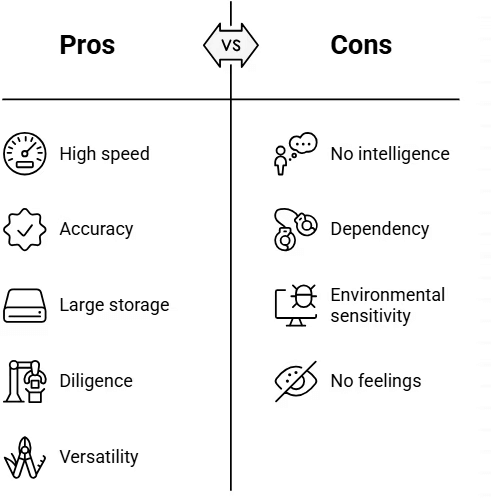
1. High Speed: Computers are extremely fast machines. They can process huge amounts of data in just a few seconds. Their speed is measured in microseconds, nanoseconds, and even picoseconds. A task that might take a human months to complete can be done by a computer in seconds.
2. Accuracy: Computers are not only fast but also very accurate. They perform calculations without making mistakes, as long as the input is correct.
3. Storage Capacity: Computers have a large memory and can store a huge amount of data. They can keep different types of files, including text, images, videos, and audio, for a long time.
4. Diligence: Unlike humans, computers do not get tired, bored, or distracted. They can work continuously without making errors, even when performing the same task repeatedly.
5. Versatility: Computers can handle many different types of tasks. They can solve complex scientific problems at one moment and run a simple game the next.
6. Reliability: Computers are reliable machines. Their electronic parts last a long time, and they are built in a way that makes maintenance easy.
7. Automation: Once a program is installed on a computer, it can perform tasks automatically without needing human supervision.
8. Reduces Paperwork and Cost: Computers help reduce the need for paper in offices, making work faster and more organized. Instead of keeping stacks of paper files, data can be stored electronically and accessed whenever needed. Though computers require an initial investment, they help save money in the long run.
Disadvantages of Computer
1. No Intelligence: A computer has no intelligence of its own. It cannot perform tasks without receiving instructions from a user. Unlike humans, it cannot make decisions by itself.
2. Dependency: A computer works entirely based on user commands, making it completely dependent on humans for functioning.
3. Sensitive to Environment: Computers need a clean and dust-free environment to function properly. Unfavorable conditions can affect their performance.
4. No Feelings: Computers do not have emotions, experiences, or personal judgment. Unlike humans, they cannot think, feel, or make decisions based on past experiences or preferences.
Conclusion
In summary, computers have become an essential part of our daily lives and work environments. They are powerful tools that help us perform tasks quickly and accurately, store vast amounts of information, and automate processes. However, it's important to remember that computers require human input and cannot function independently. While they greatly improve efficiency and productivity, we must also be aware of their limitations, such as their dependency on users and sensitivity to environmental conditions. As technology continues to evolve, understanding how to effectively use computers will remain a crucial skill in both personal and professional settings.
|
647 videos|1000 docs|305 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction of Computer - IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What is a computer? |  |
| 2. How does a computer work? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of computers? |  |
| 4. What is the role of software in a computer? |  |
| 5. What is the future of computer technology? |  |

















