Notes: Constitution | Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
Meaning of Constitution
A Constitution is a fundamental set of principles or established precedents that govern a state. It outlines the organization, powers, and limits of government institutions, as well as the rights and duties of citizens. The Constitution serves as the supreme law of the land, providing a framework for the functioning of the government, protecting individual liberties, and maintaining social order.
The Constitution is crucial for understanding the political, social, and economic aspects of a country.
- The Constitution of India serves as the supreme law of the Republic of India. It establishes the framework for the country's political system, defining the powers and responsibilities of government institutions, safeguarding fundamental rights, and outlining the principles of governance. Essentially, it is a set of rules and regulations that guide the administration of the country.
- The Constitution is the highest law in India, meaning that all other laws and policies must align with it. It was adopted on January 26, 1950, and has since been amended numerous times to address changing needs and circumstances.
Structure of Indian Constitution
The Indian Constitution is known for being one of the longest and most detailed written constitutions globally. Its structure comprises various components that organize the Constitution into different Parts, Articles, and Schedules.
Parts:
- A "Part" in the Constitution signifies a division that groups together Articles addressing similar subjects or themes.
- The Indian Constitution is divided into several Parts, each focusing on a specific aspect of the country's legal, administrative, or governmental framework.
- Initially, the Constitution had 22 Parts; currently, it comprises 25 Parts.
Articles:
- An "Article" represents a specific provision or clause within the Constitution, outlining various aspects of the country's legal and governmental framework.
- Each Part of the Constitution contains several Articles numbered in sequence.
- Originally, there were 395 Articles in the Constitution; now, there are 448 Articles.
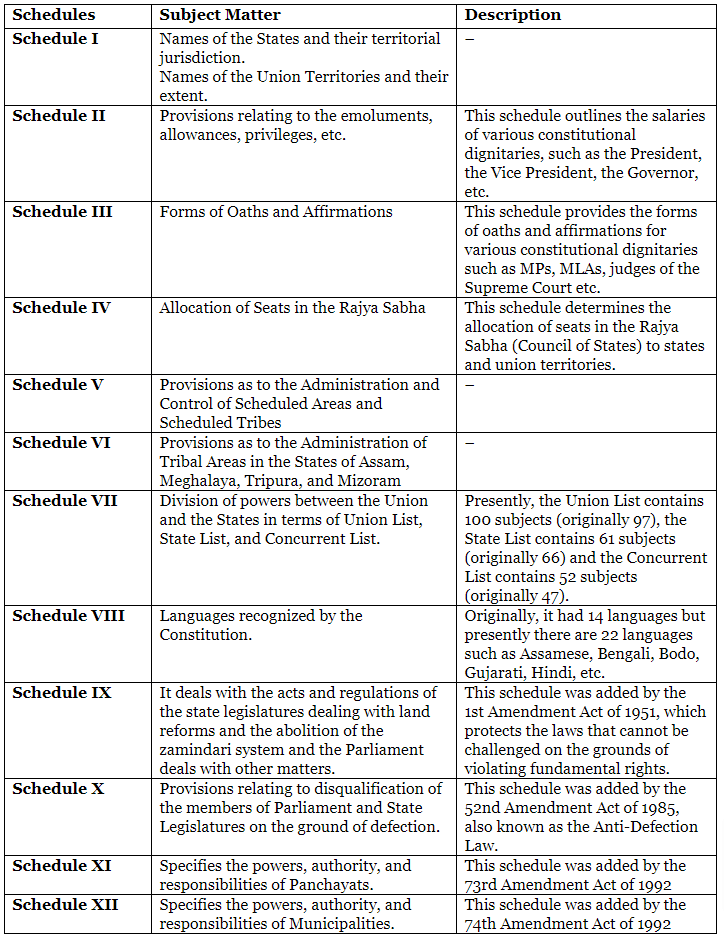
Schedules:
- A "Schedule" refers to a list or table attached to the Constitution, providing additional information or guidelines relevant to constitutional provisions.
- Schedules enhance the clarity and comprehensiveness of the Constitution by offering supplementary details.
- Initially, there were 8 Schedules in the Constitution; currently, there are 12 Schedules.
Enactment and Adoption of the Indian Constitution
The Constitution of India was created by a Constituent Assembly that was formed in 1946, with Dr. Rajendra Prasad as its President.
