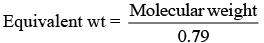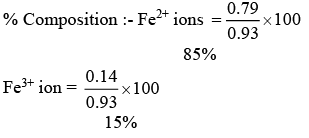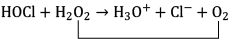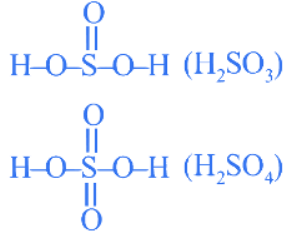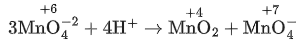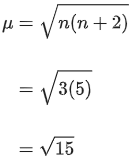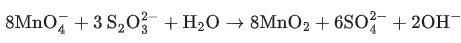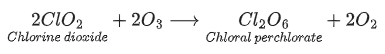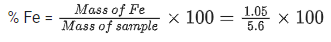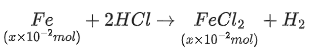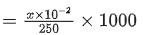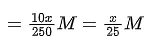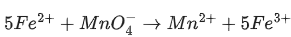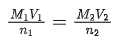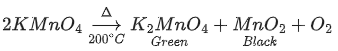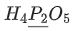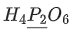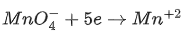Q.1. When Fe0.93O is heated in presence of oxygen, it converts to Fe2 O3. The number of correct statement/s from the following is (JEE Main 2023)
(a) The equivalent weight of Fe0.93O is 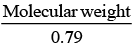
(b) The number of moles of Fe2+ and Fe3+ in 1 mole of Fe0.93O is 0.79 and 0.14 respectively
(c) Fe0.93O is metal deficient with lattice comprising of cubic closed packed arrangement of O2− ions
(d) The % composition of Fe2+ and Fe3+ in Fe0.93 O is 85% and 15% respectively
Ans. d
Fe0.93O
2x+(0.93-x)3 = 2
-x+3×0.93=2
x =0.79
0.79 = no. of Fe2+ ion
0.14 = no. of Fe3+ ion
nf = 0.79
Due to presence of Fe3+ in FeO lattice, Metal deficiency occurs.
Q.2. In which of the following reactions the hydrogen peroxide acts as a reducing agent? (JEE Main 2023)
(a) PbS + 4H2O2 → PbSO4 + 4H2O
(b) Mn2+ + H2O2 → Mn4+ + 2OH−
(c) HOCl + H2O2 → H3O+ + Cl− + O2
(d) 2Fe2+ + H2O2 → 2Fe3+ + 2OH−
Ans. c
hydrogen peroxide acts as a reducing agent
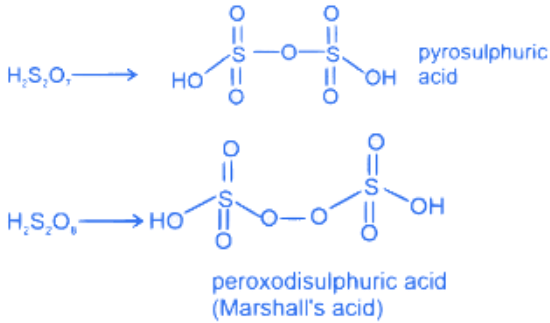
Q.3. Consider the following sulphur based oxoacids.
H2SO3, H2SO4, H2S2O8 and H2S2O7.
Amongst these oxoacids, the number of those with peroxo (O−O) bond is ________. (JEE Main 2022)
Ans. 1
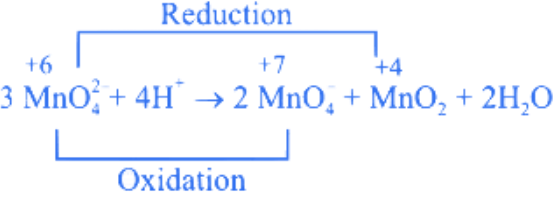
Q.4. The disproportionation of 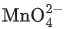 in acidic medium resulted in the formation of two manganese compounds A and B. If the oxidation state of Mn in B is smaller than that of A, then the spin-only magnetic moment (μ) value of B in BM is __________. (Nearest integer) (JEE Main 2022)
in acidic medium resulted in the formation of two manganese compounds A and B. If the oxidation state of Mn in B is smaller than that of A, then the spin-only magnetic moment (μ) value of B in BM is __________. (Nearest integer) (JEE Main 2022)
Ans. 4
Mn → 4s23d5
Mn+4 → 3d3
n = 3
= 3.87 ≈ 4 B.M
Q.5. The normality of H2SO4 in the solution obtained on mixing 100 mL of 0.1 MH2SO4 with
50 mL of 0.1MNaOH is _______________ × 10−1 N. (Nearest Integer) (JEE Main 2022)
Ans. 1
No. of equivalents of H2SO4 = 100 × 0.1 × 2 = 20
No. of equivalents of NaOH = 50 × 0.1 = 5
No. of equivalents of H2SO4 left = 20 − 5 = 15
⇒ 150 x x = 15
x = 1/10 = 0.1 N = 1 x 10-1 N
Q.6. The difference in oxidation state of chromium in chromate and dichromate salts is ___________. (JEE Main 2022)
Ans. 0
Chromate ion →, oxidation state of Cr = +6
Dichromate ion →, oxidation state of Cr = +6
∴ Difference in oxidation state = zero
Q.7. The neutralization occurs when 10 mL of 0.1M acid 'A' is allowed to react with 30 mL of 0.05 M base M(OH)2. The basicity of the acid 'A' is __________. (JEE Main 2022)
[M is a metal]
Ans. 3
Q.8. 0.01 M KMnO4 solution was added to 20.0 mL of 0.05 M Mohr's salt solution through a burette. The initial reading of 50 mL burette is zero. The volume of KMnO4 solution left in the burette after the end point is _____________ mL. (nearest integer) (JEE Main 2022)
Ans. 30
Q.9. In neutral or faintly alkaline medium, KMnO4 being a powerful oxidant can oxidize, thiosulphate almost quantitatively, to sulphate. In this reaction overall change in oxidation state of manganese will be: (JEE Main 2022)
(a) 5
(b) 1
(c) 0
(d) 3
Ans. d
In neutral or Faintly alkaline medium, thiosulphate is oxidised almost quantitatively to sulphate ion according to reaction given below,
Here the Mn changes from Mn+7 to Mn+4
Thus overall change in its oxidation number would be of 3.
