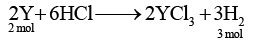JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Coordination Compounds | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. A coordination complex’s core atom/ion is also known as ________
(a) Bronsted-Lowry acid
(b) Lewis base
(c) Lewis acid
(d) Bronsted-Lowry base
Correct Answer is option (c)
A Lewis acid is a species that has the ability to receive an electron pair. Lewis acids are all cations. It is a Lewis acid because the core atom of a coordination complex is metal and always accepts electrons.
Q.2. The reaction between yttrium metal Y and dilute hydrochloric acid produces H2(g) and Y3+ ions. The molar ratio of yttrium used to hydrogen produced is
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 1 : 3
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 2 : 3
Correct Answer is option (d)
Q.3. Which of the following has a coordination number as a feature?
(a) Coordination entity
(b) Ligand
(c) Central atom
(d) Coordination compound
Correct Answer is option (c)
The coordination number of a central metal ion in a complex, also known as the secondary valency, is defined as the number of donor atoms it is directly bound to. As a result, the coordination number is a quantity related to the metal ion.
Q.4. In Fe(CO)5, the Fe—C bond possesses.
(a) π character only
(b) ionic character
(c) both σ and π character
(d) σ- character only
Correct Answer is option (c)
In metal carbonyl organometallic compounds the bond between metal atom and carbon monoxide ligand has both σ and π characters.
Q.5. Which of the following statements about coordination compounds’ bonding is incorrect?
(a) Crystal Field Theory
(b) VSEPR Theory
(c) Valence Bond Theory
(d) Molecular Orbital Theory
Correct Answer is option (b)
The VSEPR Theory uses electron pairs in atoms to explain the structure of particular molecules. The theories VBT, CFT, LFT, and MOT explain the nature of bonding in coordination compounds.
Q.6. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) HgSO4 is used as a catalyst in converting acetylene to acetaldehyde.
(b) ZnSO4.7H2O on strong heating gives ZnO with the liberation of SO2 and O2.
(c) ZnSO4.7H2O on heating at 373K gives ZnSO4.2H2O.
(d) On sublimation, black variety of HgS changes to red variety.
Correct Answer is option (c)
ZnSO4.7H2OZnSO4.H2O
ZnSO4.
Q.7. More than one sort of hybridization can occur in a complex with geometry.
(a) tetrahedral
(b) octahedral
(c) trigonal bipyramidal
(d) square planar
Correct Answer is option (b)
Depending on whether the outer or inner d orbitals are engaged in hybridisation, complexes with octahedral geometry can have either sp3d2 or d2sp3 hybridisation.
Q.8. Amongst the following complexes, select the one having highest magnetic dipole moment.
(a) [Cr (H2O)6]3+
(b) [Fe (H2O)6]2+
(c) [Cu (H2O)6]2+
(d) [Zn (H2O)6]2+
Correct Answer is option (b)
Because Fe2+ has four unpaired electrons.
Q.9. Determine which of the following statements about VBT is inaccurate.
(a) It does not explain the colour of coordination compounds
(b) It can distinguish between strong and weak ligands
(c) It does not explain the kinetic stabilities of coordination compounds
(d) It is unreliable in the prediction of geometries of 4-coordinate complexes
Correct Answer is option (b)
One of VBT’s flaws is that it can’t tell the difference between weak and powerful ligands. Other options have their own set of drawbacks.
Q.10. The co-ordination number and oxidation state of Cr in K3[Cr(C2O4)3] are respectively
(a) 6 and +3
(b) 3 and 0
(c) 4 and +2
(d) 3 and +3
Correct Answer is option (a)
Co-ordination number of Cr3+ ion is six because chromium ion is surrounded by three bidentate ligands.For oxidation state of central metal ion 3 + x – 6 = 0
[where, x is the oxidation state of central metal ion]
Q.11. Which of the following determines the position of ligands in a mononuclear coordination entity’s formula?
a) Atomicity of the ligand
b) Charge on the ligand
c) The first letter in the name of the ligand
d) Denticity of the ligand
Correct Answer is option (c)
The alphabetical order of the ligands in the formula of mononuclear coordination entities, including shortened ligands, is used. It is independent of the ligand’s atomicity, denticity, or charge.
Q.12. Which of the following statements about a charged coordinating entity is correct?