- On August 29, 1947, a resolution was proposed in the Assembly to set up a Drafting Committee for a permanent Constitution, leading to the committee's formation under Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
- The Drafting Committee took 166 days over nearly 3 years to prepare the draft, which was presented on November 4, 1948.
- After discussions and revisions, the Draft Constitution was accepted on November 26, 1949, marking the "Date of Adoption."
- Some provisions came into effect on this date, but the majority was enacted on January 26, 1950, establishing India as a sovereign republic. This date is known as the "Date of Enactment."
Salient Features of Indian Constitution
- Lengthiest Written Constitution: The Constitution of India is the longest written constitution in the world. It is very detailed and comprehensive. Its size is due to factors like India's vast diversity, the need for a single constitution for both the Center and States, and the expertise of legal professionals in the Constituent Assembly.
- Drawn from Various Sources: The Constitution borrows many provisions from the Government of India Act of 1935 and the constitutions of other countries.
- Blend of Rigidity and Flexibility: The Indian Constitution is a mix of rigid and flexible. It can be amended through both special procedures and ordinary legislative processes.
- Federal System with Unitary Bias: India has a federal system of government, but the Constitution also includes many unitary features, giving the central government significant power.
- Parliamentary Form of Government: India follows the British Parliamentary System, emphasizing cooperation between the legislative and executive branches.
- Synthesis of Parliamentary Sovereignty and Judicial Supremacy: There is a balance between Parliament's authority to make laws and the judiciary's power to review and interpret these laws, ensuring adherence to constitutional principles.
- Integrated and Independent Judiciary: India has a single system of courts (Supreme Court, High Courts, and Subordinate Courts) enforcing both central and state laws. The judiciary operates independently, free from executive and legislative influence.
- Fundamental Rights: The Constitution guarantees six fundamental rights to citizens, limiting executive power and arbitrary legislative actions.
- Directive Principles of State Policy: These principles guide the state in policy-making and law-enactment, aiming to establish a Welfare State and promote social and economic democracy.
- Fundamental Duties: Citizens have moral and civic obligations to contribute to building a strong and harmonious nation.
- A Secular State: The state treats all religions equally, without favoring or discriminating against any particular religion.
- Universal Adult Franchise: Every citizen aged 18 and above has the right to vote in elections, without discrimination.
- Single Citizenship: All citizens enjoy the same political and civil rights regardless of their state of birth or residence.
- Independent Bodies: The Constitution establishes independent bodies to strengthen the democratic system.
- Emergency Provisions: These provisions allow the President to address extraordinary situations to safeguard the country’s sovereignty, unity, integrity, security, and democratic system.
- Three-tier Government: Powers and responsibilities are divided among the central government, state governments, and local governments (Panchayats and Municipalities), promoting participatory democracy and grassroots development.
- Co-operative Societies: The 97th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2011 gave constitutional status and protection to co-operative societies.
Significance of Indian Constitution
- Rule of Law: The Constitution is based on the rule of law, meaning that everyone, including government officials, must follow the law.
- Protection of Rights: It guarantees fundamental rights to citizens, protecting their freedoms such as speech, expression, and religion. It also provides ways for people to seek legal help if these rights are violated.
- Structure of Government: The Constitution outlines how the government is organized, specifying the roles, powers, and limits of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This separation of powers prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful and ensures a system of checks and balances.
- Democratic Principles: The Constitution promotes democratic principles by ensuring that all citizens can participate in governance through free and fair elections, such as universal adult franchise.
- Stability and Continuity: It provides a stable and continuous framework for governance, guiding successive governments and preventing sudden changes in the political system.
- National Unity: The Constitution fosters national unity by acknowledging and respecting the diversity of the population while promoting a sense of common citizenship and loyalty to the nation.
- Legal Framework: It serves as the legal basis for all laws and regulations, ensuring consistency and coherence in the legal system.
- Adaptability: The Constitution allows for necessary amendments to meet changing societal needs and values, ensuring its ongoing relevance while providing a stable framework.
Sources of the Constitution of India
- Government of India Act of 1935: This act contributed to the federal scheme, the office of the governor, the judiciary, public service commissions, emergency provisions, and administrative details in the Constitution.
- British Constitution: The parliamentary system of government, rule of law, legislative procedure, single citizenship, cabinet system, prerogative writs, parliamentary privileges, and bicameralism were influenced by the British Constitution.
