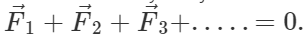JEE Advanced (Assertion-Reason Type): Laws of Motion | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements, Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer.
Q.1. Assertion: A physical quantity cannot be called as a vector if its magnitude is zero.
Reason: A vector has both magnitude and direction.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Correct Answer is option (d)
If a vector quantity has zero magnitude then it is called a null vector. That quantity may have some direction even if its magnitude is zero.
Q.2. Assertion : If a body of mass m is projected upwards with a speed V making an angle θ with the vertical, than the change in the momentum of the body along X–axis is zero.
Reason : Mass of the body remains constant along X–axis
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Correct Answer is option (b)
When a body is projected up making an angle θ the velocity component along-axis remains constant.
Therefore, Momentum along x-axis is constant. Along horizontal, mass and velocity both are constant.
Q.3. Assertion: Inertia is the property by virtue of which the body is unable to change by itself the state of rest only.
Reason: The bodies do not change their state unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (e)
Inertia is the property by virtue of which the body is unable to change by itself not only the state of rest, but also the state of motion.
Q.4. Assertion: If the net external force on the body is zero, then its acceleration is zero.
Reason: Acceleration does not depend on force.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
According to Newton's second law Acceleration = Force/Mass i.e. if net external force on the body is zero then acceleration will be zero
Q.5. Assertion: Newton's second law of motion gives the measurement of force.
Reason: According to Newton's second law of motion, force is directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
According to second law F = dp/dt = ma. If we know the values of m and a, the force acting on the body can be calculated and hence second law gives that how much force is applied on the body.
Q.6. Assertion: Force is required to move a body uniformly along a circle.
Reason: When the motion is uniform, acceleration is zero.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (b)
When a body is moving in a circle, its speed remains same but velocity changes due to change in the direction of motion of body. According to first law of motion, force is required to change the state of a body. As in circular motion the direction of velocity of body is changing so the acceleration cannot be zero. But for a uniform motion acceleration is zero (for rectilinear motion).
Q.7. Assertion: Aeroplanes always fly at low altitudes.
Reason: According to Newton's third law of motion, for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
The wings of the aeroplane pushes the external air backward and the aeroplane move forward by reaction of pushed air. At low altitudes density of air is high and so the aeroplane gets sufficient force to move forward.
Q.8. Assertion: No force is required by the body to remain in any state.
Reason: In uniform linear motion, acceleration has a finite value.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
Force is required to change the state of the body. In uniform motion body moves with constant speed so acceleration should be zero.
Q.9. Assertion: Mass is a measure of inertia of the body in linear motion.
Reason: Greater the mass, greater is the force required to change its state of rest or of uniform motion.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
According to Newton's second law of motion α = F/m i.e. magnitude of the acceleration produced by a given force is inversely proportional to the mass of the body. Higher is the mass of the body, lesser will be the acceleration produced i.e. mass of the body is a measure of the opposition offered by the body to change a state, when the force is applied i.e. mass of a body is the measure of its inertia.
Q.10. Assertion: A cyclist always bends inwards while negotiating a curve.
Reason: By bending, cyclist lowers his centre of gravity.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
The purpose of bending is to acquire centripetal force for circular motion. By doing so component of normal reaction will counter balance the centrifugal force.
Q.11. Assertion: The work done in bringing a body down from the top to the base along a frictionless incline plane is the same as the work done in bringing it down the vertical side.
Reason: The gravitational force on the body along the inclined plane is the same as that along the vertical side.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
Work done in moving an object against gravitational force (conservative force) depends only on the initial and final position of the object, not upon the path taken. But gravitational force on the body along the inclined plane is not same as that along the vertical and it varies with the angle of inclination.
Q.12. Assertion: Linear momentum of a body changes even when it is moving uniformly in a circle.
Reason: Force required to move a body uniformly along a straight line is zero.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (b)
In uniform circular motion of a body the speed remains constant but velocity changes as direction of motion changes. As linear momentum = mass × velocity, therefore linear momentum of a body changes in a circle. On the other hand, if the body is moving uniformly along a straight line then its velocity remains constant and hence acceleration is equal to zero. So force is equal to zero.
Q.13. Assertion: A rocket works on the principle of conservation of linear momentum.
Reason: Whenever there is a change in momentum of one body, the same change occurs in the momentum of the second body of the same system but in the opposite direction.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
As the fuel in rocket undergoes combustion, the gases so produced leave the body of the rocket with large velocity and give upthrust to the rocket. If we assume that the fuel is burnt at a constant rate, then the rate of change of momentum of the rocket will be constant. As more and more fuel gets burnt, the mass of the rocket goes on decreasing and it leads to increase of the velocity of rocket more and more rapidly.
Q.14. Assertion: A player lowers his hands while catching a cricket ball and suffers less reaction force.
Reason: The time of catch increases when cricketer lowers its hand while catching a ball.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (a)
By lowering his hand player increases the time of catch, by doing so he experience less force on his hand because F ∝ 1/dt.
Q.15. Assertion: Linear momentum of a body changes even when it is moving uniformly in a circle.
Reason: In uniform circular motion velocity remain constant.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
In uniform circular motion, the direction of motion changes, therefore velocity changes.
As P = mv therefore momentum of a body also changes in uniform circular motion.
Q.16. Assertion: Newton's third law of motion is applicable only when bodies are in motion.
Reason: Newton's third law applies to all types of forces, e.g. gravitational, electric or magnetic forces etc.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (c)
According to third law of motion it is impossible to have a single force out of mutual interaction between two bodies, whether they are moving or at rest. While, Newton's third law is applicable for all types of forces.
Q.17. Assertion: A reference frame attached to earth is an inertial frame of reference.
Reason: The reference frame which has zero acceleration is called a non-inertial frame of reference.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (d)
An inertial frame of reference is one which has zero acceleration and in which law of inertia hold good i.e. Newton's law of motion are applicable equally. Since earth is revolving around the sun and earth is rotating about its own axis also, the forces are acting on the earth and hence there will be acceleration of earth due to these factors. That is why earth cannot be taken as inertial frame of reference.
Q.18. Assertion: A table cloth can be pulled from a table without dislodging the dishes.
Reason: To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (b)
According to law of inertia (Newton's first law), when cloth is pulled from a table, the cloth come in state of motion but dishes remains stationary due to inertia. Therefore when we pull the cloth from table the dishes remains stationary.
Q.19. Assertion: A body subjected to three concurrent forces cannot be in equilibrium.
Reason: If large number of concurrent forces acting on the same point, then the point will be in equilibrium, if sum of all the forces is equal to zero.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (b)
A body subjected to three concurrent forces is found to in equilibrium if sum of these force is equal to zero. i.e.
Q.20. Assertion: The acceleration produced by a force in the motion of a body depends only upon its mass.
Reason: Larger is the mass of the body, lesser will be the acceleration produced.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct Answer is option (b)
According to Newton's second law, F = ma ⇒ a = F/m For constant F, acceleration is inversely proportional to mass i.e. acceleration produced by a force depends only upon the mass of the body and for larger mass acceleration will be less.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|