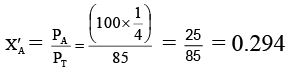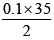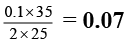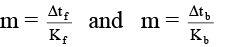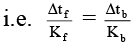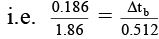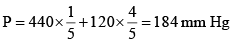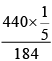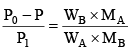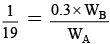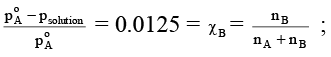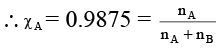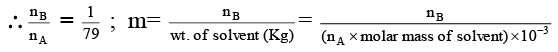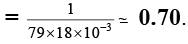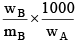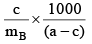JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Solutions | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. When FeCl3 reacts with K4[Fe(CN)6] in aqueous solution blue colour of ferri ferrocyanide, Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 is obtained. There are 0.1 M FeCl3 and 0.01 M K4[Fe(CN)6] solution are separated by a semi permeable membrane as shown and osmosis occurs then
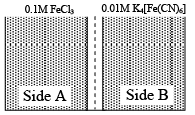 (a) blue colour is seen in side-B.
(a) blue colour is seen in side-B.
(b) blue colour is seen in side-A.
(c) blue colour is seen in both sides A and B.
(d) no blue colour is seen in either side.
Correct Answer is option (d)
During osmosis, solvent flows, not solute.
Q.2. If the freezing point of 0.1 molal HA (aq) is – 0.2046°C then pH of the solution is [kf (H2O) = 1.86° mol–1 kg ; assume molality = molarity]
(a) 1.7
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 1.3
Correct Answer is option (d)
0.2046 = (1 + α) x 1.86 x 0.1
⇒1 + α = 1.1 ⇒ α = 0.1
[H+] = C α = 0.1 x (0.1) = 10–2 (M)
pH = 2
Q.3. A mixture contains 1 mole of volatile liquid A (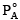 = 100 mm Hg) and 3 moles of volatile liquid B(
= 100 mm Hg) and 3 moles of volatile liquid B(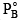 = 80 mm Hg). If solution behaves ideally, the total vapour pressure of the distillate is
= 80 mm Hg). If solution behaves ideally, the total vapour pressure of the distillate is
(a) 85 mm Hg
(b) 85.88 mm Hg
(c) 90 mm Hg
(d) 92 mm Hg
Correct Answer is option (b)
Total pressure of a mixture of 2 volatile liquids is given by
PTotal == (25 + 60) = 85 mm Hg
Mole fraction of A in the vapour phase (X'A) is given by
X'B = 0.706
These mole fractions will go into the distillate. The total vapour pressure of the distillate would be= (100 x 0.294) + (80 x 0.706)
= (29.4 + 56.48) = 85.88 mm Hg.
Q.4. The correct relationship between the boiling points of very dilute solutions of AlCl3(T1), and CaCl2(T2) having the same molar concentrations is
(a) T1 = T2
(b) T1> T2
(c) T2 > T1
(d) T2 ≥ T1
Correct Answer is option (b)
Q.5. Which one of the following solutions in water will have the highest freezing point?
(a) Solution which is 0.1 M in KNO3 and 0.2 M in Ba(NO3)2.
(b) Solution which is 0.1 M in Ca(NO3)2 and 0.1 M Ba(NO3)2.
(c) Solution which is 0.2 M in urea and 0.2 M glucose.
(d) Solution which is 0.1 M both in Al2(SO4)3 and 0.1 M K2SO4.
Correct Answer is option (c)
Q.6. A 0.6% (W/V) urea solution would be isotonic with
(a) 0.1 M glucose solution.
(b) 1 M urea solution.
(c) 0.6% (W/V) glucose solution
(d) 0.6% (W/V) NaCl solution.
Correct Answer is option (a)
On converting 0.6% (w/v) into molarity we will get, 0.1M, which is same as that of glucose solution.
Q.7. Two solutions of a substance (non electrolyte) are mixed in the following manner. 480 ml of 1.5 M of solution
(I). is mixed with 520 ml of 1.2 M of solution
(II). The molarity of final solution is
(a) 1.20 M
(b) 1.50 M
(c) 1.344 M
(d) 2.70 M
Correct Answer is option (c)
M × V = M1V1 + M2V2
M × (480 + 520) = 1.5 × 480 + 1.2 × 520
M × 1000 = 1344
M = 1.344
Q.8. 25 ml of a solution of barium hydroxide on titration with 0.1 M solution of HCl gave a titre value of 35 ml. The molarity of Ba(OH)2 is
(a) 0.28 M
(b) 0.35 M
(c) 0.07 M
(d) 0.14 M
Correct Answer is option (c)
Ba(OH)2 + 2HCl → BaCl2 + 2H2O
M × 25 =
M =
Q.9. 100 ml aqueous solution (I) containing 0.0365 g of HCl and 400 ml of 10–2 M aqueous solution (II) of Cl– ions are mixed. The molarity of Cl– ions in resulting solution is
(a) 10–3 M
(b) 10–4 M
(c) 10–2 M
(d) 10–1 M
Correct Answer is option (c)
Moles of HCl in 100 ml solution (I) == 10–3 moles
= moles of Cl– ions.
