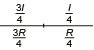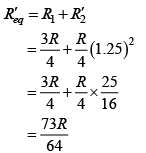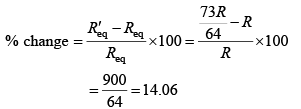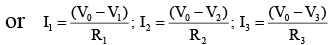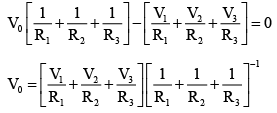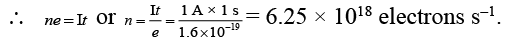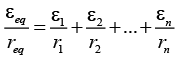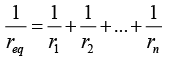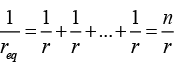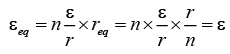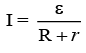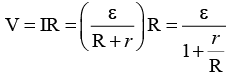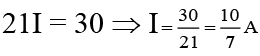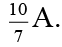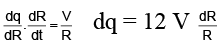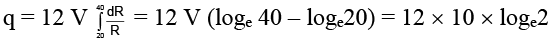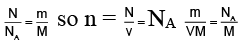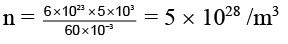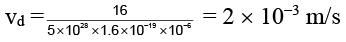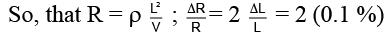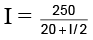JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Current Electricity | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. If 25% part of length of wire is stretched by 25%, then percentage change in resistance of wire will be about
(a) 7%
(b) 14%
(c) 25%
(d) 62.5%
Correct Answer is option (b)
Resistance of wire after stretching will be
Q.2. A boy has two spare light bulbs in his drawer. One is marked 240 V and 100 W and the other is marked 240 V and 60 W. He tries to decide which of the following assertions are correct?
(a) The 60 W light bulb has more resistance and therefore burns less brightly.
(b) The 60 W light bulb has less resistance and therefore burns less brightly.
(c) The 100 W bulb has more resistance and therefore burns more brightly.
(d) The 100 W bulb has less resistance and therefore burns less brightly.
Correct Answer is option (a)
When the same potential difference, that is the voltage, is applied as in houses,
Power = VI = V2/R
The smaller resistance consumes greater power. Here 100 W bulb has less resistance. It should glow more brightly. The 60 W bulb has more resistance and therefore statement (a) is correct.
Q.3. In parallel combination of n cells, we obtain
(a) more voltage
(b) more current
(c) less voltage
(d) less current
Correct Answer is option (b)
In parallel combination of cells the voltage across the terminals is same and resistance is minimum. Therefore from V = IR. The current drawn from cell combination will be more.
Q.4. A circuit has a section ABC as shown in figure. If the potentials at point A, B and C are V1, V2 and V3 respectively. The potential at point O is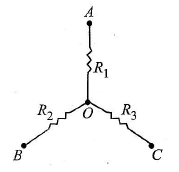 (a) V1 + V2 + V3
(a) V1 + V2 + V3
(b) 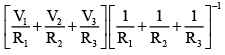
(c) Zero
(d) 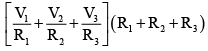
Correct Answer is option (b)
Applying junction rule to O –I1 – I2 – I3 = 0
i.e., I1 + I2 + I3 = 0 … (i)
Let, V0 be the potential at point O. By Ohm’s law for resistance R1, R2 and R3 respectively, we get
(V0 – V1) = I1R1; (V0 – V2) = I2R2 and (V0 – V3) = I3R3
So substitution these values of I1, I2 and I3 in eqn. (i), we get
Q.5. 1 ampere current is equivalent to
(a) 6.25 × 1018 electrons s–1
(b) 2.25 × 1018 electrons s–1
(c) 6.25 × 1014 electrons s–1
(d) 2.25 × 1014 electrons s–1
Correct Answer is option (a)
Q = It also Q = ne [e = 1.6 × 10–19 C]
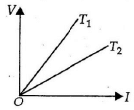
Q.6. The voltage V and current I graphs for a conductor at two different temperatures T1 and T2 are shown in the figure. The relation between T1 and T2 is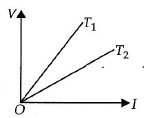 (a) T1 >T2
(a) T1 >T2
(b) T1 <T2
(c) T1 = T2
(d) T1 = 1/T2
Correct Answer is option (a)
The slope of V-I graph gives the resistance of a conductor at a given temperature. From the graph, it follows that resistance of a conductor at temperature T1 is greater than at temperature T2. As the resistance of a conductor is more at higher temperature and less at lower temperature, hence T1 > T2.
