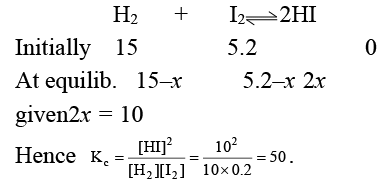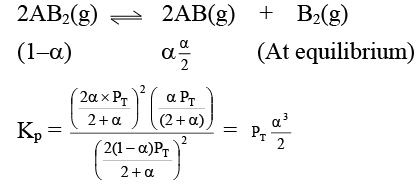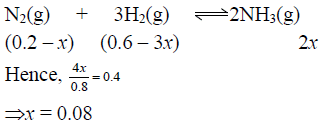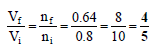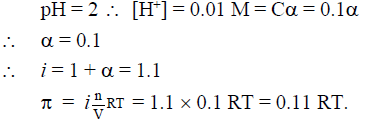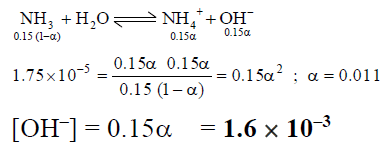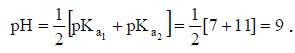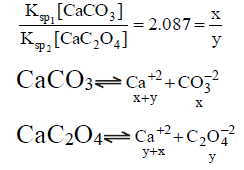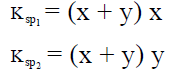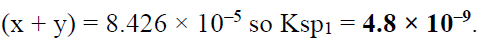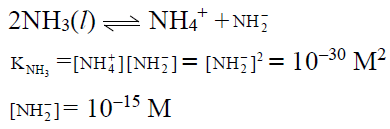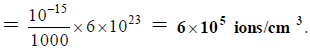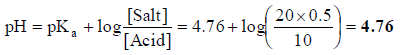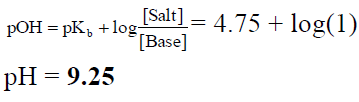JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Equilibrium | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. According to Lewis concept, an acid is:
(a) proton donor
(b) electron pair donor
(c) electron pair acceptor
(d) proton acceptor
Correct Answer is option (c)
According to Lewis concept, an acid is electron pair acceptor
Q.2. Ostwald’s dilution law is applicable to:
(a) Strong electrolytes only
(b) Weak electrolyte only
(c) Non-electrolytes
(d) Strong and weak electrolytes
Correct Answer is option (b)
Ostwald’s dilution law is applicable to weak electrolyte only
Q.3. The pH of a solution of hydrochloric acid is 4. The molarity of the solution is:
(a) 4.0
(b) 0.4
(c) 0.0001
(d) 0.04
Correct Answer is option (c)
pH = – log [H+] , Here [H+] = 10-4 , Molarity = 0.0001 M
Q.4. The strong conjugate base is
(a) NO32-
(b) Cl–
(c) SO42-
(d) CH3COO–
Correct Answer is option (d)
CH3COO– is the strongest conjugate base because CH3COOH is a weak acid.
Q.5. Which of the following pairs constitutes a buffer ?
(a) NaOH and HCl
(b) HNO3 and NH4NO3
(c) HCl and KCl
(d) HNO2 and NaNO2
Correct Answer is option (d)
HNO2 and NaNO2 represent a buffer mixture.
Q.6. Le Chatelier’s principle is applicable to:
(a) only homogeneous chemical reversible reactions
(b) only heterogeneous chemical reversible reactions
(c) only physical equilibria
(d) all systems, chemical or physical in equilibrium.
Correct Answer is option (d)
Le Chatelier’s principle is applicable to all systems, chemical or physical in equilibrium.
Q.7. Which of the following is the weakest base?
(a) NaOH
(b) Ca(OH)2
(c) NH4OH
(d) KOH
Correct Answer is option (c)
NH4OH is the weakest base.
Q.8. When NH4Cl is added to NH4OH solution the dissociation of ammonium hydroxide is reduced. It is due to:
(a) common ion effect
(b) hydrolysis
(c) oxidation
(d) reduction
Correct Answer is option (a)
ammonium hydroxide is reduced due to presence of common ion NH4+
Q.9. For the reversible reaction
N2 (g) + 3H2(g) ⇋ 2NH3 + Heat
The equilibrium shifts in forward direction
(a) by increasing the concentration of NH3(g)
(b) by decreasing the pressure
(c) by decreasing the concentration of N2 and H2
(d) by increasing pressure and decreasing temperature
Correct Answer is option (d)
Le Chatelier’s principle suggests that in the formation of ammonia, the equilibrium shifts in forward direction by increasing pressure and decreasing temperature.
