Single Correct MCQs: Biomolecules | Question Bank for JEE Main & Advanced (350+ Tests) PDF Download
Q.1. A disaccharide is formed when two monosaccharides are bonded together by a bond.
(a) glycosidic
(b) peptide
(c) ionic
(d) phosphodiester
Correct Answer is option (a)
When two monosaccharide units come together, they lose a molecule of water and form an oxide bond. The glycosidic linkage is a bond formed by an oxygen atom between two monosaccharide molecules.
Q.2. Sucrose is a ______ chemical, and the hydrolysis product combination is ______ in nature.
(a) dextrorotatory; dextrorotatory
(b) laevorotatory; laevorotatory
(c) laevorotatory; dextrorotatory
(d) dextrorotatory; laevorotatory
Correct Answer is option (d)
Sucrose is a dextrorotatory sugar that produces a combination of dextrorotatory glucose and laevorotatory fructose when hydrolyzed. The resultant mixture is laevorotatory because the specific rotation of fructose is larger than that of glucose.
Q.3. Kwashiorkar is caused by the deficiency of
(a) vitamins
(b) hormones
(c) amino acids
(d) essential amino acids
Correct Answer is option (d)
Essential amino acids are not synthesized by human body. These have to be supplied from outside in the diet. The lack of these amino acids causes kwashiorkor.
Q.4. Thymine is held by two hydrogen bonds with the base
(a) guanine
(b) cytosine
(c) adenine
(d) thymine
Correct Answer is option (c)
DNA contains adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), thymine (T) bases. But these is uracil (U) in place of thymine in case of RNA.
The pair of complimentary bases are,
A—T; A—U and G—C
Q.5. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) The phenomenon of mutarotatinreferes to the change in specific rotation of either of the two anomers in solution with time and attains a constant equilibrium value.
(b) Specific rotation of β-D glucose is +18.7º.
(c) Ring structures of sugars can be broken by periodic acid.
(d) α-D glucose in water attains a constant specific rotation of 112.2º.
Correct Answer is option (d)
The constant specific rotation in water with either α-Dglucose or β-D-glucose attain is +52.7º.
Q.6. Which of the following statements about maltose is incorrect?
(a) It consists of two glucopyranose units
(b) It is a disaccharide
(c) Glycosidic bond between C1 of one unit and C4 of the other unit
(d) It is a non-reducing sugar
Correct Answer is option (d)
The free aldehyde group, which has reducing capabilities, can be formed at the C1 carbon of the second -D-glucose unit in solution. As a result, it decreases sugar.
Q.7. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Proteins are polyamides formed from amino acids.
(b) Except glycine, all other amino acids show optical activity.
(c) Natural proteins are made up of L-isomers of amino acids.
(d) —NH2 and –COOH groups are attached to different carbon atoms in amino acids.
Correct Answer is option (d)
In amino acids, —NH2 and —COOH groups are attached to the same carbon atom.
Q.8. Which of the following statements about starch is incorrect?
(a) It gives blue colour with iodine
(b) It is a polymer of α-D-glucose
(c) It is a reducing carbohydrate
(d) It consists of branched chains
Correct Answer is option (c)
Because it does not decrease Fehling’s solution or Tollen’s reagent, starch is a non-reducing saccharide. This means that all hemiacetal hydroxyl groups of glucose units are linked by glycosidic bonds and are not free.
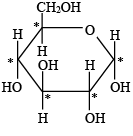
Q.9. What is the number of asymmetric carbon atoms present in a-D-glucopyranose molecule?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Five
Correct Answer is option (d)
The assymmetric C–atom of α(D) glucopyranose have been shown by (*).
Q.10. A sample of (D)–lactic acid was found to have an optical purity of 72%. How much (L)–isomer is present in the sample?
(a) 28%
(b) 50%
(c) 56%
(d) 14%
Correct Answer is option (d)
Sample have optically pure (D)–lactic acid as 72%, thus 28% is racemic lactic acid. 28% racemic mixture will contain 14% (L)–lactic acid.
