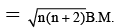JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): d & f Blocks | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. As an electroplated protective covering, what metal is used?
(a) Plutonium
(b) Chromium
(c) Nickel
(d) Iron
Correct Answer is option (b)
Chrome plating (or chromium plating, as it’s more generally known) is the process of electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal item. The chromed coating might be attractive, provide corrosion protection, make cleaning easier, or increase the hardness of the surface.
Q.2. As we proceed from left to right in groups, what happens to the non-metallic nature?
(a) Remains constant
(b) Decreases
(c) Increases
(d) Irregular
Correct Answer is option (c)
The 18th group has no reactivity, but its non-metallic character is defined as a tendency to gain electrons, resulting in significant negative electron gain enthalpies. So the non-metallic nature increases from left to right in groups leaving noble gases.
Q.3. Select the appropriate statement.
(a) Both actinoids and lanthanoids are less basic
(b) Both actinoids and lanthanoids are electropositive
(c) Both actinoids and lanthanoids do not exhibit magnetic and spectral properties
(d) Both actinoids and lanthanoids do not show same oxidation of +3
Correct Answer is option (b)
In many ways, lanthanides and actinides are similar since they both entail the filling of f-orbitals. For both lanthanides and actinides, the most frequent oxidation state is +3. Both are electropositive and, as a result, very reactive. Both lanthanides and actinides have magnetic and spectroscopic characteristics.
Q.4. Which of the following is not a lanthanide property?
(a) They are soft metals with a white silvery colour
(b) They tarnish rapidly by air
(c) The hardness of the metals increases with increase in the atomic number
(d) The melting point of the metal ranges from 500-1000K
Correct Answer is option (d)
Lanthanides are soft metals that are silvery and white in appearance. They discolour quickly when exposed to air. As the atomic number of these metals rises, so does their ability to be harnessed. Lanthanides have melting points ranging from 1000 to 1200 degrees Celsius, whereas samarium melts at 1623 degrees Celsius.
Q.5. Baeyer’s reagent is which of the following?
(a) Acidified KMnO4
(b) Aqueous KMnO4
(c) Acidified K2Cr2O7
(d) Alkaline KMnO4
Correct Answer is option (d)
Baeyer’s reagent is an alkaline KMnO4 solution. This shows a redox reaction because Baeyer’s reagent is an alkaline solution of cold potassium permanganate, which is a potent oxidant. The colour of an organic material fades from purplish-pink to brown as it reacts with double or triple bonds (-C=C- or -CC-). It’s a reaction of synergistic addition.
Q.6. __________ possesses the properties of both alkali metals and halogens.
(a) Helium
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Sodium
(d) Chlorine
Correct Answer is option (b)
Because hydrogen’s outer shell configuration (that is 1s1) contains only one electron in the s-orbital, it qualifies as an Alkali metal. A noble gas structure, which is a feature of halogen, can be obtained with only one electron.
Q.7. Which of the following statements concerning transuranium elements is incorrect?
(a) Atomic number > 92
(b) Example is Thorium
(c) Decay radioactively as they are unstable
(d) Elements after Uranium
Correct Answer is option (b)
Transuranium elements are those that come after Uranium (Z = 92), are unstable, and decay radioactively into other elements. However, because Thorium has an atomic number of 90, it is not a transuranium element.
Q.8. What happens to the atomic size of lanthanides as the atomic number increases?
(a) The radius remains unchanged
(b) The radius first increases and then decreases
(c) The radius increases
(d) The radius decreases
Correct Answer is option (d)
Lanthanide contraction is the steady decrease in the atomic and ionic radii of lanthanides as the atomic number increases. It happens because the 4f electrons have a weak shielding effect.
Q.9. What is the lanthanide’s final element?
(a) Ytterbium
(b) Erbium
(c) Thulium
(d) Lutetium
Correct Answer is option (d)
Erbium, Thulium, Ytterbium, and Lutetium have atomic numbers of 68, 69, 70, and 71, respectively. Lutetium, the final element in the lanthanide family, has the electrical configuration [Xe]4f145d16s2.
Q.10. AgCl fails to pass which of the following tests?
(a) Alkaline test
(b) Acidic test
(c) Chromyl chloride test
(d) Baeyer’s reagent test
Correct Answer is option (c)
The presence of Cl– ions is detected using the chromyl chloride assay. Silver, lead, mercury, and antimony chlorides are covalent in nature and do not produce Cl– ions, hence they do not pass the chromyl chloride test. Heavy metal chlorides, on the other hand, do not pass this test because they are not ionic.
Q.11. A magnetic moment of 1.73 B.M. will be shown by one of the following compounds.
(a) [Cu(NH3)4]2+
(b) [NI(CN)4]2-
(c) TiCl4
(d) [CoCl6]-4
Correct Answer is option (a)
Since magnetic moment.
Where n = 1 = no. of unpaired electron
Thus n = 1 for Cu2+
Q.12. A light green coloured salt soluble in water gives black ppt. on passing H2S which dissolves readily in HCl. The metal ion present is:
(a) Co2+
(b) Fe2+
(c) Ni2+
(d) Mn2+
Correct Answer is option (b)
FeS soluble in HCl also Fe2+ salts are green.
Q.13. Lead poisoning in the body can be removed by:
(a) EDTA in the form of calcium dihydrogen salt
(b) cis-platin
(c) DMG
(d) Zeisse’s salt
Correct Answer is option (a)
EDTA is very strong chelating agent and it forms stable chelate with Pb (II).
Q.14. The acid anhydride of permanganic acid is
Which equation does not involve the reduction of a transition metal compound?
(A) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
(B) TiO2 + 2C + 2Cl2 → TiCl4 + 2CO
(C) Cr2O3 + 2Al → 2Cr + Al2O3
(D) TiCl4 + 4Na → Ti + 4NaCl
Correct Answer is option (b)
No change in oxidation number takes place.
Q.15. Chemical volcano is produced on heating
(a) K2Cr2O7
(b) (NH4)2Cr2O7
(c) ZnCr2O7
(d) K2CrO4
Correct Answer is option (b)
On heating (NH4)2Cr2O7, N2 is given out with Cr2O3 produced at higher rate giving look of artificial volcano.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|