Q.10. A base according to Bronsted concept is a substance which can:
(a) lose pair of electron
(b) donate protons
(c) gain a pair of electrons
(d) accept protons
Correct Answer is option (d)
A base according to Bronsted concept is a substance which can accept protons.
Q.11. 15 moles of H2 and 5.2 moles of I2 are mixed and allowed to attain equilibrium at 500°C. At equilibrium, the concentration of HI is found to be 10 moles. The equilibrium constant for the formation of HI is:
(a) 50
(b) 15
(c) 100
(d) 25
Correct Answer is option (a)
Q.12. At temperature T, a compound AB2(g) dissociates according to the reaction
2AB2(g) ⇌ 2AB(g) + B2(g)
With degree of dissociation a, which is small compared with unity. The expression of Kp, in terms of α and total pressure PT is
(a) 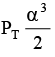
(b) 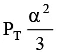
(c) 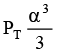
(d) 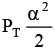
Correct Answer is option (a)
Q.13. 40% of a mixture of 0.2 mole of N2 and 0.6 mole of H2 react to give NH3 according to the equation N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) at given temperature and pressure. Then the ratio of the final volume to the initial volumes of gases are as
(a) 4:5
(b) 5:4
(c) 7:10
(d) 8:5
Correct Answer is option (a)
Total number of moles at equilibrium= 0.2 – x + 0.6 – 3x + 2x
= 0.8 – 2x = 0.8 – 2 x 0.08= 0.8 – 0.16 = 0.64
Q.14. pH of a 0.1 M monobasic acid solution is found to be 2. Its osmotic pressure of this solution at a temperature of ‘T(K)’ is
(a) 0.1 RT
(b) 0.11 RT
(c) 1.1 RT
(d) 0.01 RT
Correct Answer is option (b)
Q.15. What is the approximate OH- ion concentration of a 0.150 M NH3 solution? (Kb = 1.75x 10–5)
(a) 2.62 x 10–6
(b) 4.6 x 10–6
(c) 1.62 x 10–3
(d) 3.6 x 10–3
Correct Answer is option (c)
Q.16. Carbonic acid, H2CO3, is a diprotic acid for which K1 = 10–7 and K2 = 10–11. Which solution will produce a pH closest to 9?
(a) 0.1 M H2CO3
(b) 0.1 M Na2CO3
(c) 0.1 M NaHCO3
(d) 0.1 M NaHCO3 and 0.1 M Na2CO3
Correct Answer is option (c)
Q.17. When pure water is saturated with CaCO3 and CaC2O4, the concentration of calcium ion in the solution under equilibrium is 8.426 × 10–5 M. If the ratio of the solubility product of CaCO3 to that of CaC2O4 is 2.087, what is the solubility product of CaCO3 in pure water?
(a) 4.80 × 10–8
(b) 9.60 × 10–9
(c) 9.60 × 10–8
(d) 4.80 × 10–9
Correct Answer is option (d)
Q.18. The self-ionisation constant of NH3 at 50°C is given by 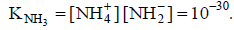
How many NH2- ions are present per cm3 of pure liquid NH3? (Assume Avogadro’s number = 6 x 1023)
(a) 6 x 106
(b) 6x 105
(c) 6 x 10-5
(d) 6 x 10-6
Correct Answer is option (b)
NH2- ions per cm3 of liquid NH3
Q.19. A buffer solution is prepared by mixing 10 ml of 1.0 M acetic acid and 20 ml of 0.5 M sodium acetate and then diluted to 100 ml with distilled water. If the pKa of CH3COOH is 4.76, what is the pH of the buffer solution prepared?
(a) 5.21
(b) 4.76
(c) 4.34
(d) 5.21
Correct Answer is option (b)
Q.20. The pKb value of ammonium hydroxide is 4.75. An aqueous solution of ammonium hydroxide is titrated with HCl. The pH of the solution at the point where half of ammonium hydroxide has been neutralised will be
(a) 9.25
(b) 8.25
(c) 7.50
(d) 4.75
Correct Answer is option (a)
|
446 docs|929 tests
|