Q.11. Diabetes is detected by testing urine of the patient with
(a) Brady’s reagent
(b) Nessler’s reagent
(c) Fenton’s reagent
(d) Benedict’s solution
Correct Answer is option (d)
Diabetes is due to disfunctioning of pancreas, which stops releasing insulin. Due to this sugar is not metabolized and thus, it is passed in the urine. Benedict’s test can detect the presence of sugar in the urine.
Q.12. RNA lacks the nitrogen base of _______.
(a) Thymine
(b) Cytosine
(c) Uracil
(d) Adenine
Correct Answer is option (a)
RNA contains the pyrimidine Uracil, whereas DNA contains Thymine. In RNA, Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Uracil, but in DNA, Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine.
Q.13. Lysine is an example of a polar but uncharged amino acid,
(a) Serine
(b) Aspartate
(c) Lysine
(d) Arginine
Correct Answer is option (a)
The amino acids Lysine and Arginine are polar and positively charged. Aspartate, on the other hand, is a polar and negatively charged amino acid. Serine is an uncharged, polar amino acid.
Q.14. Which of the following chemical classes does not belong to the vast group of carbohydrates?
(a) Polyhydroxy ketones
(b) Polyhalo aldehydes
(c) Polyamino aldehydes
(d) Polyhydroxy carboxylic acids
Correct Answer is option (a)
The OH group is absent from polyamino and polyhalo aldehydes. There is no CHO or keto group in polyhydroxy carboxylic acids. When they are hydrolyzed, they do not form OH substituted compounds.
Q.15. Which of the following statements about metabolism is false?
(a) It is due to this process that biomolecules do not have a turnover
(b) It involves the formation of biomolecules
(c) It involves the breaking down of biomolecules
(d) It involves various chemical reactions
Correct Answer is option (a)
Metabolism entails the breakdown of biomolecules as well as the creation of new ones. It entails a number of chemical processes. It is in charge of the biomolecule turnover.
Q.16. Consider following reagents, (I) Br2 water (II) Tollen’s reagent and (III) Fehling’s solution. Which reagent(s) can be used to make distinction between an aldose and a ketose?
(a) (I), (II) and (III)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) only
(d) (II) only
Correct Answer is option (c)
Br2 water oxidises aldose to corresponding acid and it get decolourised. Ketoses are not oxidised by Br2 water.
Q.17. The dipeptide, Gly.Ala has structure
(a) 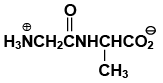
(b) 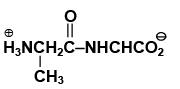
(c) 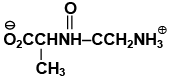
(d) 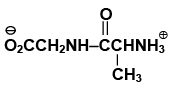
Correct Answer is option (a)
By convention, the amino acid with the free amino group (N-terminus) is written at the left end and the one with the unreacted carboxyl group (C-terminus) at the right end. Thus, the structure of Gly.Alais
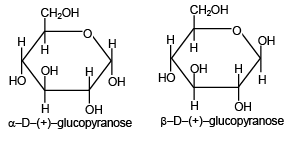
Q.18. The two forms of D-glucopyranose are
(a) epimers
(b) anomers
(c) enantiomers
(d) geometrical isomers
Correct Answer is option (a)
The a-D-(+)-glucopyranose and b-D-(+)-glucopyranose differ in their configuration at first chiral carbon atom. Such diastereomers are called anomers.
Q.19. Which pair of compounds gives Tollen’s test?
(a) Glucose & Fructose
(b) Sucrose & Glucose
(c) Hexanal & Acetophenone
(d) Fructose & Sucrose
Correct Answer is option (a)
Glucose being an aldehyde gives Tollen’s test while fructose, which is an a-hydroxy ketone, tautomerizes to glucose in basic medium. Hence, it would also give Tollen's test.
Q.20. Which one of the following statements is true for protein synthesis (translation)
(a) Amino acid are directly recognized by m-RNA
(b) The third base of the codon is less specific
(c) Only one codon codes for an amino acid
(d) Every t-RNA molecule has more than one amino acid attachment site.
Correct Answer is option (a)
In the process oftranslation amino acids are directly recognized by m-RNA.