Notes: Bloom's taxonomy | Science & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
Bloom’s taxonomy
The word ‘taxonomy’ means a lawful and orderly arrangement. This word has derived from two words taxis’ which means arrangement and nomas that means ‘law’.
In 1956, Dr. Benjamin bloom, professor of Chicago University developed a new vision for teaching. Bloom’s taxonomy is a detailed classification of educational objectives.
By the use of taxonomy and analyses the teacher can state the educational objectives with g precision and definiteness.
Three domains of bloom’s taxonomy
- Cognitive domain (knowledge)
- Affective domain (attitude, emotion)
- Psychomotor domain (skills).
In bloom’s taxonomy of learning objectives were written on ascending order of complexity or difficulty and are hierarchical in nature. Each higher objective includes all the human behaviour which has been broadly categorised into three domains or category.
What is cognitive domain of learning
Cognitive domain is concerned with the development of intellectual capability. For example (thinking or knowledge). Cognitive domain is the core of learning domain. There are six levels of cognitive domain. Which are mentioning below-
Six levels of cognitive domain
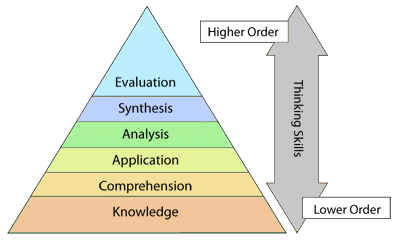
- Knowledge
it is the lowest level in cognitive domain, knowledge can be defined as recalling, or recognition of terms, ideas, theories etc. are included in the level of knowledge. - Comprehension
This is the little higher level than knowledge. Comprehension is the ability to grasp the meaning of content or material Comprehension represents the lowest level of understanding. It has three categories namely translation, interpret and extrapolate. - Application
Application refers to the ability to use the principle or idea in different situation from the one in which it was originally learn. - Analysis
Analysis is the ability to breaking things into its constituent’s parts and an understanding of organization and relationship between the parts. - Synthesis
it involves combining the constituent’s parts to make it as a whole. Synthesis emphasis the ability of making something new, bringing ideas into together, providing new insight and helping the pupil to create new ideas. - Evaluation
Evaluation is the highest level in the hierarchical development of intellectual abilities. All the earlier categories are the prerequisite for this category. Evaluation refers to the ability to judge the value of concept, material and procedures for a specific purpose.
Affective domain levels
This domain proposed by Krathwahl. Affective domain deals with feelings, attitude, and emotion. A degree of acceptance or rejection. Affective domain includes the following six levels.
- Receiving
It refers to the willingness of student’s to attend to particular phenomena or stimuli. Affective domain represents lowest level of learning outcomes in the affective domain. - Responding
It refers to the willingness to participate. When students are sufficiently motivated he responds or actively attends and thus, finds pleasure or enjoy the activity. - Valuing
Valuing includes the worth of a thing or behaviour. Instructional objectives that are commonly classified under attitudes and appreciation are included in this category of objectives. - Organization
Bringing together the different values resolving conflict between them and building of an internal value system and like other activities are included in the category of organization. Here more emphasis is given on comparing relating and synthesizing the values. - Characterization
At this level of affective domain an individual responds in relation to the values that he has internalized and develops a characteristic life style. The behaviour therefore becomes pervasive, consistent and predictable.
What are the levels of psychomotor domain
This domain of bloom’s taxonomy deals with the abilities and skills which are physical in nature. It concerns with the motor activities i.e. skills. Psychomotor domain is classified into six categories by Harrow (1972).
- Perception
Perception means the ability of learner to become aware of actions, objects, qualities and relations. This is achieve through sense organs and it helps in making preparatory adjustments- mentally, physically and emotionally. - Imitation
It refers to the learning ability of the learner to perform an action according to a given instruction. - Manipulation
Manipulation means the learner is able to perform an act according to given instruction rather than doing an imitation pattern. - Precision
Accuracy in performing various acts increases with practice. - Articulation
Achieving a desired level of competence and effectiveness through practice. - Naturalization
The internalized skill and an individual is able to adapt, modify or design new technique, methods or procedures according to the requirements of a situation.
Conclusion
Thus from the above discussion we can conclude that bloom’s taxonomy of behavioural objectives is one of the most widely used ways of organizing levels of expertise. Bloom’s taxonomy uses a multi-tired scale to express the level of expertise required to achieve each measureable student’s outcome. .Although, bloom’s taxonomy was revised by Lorin Anderson in order to better reflect the forms of thinking in each category.
|
35 videos|145 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Bloom's taxonomy - Science & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What is Bloom's taxonomy and why is it important for CTET and State TET exams? |  |
| 2. What are the six levels of Bloom's taxonomy? |  |
| 3. How can teachers incorporate Bloom's taxonomy in their teaching strategies? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of Bloom's taxonomy in assessing student learning? |  |
| 5. How can Bloom's taxonomy be used to promote inclusive education in CTET and State TET exams? |  |
















