Notes: Natural Phenomena | Science & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Lightning |

|
| Electric Discharge |

|
| Earthquakes |

|
| Floods |

|
| Tsunamis |

|
| Droughts |

|
| Man-Made Disasters |

|
| Global Warming |

|
| Ozone Layer Depletion |

|
Natural phenomena refer to various events that occur due to natural forces. Some of these phenomena are beneficial, while others can be highly destructive, leading to disasters such as earthquakes, cyclones, tsunamis, and droughts. These events are largely beyond human control and can significantly disrupt life. Today, climate change has become a global concern, as human activities have accelerated its effects.
Lightning
- During thunderstorms, air currents move upwards and water droplets move downwards. This causes separation of charges between clouds and between clouds and earth.
- When the magnitude of charges increases, air (normally a bad conductor) starts conducting and allows the flow of electricity. This is called as lightning, as this flow of charge is accompanied by bright streaks of light and sound.
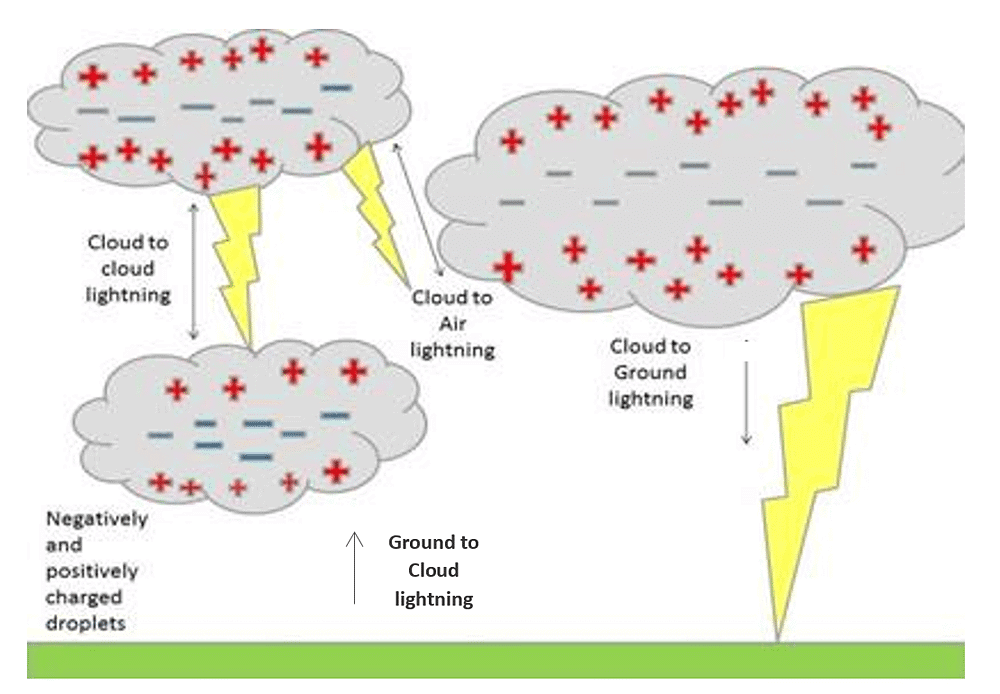
Electric Discharge
The process of flow of charge from cloud to cloud or from cloud to earth due to the separation of positive and negative charges is called an electric discharge.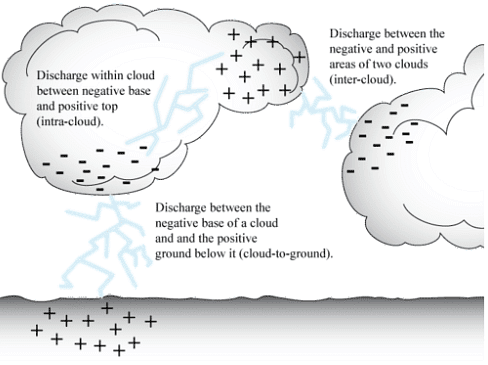
Lightning safety: Steps to follow
- Outside the house: (a) Find a safe place or shelter under small trees (b) If inside a car or vehicle, stay inside with doors and windows shut (c) Stay away from metal poles (d) Do not lie on the ground. Instead, crouch with your head in between your hands.
- Inside the house: (a) Avoid contact with telephone and electrical wires (b) avoid bathing (c) Unplug electrical appliances.
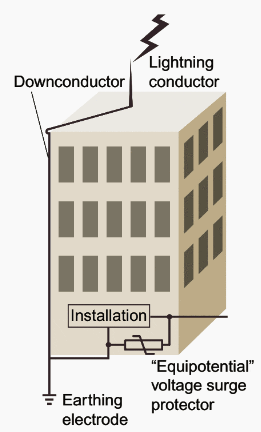
Lightning Conductors
- Lightning conductors help to protect buildings during lightning.
- They consist of a metal rod that is taller than the building which is installed within the walls during construction. They run all the way to the earth and act as a direct passage for electric discharge during lightning.
Earthquakes
- Earthquake is the sudden trembling of the surface of the earth due to disturbance deep inside the earth’s crust.
- Causes large-scale damage to life and property.
- Cannot be predicted.
Causes of earthquake
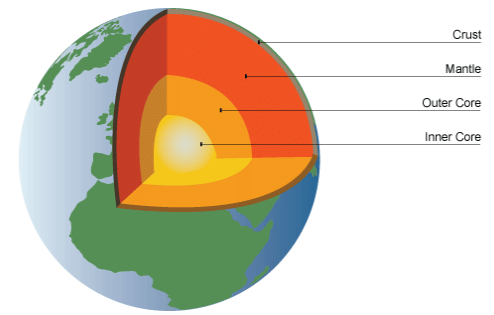
Earthquakes are caused due to movement or collision of tectonic plates in the uppermost layer of the earth’s crust.
Movement of plates
Earth’s crust is fragmented and each such fragment is known as a plate. These plates are constantly in motion and sometimes can collapse under another, causing an earthquake on the surface.
Structure of the earth
Seismic/fault Zones
Boundaries of the plates on the earth’s crust are weak zones where earthquakes are most likely to occur. These are known as seismic or fault zones.
- Power of earthquake
Power of an earthquake is expressed in terms of magnitude on a scale. This scale is called as a Richter Scale. - An earthquake with magnitude > 7 on the Richter scale is considered destructive.
- This scale is not linear. i.e. an increase of 2 in magnitude implies 1000 times more destructive energy.
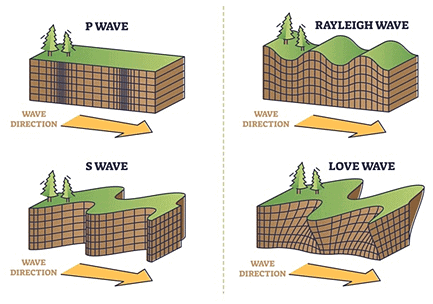
Seismic Waves
Tremors deep inside the earth produce waves, which are called seismic waves.
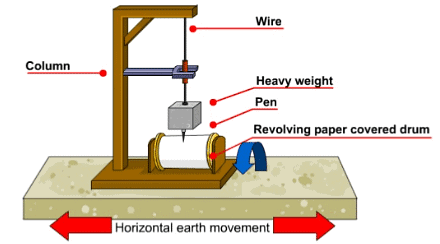
Seismograph
- An instrument that records seismic waves is called a seismograph.
- Consists of a vibrating rod or pendulum that starts vibrating when tremors occur.
Protection from an earthquake: Steps to follow
- Outdoors: (a) Find a clear spot, away from overhead lines and buildings (b) if in a car then go to a clear spot and stay inside the car till the tremors stop.
- Indoors: (a) stay under a table till tremors stop (b) Avoid staying near tall heavy objects.
- Structural measures: (a) in highly seismic areas build mud houses with light roofs in order to minimize damage (b) Fix cupboards and shelves to the walls (c) During an earthquake, some buildings catch fire and therefore must have proper working firefighting equipment.
Floods
A flood occurs when an area is submerged due to excessive water, often caused by heavy rainfall, river overflow, or dam failures.Causes:
Heavy rainfall
Collapse of dams and river embankments
Strong tidal waves, storm surges, and hurricanes
Unplanned urban development in flood-prone areas