(a) The sign of the charge is written after the number
(b) The charge of the complex ion is written in parenthesis while naming the entity
(c) The charge is indicated as a subscript outside the square bracket on the right
(d) The charge on the complex ion is depicted along with the counter ion
Correct Answer is option (a)
The charge of a coordination entity is written outside the square brackets on the right side as a superscript with the number before the sign of charge, without the existence of the counter ion.
Q.13. Which of the following compounds is expected to exhibit optical isomerism? [en = ethylenediamine]
(a) cis-[Co(en)2Cl2]
(b) cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
(c) trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]
(d) trans-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
Correct Answer is option (a)
Compound ‘a’ does not have any element of symmetry and thus exhibit optical isomerism.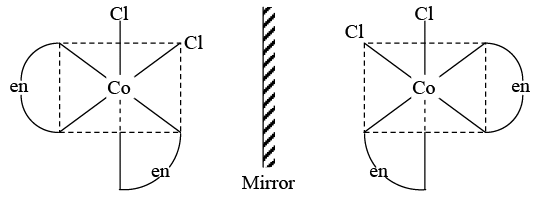
Q.14. Hybridization of Fe in K3[Fe(CN)6] is
(a) sp3
(b) d2sp3
(c) sp3d2
(d) dsp3
Correct Answer is option (a)
In the given complex of Fe3+, as the co-ordination number is ‘6’, there are two possibilities. It can be d2sp3 or sp3d2. But the ligand attached with central metal ion, Fe3+, is strong field ligand so it will promate inner orbital complex, d2sp3.
Q.15. Determine the proper name for K2[PdCl4].
(a) Potassium tetrachlorinepalladium(II)
(b) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II)Potassium
(c) Potassium tetrachloridopalladium(II)
(d) tetrachlorinepalladate(II)
Correct Answer is option (b)
Because Cl is an anionic ligand, it has the suffix -o, therefore chlorido. Furthermore, because the complex ion is anionic, the metal must end in -ate, so palladate.
Q.16. Which substance is used to determine the hardness of water using a simple titration?
(a) Mg(EDTA)
(b) Fe(EDTA)
(c) Na2(EDTA)
(d) Co(EDTA)
Correct Answer is option (c)
With EDTA, the ions Ca2+ and Mg2+ form stable complexes, and the difference in the stability constants of the Ca and Mg complexes aids in the assessment of water hardness.
Q.17. Transition metal compounds are usually coloured. This is due to the electronic transition
(a) from p orbital to s-orbital
(b) from d orbital to s-orbitals
(c) from d orbital to p-orbital
(d) within the d-orbitals
Correct Answer is option (d)
Many ionic and covalent compounds of transition elements are coloured and this colouring property is due to d—d electronic excitation. The colour of the compound is complimentary to the colour absorbed.
Q.18. A compound has an empirical formula CoCl3.5NH3. When an aqueous solution of this compound is mixed with excess of silver nitrate, 2 moles of AgCl precipitates per mole of the compound. On reaction with excess of HCl, no 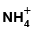 is detected. Hence the compound is
is detected. Hence the compound is
(a) [Co(NH3)5Cl2]Cl
(b) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
(c) [Co(NH3)5Cl3]
(d) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl.NH3
Correct Answer is option (b)
As the moles of AgCl precipitated is 2 and nois detected on reaction with excess of HCl, so the compound would be [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2.
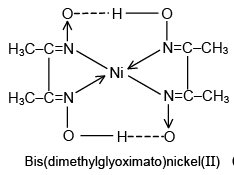
Q.19. The IUPAC name of the complex [Ni(C4H7O2N2)2] formed from the reaction of Ni2+ with dimethyl glyoxime is
(a) Bis(methylgloxal)nickel(II)
(b) Bis(dimethyloxime)nickelate(IV)
(c) Bis(2,3-butanedioldioximato)nickel(II)
(d) Bis(2,3-butanedionedioximato)nickel(II)
Correct Answer is option (d)
Bis(2,3-butanedionedioximato)nickel(II)
Q.20. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) [Co(NH3)6]2+ is oxidized to diamagnetic [Co(NH3)6]3+ by the oxygen in air.
(b) [Fe(CN)6]3- is stable but [FeF6]3- is unstable.
(c) [NiCl4]2-is unstable with respect to [NiBr4]2-.
(d) None of these.
Correct Answer is option (a)
With the promotion of one 3d-electron to 5s or 4d, it becomes loosely bonded to the nucleus and hence, it may easily be removed and so, Co(II) will easily be oxidised into Co(III).
|
446 docs|929 tests
|