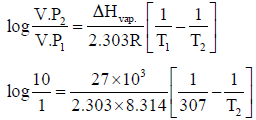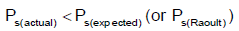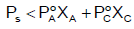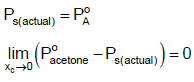JEE Advanced (One or More Correct Option): Solutions | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. In which of the following is/are in correct order
(a) HI > HBr > HCl > HF (acidic strength in solution phase)
(b) HF > HCl > HBr > HI (acidic strength in vapour phase)
(c) HF < HCl < HBr < HI (acidic strength in vapour phase)
(d) HI < HBr < HCl < HF (acidic strength in solution phase)
Correct Answer is option (a and b)
HI is strongest acid in solution phase and HF is strongest acid in vapour phase.
HF forms strong inter molecular H-bonding in solution phase which decreases the H+ ion concentration.
Q.2. The normal boiling point of ether is 307 K. Ether is to be stored in aluminium drum that can withstand a pressure of 10 atm. If the enthalpy of vapoursiation of ether is 27 kJ mol–1 at 307K, the temperature to which the drum of ether could be safely exposed is
(a) 290 K
(b) 317K
(c) 390 K
(d) 428 K
Correct Answer is option (a, b and c)
On solving we get T2 = 392K
The maximum temperature to which drum can be exposed safely = 392K
Q.3. A solution is made of 162 g of HBr in 500 g water. Assume that the acid is 90% ionized. The freezing point constant for water is –1.86°/mol. The incorrect statements are
(a) the number of moles of HBr is 2
(b) the molality is 4m
(c) the effective molality after ionization is 7.6 m
(d) the freezing point of water lowered by 14.1°
Correct Answer is option (a, c and d)
A solution is made of 162 g of HBr in 500 g water.
Assume that the acid is 90% ionized. The freezing point constant for water is 1.86°/mol. The correct statements are(a) the number of moles of HBr is 2
(b) the molality is 4m
(c) the effective molality after ionization is 7.6 m
(d) the freezing point of water lowered by 14.1°.
Q.4. Which of the following statements is/are true about an azeotropic mixture?
(a) An azeotropic mixture boils at constant temperature
(b) The composition of an azeotropic mixture changes on distillation
(c) An azeotropic solution of two liquids has a boiling point lower than that of either of them when it shows positive deviation from the Raoult’s law
(d) An azeotropic solution of two liquids has a boiling point higher than that of either of them if it shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law
Correct Answer is option (a and c)
Azeotropic mixtures are constant boiling mixtures that boil at constant temperature and its boiling point is less than the boiling point of the components.
Hence, (a) and (c) are correct answers.
Q.5. Which statement(s) is/are correct about osmotic pressure (P), volume (V) and temperature (T)?
(a) P ∝ 1 / V if T is constant
(b) P ∝ T if V is constant
(c) P ∝ V if T is constant
(d) PV is constant if T is constant
Correct Answer is option (a, b and d)
PV = nRT if n = 1, PV = RT where R is constant, hence PV ∝ T or P ∝ (T/V)
Hence, (A), (B) and (D) are correct answers.
Q.6. Which inorganic precipitate(s) acts(s) as semipermeable membrane?
(a) Calcium phosphate
(b) Barium oxalate
(c) Nickel phosphate
(d) Copper ferrocyanide
Correct Answer is option (a and d)
Calcium phosphate and copper ferrocyanide are used to prepare semipermeable membrane.
Hence, (A) and (D) are the correct answers.
Q.7. When common salt is dissolved in water, the
(a) partial pressure of the solution decreases
(b) melting point of the solution increases
(c) boiling point of the solution increases
(d) vapour pressure of the solution decreases
Correct Answer is option (c and d)
When one mole of NaCl is dissolved in water it ionizes to give one mole Na+ and Cl- ions each. Hence number of moles in the solution increases which affects the colligative properties. Hence, (C) and (D) are the correct answers.
Q.8. If P0 & Ps be the vapour pressure of solvent and its solution respectively and N1 and N2 be the mole-fractions of solvent and solute respectively, then:
(a) PS = P0.N2
(b) P0 = Ps = P.N2
(c) PS = P0N1
(d) 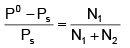
Correct Answer is option (a and b)
According to Raoult’s Laws
Vapour pressure of solution = V.P. of solvent X solvent
W1 PS =P°
∴ PS =P° (1–N2) ∴ N1 + N2 = 1
W1 P° – PS = PSN2
∴ (A) and (B)
Q.9. Which one of the following pairs of solution will be isotonic at the same temperature?
(a) 1 M NaCl & 2 M – Urea
(b) 1 M CaCl2 & 1.5 M – KCl
(c) 1.5 M AlCl3 & 2 M Na2SO4
(d) 2.5 M KCl and 1 M – Al2(SO4)3
Correct Answer is option (a, b, c and d)
For (A)
1M NaCl solution (i x Cm) = 2 x 1M = Cm = Molarity
2M orea solution (i x Cm) = 2M
1M CaCl2 solution (i x Cm) = 3 x 1M = 3M
1.5 M KCl solution (i x Cm) = 2 x 1.5M = 3M
Similarly for 1.5 M AlCl3 and 2M Na2SO4
The value of i x Cm be 6 and 2.5 M KCl and 1M
Al2(SO4)3 has 5 M each.
So, the each pair of solution A,B,C and D have same concentration so, all pairs of solution be isotomic,
∴ A, B, C and D
Q.10. For a solution of chloroform and acetone if PS (actual) is compared with PS (Raoult) then which of the following is/are true?
(a) Ps(actual) <Ps(Raoult)
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 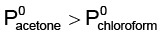 near room temperature
near room temperature
Correct Answer is option (a, b, c and d)
A solution of chloroform and acetone shows negative deviation. Thereby, actual vapor pressure of solution will be less than the expected vapor pressure of solution.
(a)
(b) Although,
But as XC → 0 , solution will have almost pure acetone and hence, XA → 1
(c) Similar to (b)
(d) Acetone is more volatile than chloroform due to relatively weaker intermolecular forces of attraction in acetone than that in chloro-form.
|
481 docs|964 tests
|