Linear Model - Communication Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| Communication Models |

|
| 1. Lasswell’s model |

|
| 2. Aristotle’s Model |

|
| 3. Shannon Weaver Model |

|
| 4. Berlo’s S-M-C-R Model |

|
Communication Models
Communication Models are theoretical frameworks that aim to describe and clarify the process of human communication. These models provide insights into how messages are transmitted, received, and interpreted between individuals or groups.
In this section, we will explore four distinct models of communication that offer different perspectives on the communication process:
- Lasswell’s model
- Aristotle’s Model
- Shannon Weaver Model
- Berlo’s S-M-C-R Model
Linear Model of Communication
The Linear Model of Communication represents a simple and direct form of communication where a message flows in a straight line from the sender to the receiver. In this model, feedback from the receiver is not considered, and their role is limited to accepting the message. The focus is on the transmission of information without any interactive element.
The following models are examples of the Linear Model of Communication:
1. Lasswell’s model
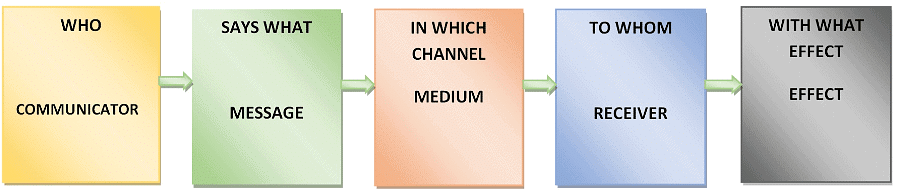
- Lasswell’s communication model was developed by communication theorist Harold D. Lasswell in 1948. Lasswell’s model of communication (also known as action model or linear model or one way model of communication) is regarded as one the most influential communication models.Harold Dwight Lasswell, states that a convenient way to describe an act of communication is to answer the following questions:
- Who: Refers to the person who creates the message.
- What: Relates to the content of the message.
- Channel: Involves the medium used to convey the message.
- Whom: Pertains to the recipient(s) of the message.
- Effect: Indicates the result or impact of the message.
Advantages
- The model is easy to understand and apply.
- It is suitable for almost all types of communication.
- The focus on the effect of the message is a key strength.
Disadvantages
- The model does not account for feedback in the communication process.
- It overlooks the impact of noise or interference in communication.
- Being a linear model, it simplifies the communication process.
2. Aristotle’s Model
Aristotle's Model of Communication, created by Aristotle, is a simple framework for understanding communication, particularly in the context of speaking. It is considered the first communication model and dates back to before 300 B.C. This model is widely accepted and focuses on the speaker and their speech.
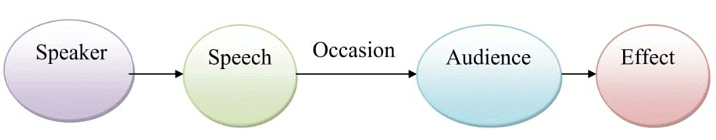
Aristotle Model is mainly focused on speaker and speech. It can be broadly divided into 5 primary elements:
- Speaker: The individual delivering the message.
- Speech: The content or message being conveyed.
- Occasion: The context or setting in which the communication takes place.
- Audience: The group receiving the message.
- Effect: The impact or outcome of the communication.
In Aristotle's Model, the speaker is central to the communication process. The speaker's words aim to influence the audience's thoughts and opinions. The audience, in this model, is mostly passive, receiving and being influenced by the speech. This creates a one-way flow of communication from the speaker to the audience.
3. Shannon Weaver Model
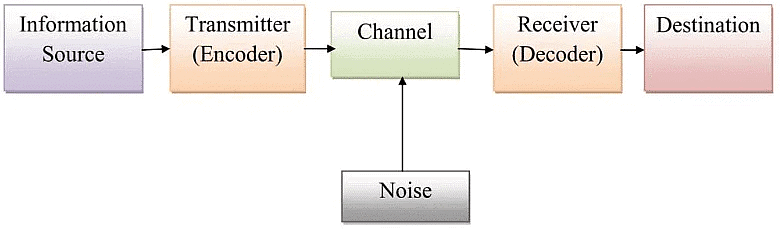
In 1948, Shannon was an American mathematician, Electronic engineer and Weaver was an American scientist both of them join together to write an article in Bell System Technical Journal‖ called “A Mathematical Theory of Communication” and also called as Shannon Weaver model of communication .According to the Shannon-Weaver Model, communication includes the following concepts: sender, encoder, channel, decoder, receiver and feedback. Furthermore, there is also concept of noise included in the model.
Elements of Model
- Sender(Information Source): The originator of message or the information source selects desire message.
- Encoder(Transmitter): The transmitter which converts the message into signals.
- Channel: Channel is the medium used to send message.
- Decoder (Receiver): Decoder is the machine used to convert signals or binary data into message or the receiver who translates the message from signals.
- Receiver (Destination): Receiver is the person who gets the message or the place where the message must reach. The receiver provides feedback according to the message.
- Noise: Noise is the physical disturbances like environment, people, etc. which does not let the message get to the receiver as what is sent.
Advantages
- Concept of noise helps in making the communication effective by removing the noise or problem causing noise.
- This model takes communication as a two way process. It makes the model applicable in general communication.
- Communication is taken as quantifiable in Shannon Weaver model.
Disadvantages
- Feedback is taken as less important in comparison to the messages sent by the sender.
- The model is taken by some critics as a “misleading misrepresentation of the nature of human communication” as human communication is not mathematical in nature.
- The Shannon-Weaver model, by its very nature, encounters some difficulty when applied to human communication. Its origin as a model to be applied to telecommunication, rather than to interpersonal human communication, limits its application due to the linear, unidirectional makeup.
