UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English) > NCERT Summary: The Early Societies (Theme 11: Paths to Modernization)
NCERT Summary: The Early Societies (Theme 11: Paths to Modernization) | NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English) - UPSC PDF Download
Paths to Modernization
- China and Japan present a marked physical contrast.
- China is a vast continental country with many climatic zones.
- China and Japan are situated in far East Asia.
- China dominated the East in the beginning of the 19th century.
- China is dominated by three major rivers. These rivers are Huang He, the Yangtse and the Pearl river.
- A large part of China is mountainous.
- The most dominant ethnic group of China is ‘Han’ and the major language is Chinese ‘Putonghua’.
- Chinese foods reflect the regional diversity. The best known is southern or cantonese cuisine.
- Japan was divided into more than 250 domains under the rule of lords called daimyo.
- Japan is situated in the Pacific ocean.
- Japan is a string of islands. It is an archipelago consisting of more than 3,000 islands. Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku and Hokkaido are the four largest islands of Japan.
- Japan is also known as the ‘Land of Rising Sun’.
- The Shoguns made Edo, the capital of Japan.
- The tradition of animal rearing is not prevalent.
- Edo is modem Tokyo.
- Japanese emperor was known as Mikado.
- Uighur, Hui, Manchu and Tibetan are the other nationalities of the Chinese.
- The Samurai were warriors and helped the Shogun in running the administration.
- Printing was done with wood blocks in Japan. The Japanese were not interested in European printing.
- Edo, the capital city of Japan became the most populated city in the middle of the 17th century.
- The Meiji restoration is termed as one of the most momentous events in the Japanese history.
- In 1871, under Meiji’s rule feudalism was abolished.
- Tokyo University was established under the rule of Meiji in 1877.
- Military reforms were also introduced during Meiji rule.
- In 1872, modem banking institutions were launched.
- Under Meiji’s rule new constitution was introduced.
- In 1889, Japan adopted the new constitution.
- Miyake Setsurei was a well-known Japanese philosopher.
- Miyake Setsurei believed that every nation must develop its special talent in the interest of the world civilization.
- In Sino-Japanese War in 1894-95, China faced a humiliating defeat at the hands of Japanese.
- On April 17, 1895, Treaty of Shimonoseki was signed between China and Japan.
- Defeat of China at the hands of Japan made China vulnerable.
- The Chinese declared after the war that both China and Japan needed reforms for modernization.
- Sino-Japanese war served the basis for the Anglo-Japanese alliance in 1902.
- Two opium wars were fought between China and England between 1839-42 and 1856-60 respectively.
- After the decline of Manchu empire, a republic was established in 1911 in China.
- In 1912, Dr. Sun Yat-sen formed a national party of China. It was known as Guomindang.
- The People’s Republic of China came into existence in 1949.
- In 1949, Communist Government was established in China and began a new age in the history of China.
Important terms
- Soviet: Elected council of peasants and workers
- Daimyo: Lords of the domain under their possession.
- Shogun: Official title of sell-Taishogun.
- Zaibatsu: Large business houses controlled by individual families.
- Triangular trade: Trade carried out among three countries.
- Comintern: Communist International
- Meiji: Enlightened rule
- Fukoku Kyohei: Government slogan given during Meiji period, which means rich country and strong army.
- Dim sum: Touch your heart.
Timeline
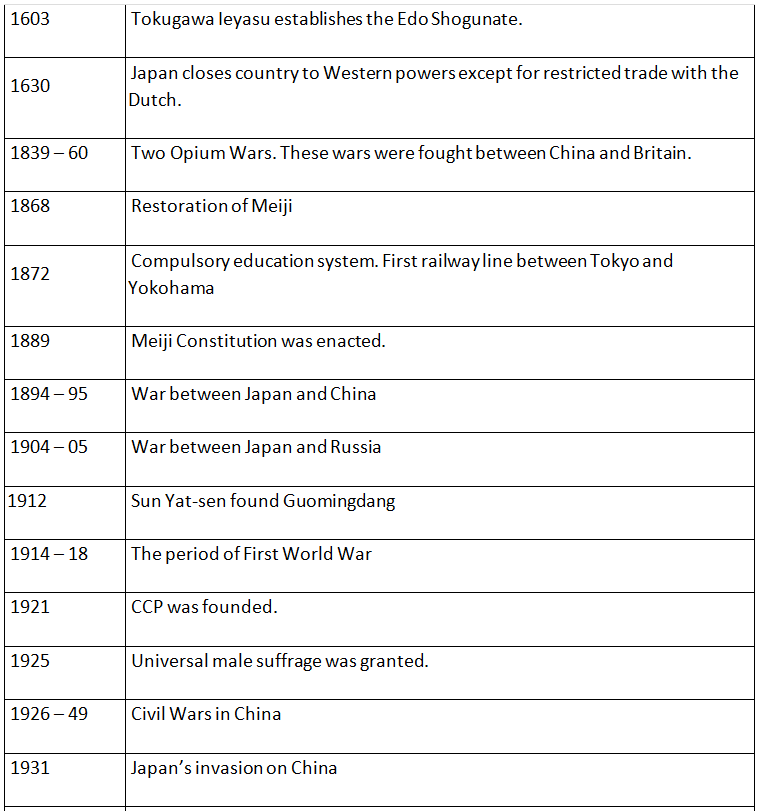

The document NCERT Summary: The Early Societies (Theme 11: Paths to Modernization) | NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English) - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
476 videos|360 docs
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: The Early Societies (Theme 11: Paths to Modernization) - NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English) - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of the Early Societies in the process of modernization? |  |
Ans. The Early Societies play a crucial role in the process of modernization as they lay the foundation for the development of complex social, economic, and political systems. These societies provide important insights into the origins of various cultural practices, technological advancements, and social structures that eventually shaped the modern world.
| 2. How did Early Societies contribute to the growth of agriculture and civilization? |  |
Ans. Early Societies played a pivotal role in the development of agriculture and civilization. They transitioned from hunter-gatherer lifestyles to settled agricultural communities, which led to the domestication of plants and animals. This shift in lifestyle allowed for a surplus of food production, leading to the growth of population, specialization of labor, and the emergence of complex social structures and civilizations.
| 3. What were the major factors that influenced the transformation of Early Societies into modern societies? |  |
Ans. Several factors influenced the transformation of Early Societies into modern societies. These include technological advancements, such as the invention of writing systems and tools, which facilitated communication and trade. Additionally, the development of complex political systems, formation of empires, and the spread of ideas and religions played a significant role in shaping modern societies.
| 4. How did trade and cultural exchanges contribute to the development of Early Societies? |  |
Ans. Trade and cultural exchanges played a crucial role in the development of Early Societies. Through trade, societies were able to access valuable resources, technologies, and ideas from distant regions. This exchange of goods and knowledge facilitated economic growth, cultural diversity, and the spread of innovations, ultimately contributing to the development and advancement of these societies.
| 5. What were the major challenges faced by Early Societies in their path towards modernization? |  |
Ans. Early Societies faced various challenges in their path towards modernization. These included environmental factors such as climate change, natural disasters, and resource scarcity, which could disrupt food production and lead to conflicts. Additionally, social and political challenges, such as the consolidation of power, maintaining social order, and dealing with external invasions, posed significant obstacles for these societies in their journey towards modernization.
|
476 videos|360 docs
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















