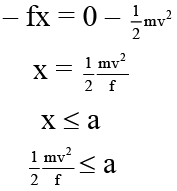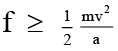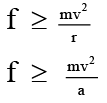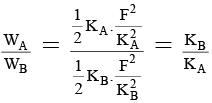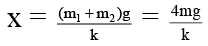JEE Advanced (One or More Correct Option): Work, Power & Energy | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
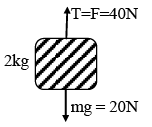
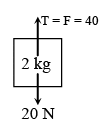
Q.1. A block of mass 2 kg is hanging over a smooth and light pulley through a light string. The other end of the string is pulled by a constant force F = 40 N. The kinetic energy of the particle increase 40 J in a given interval of time. Then: (g = 10 m/s2) -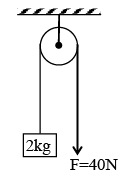 (a) tension is the string is 40 N.
(a) tension is the string is 40 N.
(b) displacement of the block in the given interval of time is 2m.
(c) work done by gravity is – 20J
(d) work done by tension is 80 J
Correct Answer is option (a, b and d)
(Moderate) Free body diagram of block is as shown in figure. From work – energy theorem
Wnet = ΔKE
Or (40 - 20)s = 40
∴ s = 2m
Work done by gravity is - 20 × 2 = - 40J
And work done by tension is 40 × 2 = 80 J
Q.2. The driver of a car travelling at velocity v suddenly sees a broad wall in front of him at a distance ‘a’:
(a) If the brakes are applied force required to stop the car not to be smashed up with wall is mv2/2a
(b) To avoid crashing with wall if the car turns in circle, then force required is a mv2/a .
(c) It is better to apply the brakes than to turn the car in circular path to avoid crashing with wall.
(d) When car stops then its kinetic energy is expended in work against force of friction.
Correct Answer is option (a, b, c and d)
When brakes are applied to avoid crash By work-energy theorem Wf = ΔK
Force required to avoid crash by braking
If car turns in circle then, force required is
Half force is required in braking than in turning the car in circle to avoid crash with the wall.
Q.3. A particle of mass m is at rest in a train moving with constant velocity with respect to ground. Now the particle is accelerated by a constant force F0 acting in the direction of motion of train for time t0. A girl in the train and a boy on the ground measure the work done by this force. Which of the following are incorrect?
(a) Both will measure the same work.
(b) Boy will measure higher value than the girl.
(c) Girl will measure higher value than the boy.
(d) Data are insufficient for the measurement of work done by the force F0.
Correct Answer is option (a and c)
(b) For boy measuredis more.
(d) is correct statement as velocity of train i.e.is unknown.
Q.4. A body starting from rest is moved along straight line by a machine delivering constant power. Choose the correct graph -
(a) 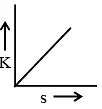
(b) 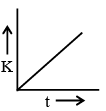
(c) 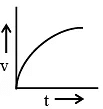
(d) 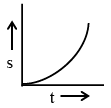
Correct Answer is option (b, c and d)
P = constant
⇒ dK/dt = constant
⇒ K ∝ t .... (i)
⇒ v ∝ t ... (ii)
⇒ s ∝ t3/2 .... (iii)
Q.5. There are two massless springs A and B of spring constant KA and KB respectively and KA > KB. If WB and WB be denoted as work done on A and work done on B respectively, then -
(a) If they are compressed to same distance, WA > WB.
(b) If they are compressed by same force (up to equilibrium state) WA < WB.
(c) If they are compressed by same distance, WA = WB.
(d) If they are compressed by same force (up to equilibrium state) WA > WB.
Correct Answer is option (a and b)
If the springs are compressed to same amount :
WA = 1/2 KA X2 ; WB = 1/2 KB X2
KA > KB ⇒ WA > WB
If the springs are compressed by same force
F = KAXA = KB XB ; XA = F/KA ; XB = F/KB;
Hence, WA < WB
Q.6. Work done by a force on an rigid object having no rotational motion will be zero, if -
(a) the force is always perpendicular to acceleration of object.
(b) the object is at rest relative to ground but the point of application of force moves on the object.
(c) the force is always perpendicular to velocity of object
(d) the point of application of force is fixed relative to ground by the object moves.
Correct Answer is option (b and c)
(a) If velocity and acceleration are not in same direction. Work done by force perpendicular to acceleration will not be zero.
(b) If the object is at rest no force can do work
(c) If force is perpendicular to velocity work done will be zero.
(d) If the point on the body has velocity component in direction of application of force work done will be nonzero.
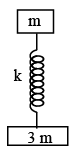
Q.7. A disc of mass 3m and a disc of mass m are connected by massless spring of stiffness k. The heavier disc is placed on the ground with the spring vertical and lighter disc on top. From its equilibrium position the upper disc is pushed down by a distance δ and released. Then
(a) if δ > 3 mg/k, the lower disc will bounce up.
(b) if δ = 2mg/k, maximum normal reaction from ground on lower disc = 6 mg.
(c) if δ = 2mg/k, maximum normal reaction from ground on lower disc = 4mg.
(d) if δ > 4 mg/k, the lower disc will bounce up.
Correct Answer is option (b and d)
To bounce up the lower block initial compression to be given after equilibrium.
Q.8. A block of mass 2 kg is hanging over a smooth and light pulley through a light string. The other end of the string is pulled by a constant force F = 40 N. The kinetic energy of the particle increases 40 J in a given interval of time. Then: (g = 10 m/s2)
(a) tension in the string is 40 N.
(b) displacement of the block in the given interval of time is 2m.
(c) work done by gravity is – 20 J.
(d) work done by tension is 80 J.
Correct Answer is option (a, b and d)
From W – E theorem,
Wnet = Δ(KE)
(40 - 20)S = 40S = 20m
Wg = –20 × 2 = – 40 J
WT = 40 × 2 = 80 J
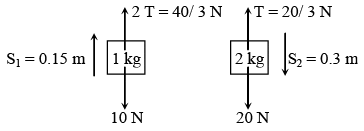
Q.9. In the pulley-block system shown in figure strings are light. Pulleys are massless and smooth. System is released from rest. In 0.3 second -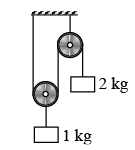 (a) work done on 2 kg block by gravity is 6 J
(a) work done on 2 kg block by gravity is 6 J
(b) work done on 2 kg block by string is – 2J
(c) work done on 1 kg block by gravity is –1.5 J
(d) work done on 1 kg block by string is 2 J
Correct Answer is option (a, b, c and d)
So from definition of work we can find out corresponding work.
Q.10. A body of mass m was hauled up the hill with constant speed v by a force F which at each point was directed along tangent to the path. If length of base is λ and height of hill is h, then which of the following are correct?
(a) Work done by gravity is - mgh
(b Work done by friction is - μmgλ
(c) Work done by gravity is path independent
(d) Work done by friction is path independent
Correct Answer is option (a and c)
Gravity is a conservative force and here frictional force depends on radius of curvature.
|
481 docs|964 tests
|