Introduction
- Carbon is probably the most important compound in the whole periodic table, versatile for everything and the forming basics of every chemical science. With the help of this tetravalent and unique compound, the Wurtz–Fittig reaction was discovered.
- In the year 1855, Charles Adolphe Wurtz found the reaction called the Wurtz reaction. The reaction involved a new carbon–carbon which is followed up by a coupling reaction between two alkyl halides.
- This was further extended by another scientist, Wilhelm Rudolph Fitting, in the year 1860. Hence, the reaction is later known as the Wurtz–Fittig reaction.
- Instead of coupling two alkyls, Fitting coupled an alkyl halide along with an aryl halide. The reaction best works for asymmetric products. It is one of the important reactions of organic chemistry which is used to synthesise carbon–carbon bonds.
- Aryl halide reacts with alkyl halide with sodium metal in presence of dry ether to form alkyl substituted benzene.
- In this reaction, ethane and biphenyl are also formed in small amounts.
What is Wurtz–Fittig Reaction?
The reaction of an alkyl halide with aryl halide and sodium metal in presence of dry ether to form substituted aromatic compounds by the formation of new carbon–carbon bond is called Wurtz–Fittig reaction. The reaction is given below – It is a coupling reaction. It is a modified form of Wurtz reaction. Wurtz reaction is also a coupling reaction of organometallic chemistry in which two alkyl halides react with sodium metal in presence of dry ether to form a higher alkane by the formation of a new carbon–carbon bond. Wurtz Reaction is given below –
2R – X + 2Na → R – R + 2NaX
Where R = alkyl group
X = Halide ion
Wurtz–Fittig reaction is best for the formation of asymmetrical products if halide reactants are different in their relative chemical reactivities. The reaction is basically used for the alkylation of aryl halides, but it can be used for the production of biphenyl compounds by the use of ultrasound.
Fitting Reaction
- Wurtz–Fittig reacts in two different ways. The first one is the one which is described as above and the other one can be defined as stated below:
- When two molecules of aryl halide react with sodium metal in presence of dry ether to form diphenyl.
- Except for sodium, many other metals can also be used in order to give rise to similar products. This includes potassium, iron, copper, and lithium. While using lithium, the reaction needs ultrasound presence, in order to obtain the product.
Mechanism of Wurtz–Fittig Reaction
- In order to understand the Wurtz–Fittig reaction, let us take an example.
- Consider the following generic reaction.
- In this reaction, sodium metal reacts separately with two types of halide to form aryl sodium and alkyl sodium.
- The more reactive alkyl halide forms an organo sodium first, and this reacts as a nucleophile with an aryl halide.
- Mechanism of Wurtz–Fittig reaction is not certain as there are two approaches available to describe the mechanism of Wurtz–Fittig reaction and empirical evidence are available for both approaches. Both the approaches are listed below –
- Radical mechanism
- Organo-alkali mechanism
1. Radical Mechanism
The radical approach involves the sodium-mediated aryl radical and alkyl radical formation. According to this mechanism, sodium metal acts as a mediator and the formation of an alkyl radical and aryl radical takes place. Then, alkyl radical and aryl radical combine to form a substituted aromatic compound. This mechanism is supported by the formation of side products which cannot be explained by the organo-alkali mechanism. For example, Bachmann and Clarke found that in the reaction of sodium and chlorobenzene, one of the many side products is triphenylene whose formation can be explained by free radical mechanism only.
2. Organo-Alkali Mechanism
The organo-alkali approach involves the formation of an intermediate organo – alkali compound by reaction of an aryl halide with sodium metal. According to this approach, first aryl halide reacts with sodium metal and forms an organo-alkali compound, then nucleophilic attack of alkyl halide takes place. This mechanism is supported by indirect evidence such as many investigators observed that an organo-alkali intermediate is actually formed during the reaction.
Use of Other Metal in Place of Sodium
Wurtz–Fittig reactions can be carried out using other metals such as copper, iron, potassium, and lithium than sodium metal. When we use lithium in place of sodium, the reaction gives an appreciable yield, but the reaction takes place only under ultrasound. It takes place by a free radical mechanism.
Wurtz Reaction, Fittig Reaction, and Wurtz–Fittig Reaction
Generally, students get confused between Wurtz reaction, Fittig reaction, and Wurtz–Fittig reaction. So, we are giving here a comparative study of all these three reactions in a tabular form.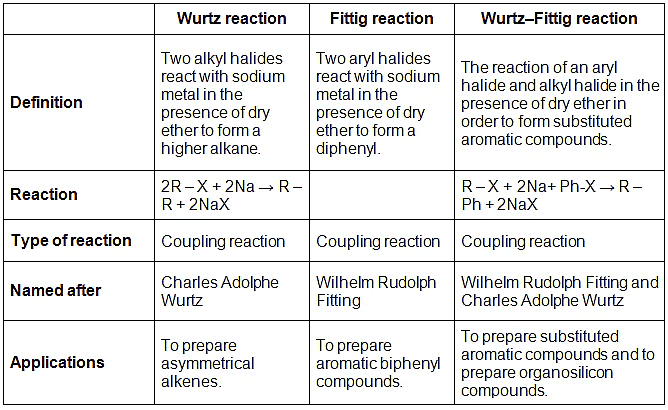
Applications of Wurtz–Fittig Reaction
- Wurtz–Fittig reaction is useful in the laboratory for the synthesis of organosilicon compounds. For example, t-butyl trimethoxysilane can be prepared by Wurtz–Fittig reaction. In this 40% yield is obtained.
- Applications of Wurtz–Fittig reactions are limited. It is not used at a large scale for industrial purposes. However, it is useful in the laboratory synthesis of substituted aromatic compounds.
- The reaction doesn't have many applications. This is because of the side reaction, which further undergoes rearrangement and elimination. This is one of the major limitations of this reaction making it unsuitable for many production processes.
- The production of organosilicon is done using this particular reaction although it is quite a big challenge to overcome the production in a larger quantity.


