Safety Measures:
Prevent deforestation and promote reforestation.
Construct strong embankments along riverbanks.
Use flood-prone areas for agriculture or recreation rather than settlements.
Tsunamis
A tsunami is a series of massive ocean waves triggered by disturbances such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and underwater landslides.
Key Features:
Tsunamis travel at 600-800 km/h.
More frequent in the Pacific Ocean than in the Indian Ocean.
The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami was caused by an earthquake of magnitude 9.0 near Sumatra.
Droughts
A drought is a prolonged period of below-average precipitation, leading to water shortages.
Causes:
Scarcity of rainfall
Lack of irrigation facilities
Absence of rainwater harvesting
Deforestation, reducing soil’s water retention capacity

Safety Measures:
Conserve rainwater through improved harvesting methods.
Educate people on water conservation.
Discourage deforestation and encourage afforestation.
Construct dams to store water.
Wind and Cyclones
Wind Formation:
Wind is caused by differences in atmospheric pressure.
Heated air rises, creating a low-pressure zone, which is filled by cooler air, resulting in wind currents.
Cyclones
A cyclone is a powerful rotating wind storm with speeds ranging from 120-200 km/h.
The center of a cyclone is known as the eye, which has very low pressure.
Cyclones can cause floods due to storm surges.
Different names in various regions:
Hurricane (USA)
Typhoon (Japan, China, Philippines)
Tornado (Rotating funnel-shaped storm)

Safety Measures:
Install cyclone forecasting systems.
Keep track of meteorological warnings.
Stay in safe shelters during a cyclone.
Man-Made Disasters
Man-made disasters result from human negligence or technological failures. They can be:
Types:
Direct Disasters:
Small Scale: Train accidents, terrorism, plane crashes.
Large Scale: Wars, industrial disasters (e.g., Bhopal Gas Tragedy).
Indirect Disasters:
Floods due to dam failures.
Landslides due to mining activities.
Global Warming
Global warming refers to the rapid increase in Earth's temperature due to greenhouse gas emissions.
Causes:
Burning fossil fuels
Deforestation
Increased levels of greenhouse gases (CO₂, CH₄, N₂O, CFCs)

Greenhouse Effect:
Greenhouse gases trap solar radiation, preventing heat from escaping the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures.
Ozone Layer Depletion
The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere (17-26 km above Earth), absorbs 99% of harmful UV radiation.
Causes of Ozone Depletion:
Excessive use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Industrial chemicals like carbon tetrachloride and halons
Consequences:
Increased UV exposure, leading to skin cancer and cataracts.
Disturbance in ecosystems and marine life.
|
35 videos|145 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Natural Phenomena - Science & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are some examples of natural phenomena? |  |
| 2. How do earthquakes occur? |  |
| 3. What causes hurricanes? |  |
| 4. How does lightning form? |  |
| 5. What is the formation process of a rainbow? |  |
