- US Constitution: Fundamental rights, independence of the judiciary, judicial review, impeachment of the president, removal of Supreme Court and High Court judges, and the post of the vice-president in India were inspired by the US Constitution.
- Irish Constitution: The directive principles of state policy, nomination of members to the Rajya Sabha, and method of election of the president were derived from the Irish Constitution.
- Canadian Constitution: Federation with a strong centre, residuary powers vested in the centre, appointment of state governors by the centre, and advisory jurisdiction of the Supreme Court were influenced by the Canadian Constitution.
- Australian Constitution: The concurrent list, freedom of trade, commerce and intercourse, and joint sitting of the two Houses of Parliament were inspired by the Australian Constitution.
- Weimar Constitution of Germany: Suspension of fundamental rights during an emergency was derived from the Weimar Constitution.
- Soviet Constitution: Fundamental duties and the ideal of justice (social, economic, and political) in the preamble were influenced by the Soviet Constitution.
- French Constitution: Republic and ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity in the preamble were derived from the French Constitution.
- South African Constitution: Procedure for amendment of the Constitution and election of members of the Rajya Sabha were influenced by the South African Constitution.
- Japanese Constitution: Procedure established by law was derived from the Japanese Constitution.
Various Schedules of the Indian Constitution
Parts of the Constitution
The Constitution of India is divided into 22 parts, each dealing with specific subjects. Here’s a brief overview of each part: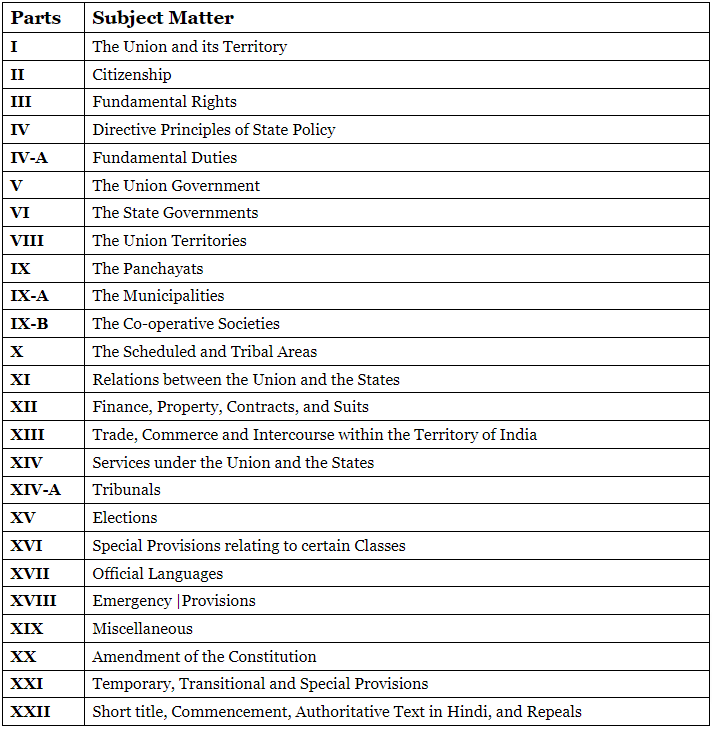
Note – Part-VII (The States in Part B of the First Schedule), has been deleted by the 7th Constitutional Amendment of 1956.
Conclusion
- The Indian Constitution is an important symbol of the country's democratic values and dreams.
- It was carefully created, drawing from historical struggles and visionary ideas.
- The Constitution continues to lead India towards a society that is fair, inclusive, and prosperous.
- It plays a crucial role in maintaining its values, bringing people together despite their differences.
- The Constitution protects the rights and freedoms of every citizen.
- By doing so, it helps create a better future for upcoming generations.
|
75 videos|311 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Constitution - Social Studies & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What is the significance of the Constitution in the CTET and State TET exams? |  |
| 2. What are the main topics covered under the Constitution in the CTET and State TET syllabus? |  |
| 3. How can candidates prepare for questions related to the Constitution in the CTET and State TET exams? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific articles of the Constitution that candidates should focus on for the CTET and State TET exams? |  |
| 5. What role does the Constitution play in shaping educational policies in India? |  |





















