Basics of Internet - 2 - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| Key Internet Components |

|
| Structure of a URL |

|
| Types of Domains |

|
| Domain Name System (DNS) & IP Addresses |

|
The Internet is a worldwide telecommunications system that provides connectivity for millions of other, smaller networks; therefore, the Internet is often referred to as a network of networks.
It allows computer users to communicate with each other across distance and computer platforms (including other ICT-based devices such as mobile & other electronic devices).
The Internet began in 1969 as the U.S. Department of Defense’s Advanced Research Project Agency (ARPA) for war communication.
The World Wide Web (Web) is a collection of different websites you can access through the Internet.
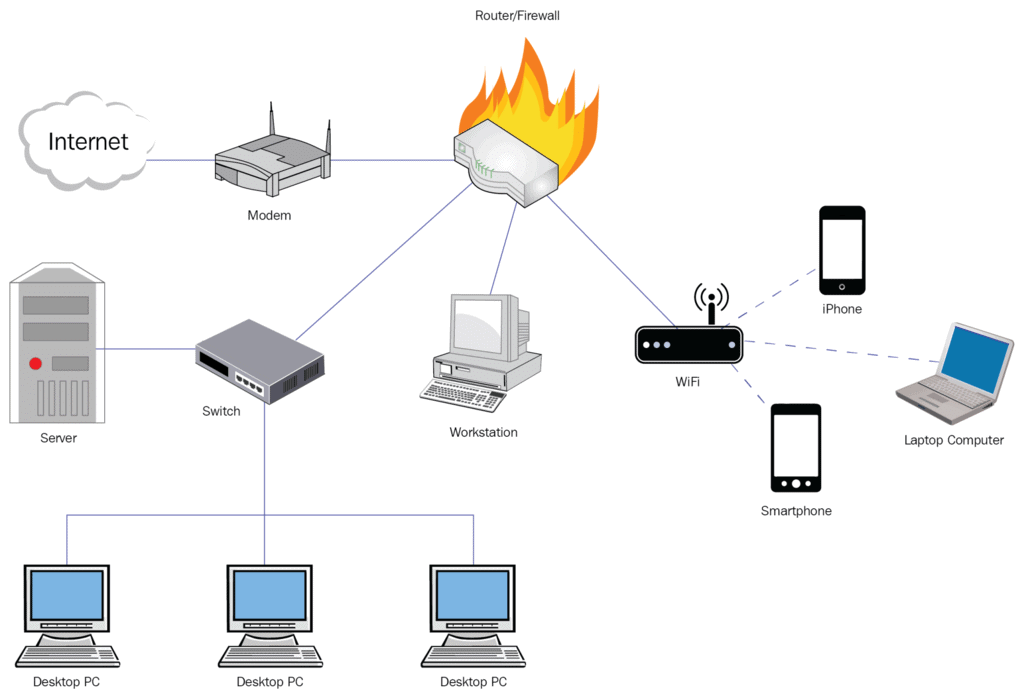
Key Internet Components
Internet Service Provider (ISP) – Offers services such as web page access, email, and web hosting, often at different speeds for a monthly fee.
Browser – A program that allows you to view and interact with the Web. Examples include Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer (IE), and Safari.
Webpage – What you see in your browser when using the Internet, containing text, images, links, and more.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) – The web address of internet pages and files.
Structure of a URL
A URL consists of three parts:
Protocol – Most web pages use http or https.
Host or Top-Level Domain (TLD) – Common examples include .com, .net, .edu, .org.
Filename/Page Name – The actual webpage or file being accessed.
A domain name is the unique, alphabetically-based part of a URL, registered by individuals, businesses, or organizations.
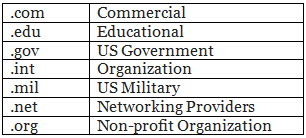
Types of Domains
Top-Level Domains (TLDs) – Examples:
.com (commercial)
.org (organizations)
.edu (educational institutions)
Country Code Domains – Examples: .uk, .ca, .au, .jp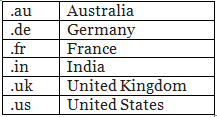
 |
Download the notes
Notes: Basics of Internet - 2
|
Download as PDF |
Domain Name System (DNS) & IP Addresses
An Internet address consists of four fields with numbers, separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1), known as an IP address.
The Domain Name System (DNS) translates numerical IP addresses into words for easier use.
Security & Web Technologies
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) – A secure encryption protocol used to protect data transmitted over the Internet.
Web Hosting – A service that provides storage and connectivity for websites.
Web Server – A specialized computer system designed to host websites.
Programming Languages for the Web
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) – The language that structures webpages.
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) – Used for organizing and storing data.
XHTML – A combination of HTML and XML.
Internet Protocols
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) – The protocol that allows web browsers and servers to communicate.
|
24 videos|19 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Basics of Internet - 2 - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes
| 1. What is the Internet and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of Internet connections? |  |
| 3. What are the basic components of the Internet? |  |
| 4. How does the World Wide Web differ from the Internet? |  |
| 5. What are some common Internet safety practices? |  |



