Q.7. Figure (a) and figure (b) both are showing the variation of resistivity (ρ) with temperature (T) for some materials. Identify the type of these materials.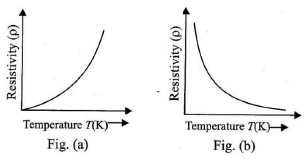 (a) Conductor and semiconductor
(a) Conductor and semiconductor
(b) Conductor and Insulator
(c) Insulator and semiconductor
(d) Both are conductors
Correct Answer is option (a)
In conductors due to increase in temperature the resistivity increases and in semiconductors it decreases exponentially.
Q.8. If n cells each of emf e and internal resistance r are connected in parallel, then the total emf and internal resistances will be
(a) 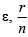
(b) ε, nr
(c) 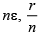
(d) nε, nr
Correct Answer is option (a)
In the parallel combination,
(∵ ε1 = ε2 = ε3 = .... = εn = ε and r1 = r2 = r3 = ....rn = r )........(i)
req = r/n ........(ii)
From (i) and (ii),
Q.9. Figure shows current in a part of an electric circuit, then current I is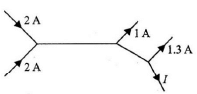
(a) 1.7 A
(b) 3.7 A
(c) 1.3 A
(d) 1 A
Correct Answer is option (a)
Applying Kirchhoff’s first law,
I = 2 + 2 – 1 – 1.3 = 1.7 A
Q.10. In the given circuit the potential at point B is zero, the potential at points A and D will be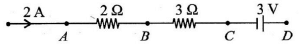 (a) VA = 4V; VD = 9V
(a) VA = 4V; VD = 9V
(b) VA = 3V; VD = 4V
(c) VA = 9V; VD = 3V
(d) VA = 4V; VD = 3V
Correct Answer is option (d)
∴ VA - 0 = 4V ⇒ V = 4 V
According to question VB = 0
Point D is connected to positive terminal of batter of emf 3 V.
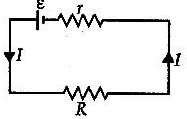
Q.11. A cell having an emf e and internal resistance r is connected across a variable external resistance R. As the resistance R is increased, the plot of potential difference V across R is given by
(a) 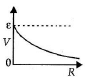
(b) 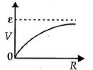
(c) 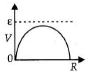
(d) 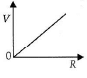
Correct Answer is option (b)
Current in the circuit,
Potential difference across R,
When R = 0, V = 0 or R = ∞, V = ε
Q.12. AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in the value of resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be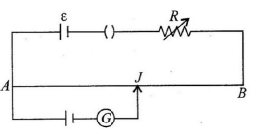 (a) towards B
(a) towards B
(b) towards A
(c) remains constant
(d) first towards B then back towards A.
Correct Answer is option (a)
Due to increase in resistance R the current through the wire will decrease and hence the potential gradient also decreases, which results in increase in balancing length. So J will shift towards B.
Q.13. In the shown figure, bridge is balanced, the current flowing through 2Ω resistance is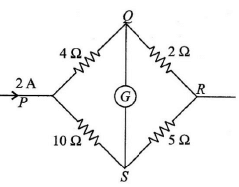 (a)
(a) 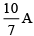
(b) 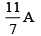
(c) 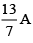
(d) 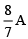
Correct Answer is option (a)
Let I be the current flowing through PQR then the current flowing through PSR is (2 – I)A.