4. Berlo’s S-M-C-R Model
While the Aristotle model of communication puts the speaker in the central position and suggests that the speaker is the one who drives the entire communication, the Berlo’s model of communication takes into account the emotional aspect of the message.Berlo’s Model has mainly, four components to describe the communication process. They are sender, message, channel and receiver. Each of the component is affected by many factors. Berlo’s model of communication operates on the SMCR model.
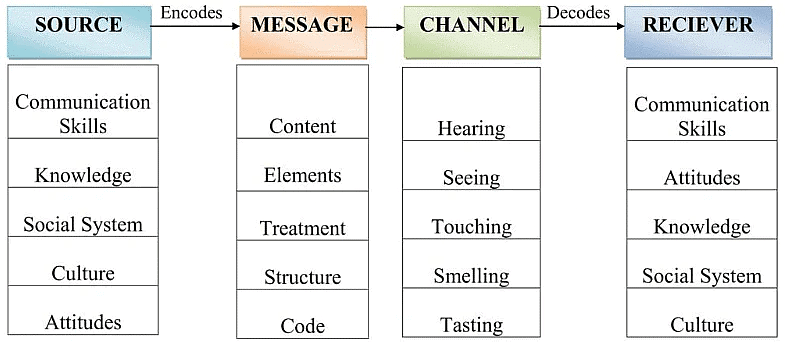 In the SMCR model:
In the SMCR model:
S– Stands for Source
Sender is the source of the message or the person who originates the message. The person or source sends the message to the receiver. The following are the factor related to sender and is also the same in the case of receiver:
- Communication Skills: Effective communication skills, including reading, writing, speaking, and listening, are crucial for both the sender and receiver. Strong communication skills ensure that the message is conveyed clearly and understood accurately, while poor communication skills can lead to misunderstandings.
- Attitude: The attitudes of the sender and receiver play a significant role in how the message is perceived. Their attitudes towards themselves, each other, and the context of the communication can influence the meaning and interpretation of the message.
- Knowledge: Having a good understanding of the topic being communicated enhances the effectiveness of the message. The sender's knowledge allows them to convey the message accurately and comprehensively.
- Social Systems: Factors such as values, beliefs, laws, and cultural norms influence how the sender communicates. These social system factors can create variations in how messages are constructed and understood.
- Culture: Cultural differences can significantly impact the interpretation of messages. What is considered acceptable or appropriate in one culture may be offensive or misunderstood in another culture.
M – Message
A message is the substance that is being sent by the sender to the receiver. It might be in the form of voice, audio, text, video or other media. The key factors affecting the message are
- Content: A thought has to be put into words and content has to be prepared. Content is actually the matter or the script of the conversation. It is in simpler words, the backbone of any communication.
- Elements: Elements are the non verbal things that tag along with the content like gestures, postures, facial expressions, body signs, language, etc.
- Treatment: Treatment is the way in which the message is conveyed to the receiver. Treatment also effects the feedback of the receiver.
- Structure: A message cannot be expressed in one go. It has to be properly structured in order to convey the message in the most desired form.
Code
Code is the form in which the message is sent. It might be in the form of language, text, video, etc.
- C – Channel: Channel actually refers to the medium how the information flows from the sender to the receiver. In mass communication and other forms of communication, technical machines might be used as a channel like telephone, internet, etc. But in general communication, all the five senses are the channels which help human beings to communicate with each
- Hearing- We receive the message through hearing.
- Seeing- We perceive through seeing. We also get non-verbal messages by seeing.
- Touching- Many of the non-verbal communication happens from touching like holding hands.
- Smelling- We collect information from smelling.
- Tasting- Taste also provides the information to be sent as a message.
R – Receiver
Receiver is the person who gets the message sent in the process. This model believes that the thinking pattern and all other factors mentioned above must be in sync to that of the sender for the communication to be effective. The message might not have the same effect as intended if the receiver and sender are not similar. The receiver must also have a very good listening skill. Other factors are similar to that of the sender.
- Communication skills
- Attitudes
- Knowledge
- Social Systems
- Culture
Criticism
- The model lacks the concept of feedback, failing to acknowledge the impact of the communication process.
- It does not address potential barriers to communication, such as noise or interference.
- The model adheres to a linear approach to communication, lacking the element of two-way interaction.
- A significant limitation is the model's failure to clarify recognized communication channels.
- Both individuals involved in the communication need to share similarities in the factors mentioned, which may not always be the case.
|
6 videos|28 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Linear Model - Communication Notes
| 1. What are the different communication models mentioned in the article? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the linear model in communication? |  |
| 3. Who proposed the Shannon Weaver Model of communication? |  |
| 4. How does Berlo’s S-M-C-R Model differ from other communication models mentioned in the article? |  |
| 5. How does Aristotle’s Model of communication differ from the other models mentioned in the article? |  |