Number of moles of Cl– ions in solution (II) = 400 × 10–2 × 10–3 = 4 × 10–3 moles
Moles of Cl– ions in resulting solution = 4 × 10–3 + 10–3 = 5 × 10–3
Molarity of Cl– ions in resulting solution == 10–2 M.
Q.10. Freezing point of an aqueous solution is –0.186°C. Elevation of boiling point of same solution would be (Kb = 0.512 K molality–1 and Kf = 1.86 K molality–1)
(a) 0.186°C
(b) 0.0512°C
(c) 0.092°C
(d) 0.237°C
Correct Answer is option (b)
Δtf = Kf × m, Δtb = Kb × m
⇒
i.e. Δtb = 0.0512°C
Q.11. A solution has a 1: 4 mole ratio of pentane to hexane. The vapour pressure of the pure hydrocarbons at 20ºC are 440 mm Hg for pentane and 120 mm Hg for hexane. The mole fraction of pentane in the vapour phase would be:
(a) 0.786
(b) 0.549
(c) 0.478
(d) 0.200
Correct Answer is option (c)
(Xpentane)vapour phase =
= 0.478 mm Hg.
Q.12. Which one of the following equimolal aqueous solutions will have maximum freezing point? (Assume equal ionisation in each case)
(a) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
(b) [CrCl(H2O)5]Cl2 H2O
(c) [CrCl2 (H2O)4] Cl 2H2O
(d) [Fe(H2O)3 Cl3] 3H2O
Correct Answer is option (d)
Higher the value of i, lower will be the freezing point of the solution.
Q.13. The VP of a solvent decreased by 10 mm of Hg when a non-volatile solute was added to the solvent. The mol fraction of the solute in the solution is 0.2. What should be the mol fraction of solvent, if the decrease in VP is to be 20 mm of Hg?
(a) 0.8
(b) 0.6
(c) 0.4
(d) 0.2
Correct Answer is option (b)
Kf is characteristic constant for given solvent.
Q.14. Which of the following statement is true for aqueous solution of 0.1 M urea, 0.2 M glucose and 0.3 M sucrose
(a) The vapour pressure and freezing point are the lowest for urea.
(b) The vapour pressure and boiling point are the lowest for urea.
(c) The depression in freezing point is the highest for urea.
(d) The elevation in boiling point is the highest for urea.
Correct Answer is option (b)
Q.15. The vapour pressure of a solution of a non-volatile solute B in a solvent A is 95% of the vapour pressure of the solvent at the same temperature. If the molecular weight of the solvent is 0.3 times the molecular weight of the solute, what is the weight ratio of solvent to solute?
(a) 7.5
(b) 5.7
(c) 3.6
(d) 6.3
Correct Answer is option (b)
From Raoult’s law,
or,
∴ WA/WB = 0.3 × 19 = 5.7.
Q.16. Relative lowering of vapour pressure of an aqueous solution containing non-volatile solute is 0.0125. Molality of the solution is
(a) 0.4
(b) 0.5
(c) 0.6
(d) 0.7
Correct Answer is option (d)
Q.17. Which of the following represents the correct order of decreasing freezing point?
(a) 0.05 M KNO3> 0.04 M CaCl2> 0.140 M glucose > 0.075 M CuSO4.
(b) 0.04 M CaCl2> 0.14 M Sucrose > 0.075 M CuSO4> 0.05 M KNO3.
(c) 0.075 M CuSO4> 0.14 M Sucrose > 0.04 M BaCl2> 0.05 M NaNO3.
(d) 0.075 M CuSO4> 0.05 M NaNO3> 0.14 M Sucrose > 0.04 M BaCl2.
Correct Answer is option (a)
ΔTf = Tsolvent- Tsolution = Kf × mobserved.
Greater the value of mobserved, lower is the Tsoluton.
In option (a), the correct order would have been(assuming 100% dissociation for each salt)
0.05 M KNO3> 0.04 M CaCl2> 0.14 M glucose > 0.075 M CuSO4.
Q.18. When mercuric iodide is added to the aqueous solution of potassium iodide, the
(a) freezing point is raised.
(b) freezing point does not change.
(c) freezing point is lowered.
(d) boiling point does not change.
Correct Answer is option (a)
2KI + HgI2→ K2[HgI4] ⇌ 2K+ + [HgI4]2–
Thus, there is net decrease in number of ions present in solution and freezing point is raised.
Q.19. A 0.001 molal solution of Pt(NH3)4Cl4 in water had a freezing point depression of 0.0054°C. If Kf for water is 1.80, the correct formula for the above compound assuming its complete dissociation is
(a) [Pt(NH3)4Cl3]Cl
(b) [Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Cl2
(c) [Pt(NH3)4Cl]Cl3
(d) [Pt(NH3)4Cl4]
Correct Answer is option (b)
ΔTf = i × Kf × m0.0054 = i × 1.80 × 0.001
i = 3
i = 1 + (n - 1)α
n = 3
The correct formula of the compound is [Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Cl2
Q.20. A solution weighing a gm has molality b. The molecular mass of solute if the mass of solute is c gm, will be:
(a) 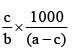
(b) 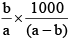
(c) 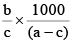
(d) 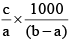
Correct Answer is option (a)
Molality =
b =
mB =
|
446 docs|929 tests
|