Now since, galvanometer shows no deflection then the voltage through arm PQR is same as the voltage through arm PSR
I(4 + 2) = (2 – I)(10 + 5); 6I = 30 – 15I
Hence the current through 2 W resistor is
Q.14. A battery of 10 volt is connected to a resistance of 20 ohm through a variable resistance R. The amount of charge which has passed in the circuit in 4 minutes, if the variable resistance R is increased at the rate of 5 ohm/min, is
(a) 120 coulomb
(b) 120 loge 2 coulomb
(c) 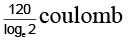
(d) 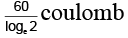
Correct Answer is option (b)
I = dq/dt = V/R
Q.15. An electric current of 16 A exists in a metal wire of cross section 10-6 m2 and length 1 m. Assuming one free electron per atom. The drift speed of the free electrons in the wire will be (Density of metal = 5 x 103 kg/m3, atomic weight = 60)
(a) 5 x 10-3 m/s
(b) 2 x 10-3 m/s
(c) 4 x 10-3 m/s
(d) 7.5 x 10-3 m/s
Correct Answer is option (b)
According to Avogadro's hypothesis
Hence total number of atoms
As I = ne eA vd
Hence drift velocity vd = I/neeA
Q.16. A 10-km-long underground cable extends east to west and consists of two parallel wires, each of which has resistance 13Ω /km. A short develops at distance x from the west end when a conducting path of resistance R connects the wires (figure). The resistance of the wires and the short is then 100Ω when the measurement is made from the east end, 200Ω when it is made from the west end. What is value of R (in ohm).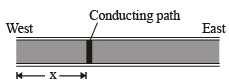
 (a) 20 Ω
(a) 20 Ω
(b) 25 Ω
(c) 30 Ω
(d) 35 Ω
Correct Answer is option (a)
13(2x) + R = 200
13(2 (10 – x)) + R = 100
260 + 2R = 300
R = 20Ω
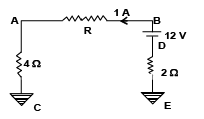
Q.17. Referring to the adjoining circuit, which of the following is/are true?
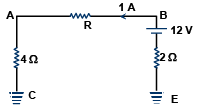 (a) R = 80 ohms
(a) R = 80 ohms
(b) R = 6 ohms
(c) R = 10 ohms
(d) Potential difference between points A and E is 2 V
Correct Answer is option (b)
As current is 1 A
VAC = 4 x 1 = 4V
As Vc = 0
∴ VA = 4 V
VED = 2 x 1 = 2V, ∴ VD = - 2V
∴ VB = 10 V
VBA = 10 – 4 = 6 V
R = 6/1 = 6 Ω
Q.18. For the circuit shown, which of the following statements is true?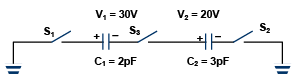 (a) With S1 closed, V1 = 1 5 V, V2 = 20 V
(a) With S1 closed, V1 = 1 5 V, V2 = 20 V
(b) With S3 closed V1 = V2 = 25V
(c) With S1 and S2 closed, V1 = V2 = 0
(d) With S1 and S3 closed, V1 = 30 V, V2 = 20 V
Correct Answer is option (d)
Let us consider the first alternative. When switch S1 is closed the charge on plate 2 will not change because this plate remains isolated. Hence the bound charge on plate will not change.
Thus the potential difference across C1 will remains same. Similarly when S3 is closed V1 and V2 do not change.
When S1 and S2 are closed, the charge on plates 2 and 3 will not change.
Thus V1 and V2 remain the same.
With S1 and S3 closed, the charge on the plate 4 will remain the same. So, the bound charges on plates will not change. Hence V1 and V2 remain the same.
Q.19. If a copper wire is stretched to make it 0.1% longer, the percentage change in its resistance is
(a) 0.2% increase
(b) 0.2% decrease
(c) 0.1% increase
(d) 0.1% decrease
Correct Answer is option (a)
For a given wire, R = ρL/s
with L x s = volume = V = constant
= 0.2 % (increase).
Q.20. In the given circuit, the resistance R has a value that depends on the current. Specifically, R is 20 ohms when I is zero and the increase in resistance (in ohms) is numerically equal to one-half of the current in amperes. What is the value of current I in the circuit?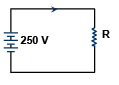 (a) 8.33 amp
(a) 8.33 amp
(b) 10 amp
(c) 12.5 amp
(d) 18.5 amp
Correct Answer is option (b)
The value of resistor R in the circuit is
R = 20 + I/2 ;
I (20 + I/2) = 250
I2 + 4I – 500 = 0 ⇒ (I – 10) (I + 50) = 0
i.e. I = 10 amp.
|
481 docs|964 tests
|