Q.10. The dark purple colour of KMnO4 disappears in the titration with oxalic acid in acidic medium. The overall change in the oxidation number of manganese in the reaction is : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) 5
(b) 1
(c)7
(d) 2
Ans. 5
Q.11. Which of the given reactions is not an example of disproportionation reaction? (JEE Main 2022)
(a) 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
(b) 2NO2 + H2O → HNO3 + HNO2
(c) 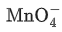 + 4H+ +3e− → MnO2 + 2H2O
+ 4H+ +3e− → MnO2 + 2H2O
(d) 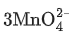 + 4H+ →
+ 4H+ → 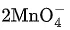 + MnO2 + 2H2O
+ MnO2 + 2H2O
Ans. c
Q.12. Which one of the following is an example of disproportionation reaction ? (JEE Main 2022)
(a) 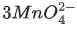 + 4H+ →
+ 4H+ → 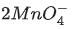 + MnO2 + 2H2O
+ MnO2 + 2H2O
(b) 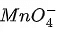 + 4H+ + 4e− → MnO2 + 2H2O
+ 4H+ + 4e− → MnO2 + 2H2O
(c) 10I− + 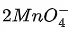 + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O + 5I2
+ 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O + 5I2
(d) 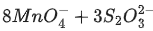 + H2O → 8MnO2 +
+ H2O → 8MnO2 + 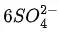 + 2OH−
+ 2OH−
Ans. a
is an intermediate oxidation state and is converted into compounds having higher and lower oxidation states.
Q.13. Among the following, basic oxide is : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) SO3
(b) SiO2
(c) CaO
(d) Al2O3
Ans. c
Since, oxides of metals are basic in nature. Hence CaO is a basic oxide.
SO3 and SiO2 are acidic oxides and Al2O3 is a amphoteric oxide.
Q.14. Ozonolysis of ClO2 produces an oxide of chlorine. The average oxidation state of chlorine in this oxide is __________. (JEE Advanced 2021)
Ans. 6
Oxidation state of Cl in Cl2O6 = 2x + 6(−2) = 0
2x − 12 = 0
2x = 12 ⇒ x = + 6
Average oxidation state of Cl in Cl2O6 is 6.
Q.15. A sample (5.6 g) containing iron is completely dissolved in cold dilute HCl to prepare a 250 mL of solution. Titration of 25.0 mL of this solution requires 12.5 mL of 0.03 M KMnO4 solution to reach the end point. Number of moles of Fe2+ present in 250 mL solution is x × 10−2 (consider complete dissolution of FeCl2). The amount of iron present in the sample is y% by weight
(Assume : KMnO4 reacts only with Fe2+ in the solution
Use : Molar mass of iron as 56 g mol−1) (JEE Advanced 2021)
Ans. 18.75
The value of y is ______.
Mass of sample = 5.6 g
Number of moles of Fe = 1.88 × 10−2 mol
Molar mass of Fe = 56 g/mol
Mass of Fe = Moles of Fe × Molar mass
= 1.88 × 10−2 × 56 = 1.05 g
⇒ y = 18.75%
The value of y is 18.75.
Q.16. A sample (5.6 g) containing iron is completely dissolved in cold dilute HCl to prepare a 250 mL of solution. Titration of 25.0 mL of this solution requires 12.5 mL of 0.03 M KMnO4 solution to reach the end point. Number of moles of Fe2+ present in 250 mL solution is x × 10−2 (consider complete dissolution of FeCl2). The amount of iron present in the sample is y% by weight.(Assume : KMnO4 reacts only with Fe2+ in the solution
Use : Molar mass of iron as 56 g mol−1)
The value of x is ______. (JEE Advanced 2021)
Ans. 1.875
Concentration of Fe2+, M1 =
Volume of Fe2+ solution titrated, V1 = 25.0 mL
Concentration of, M2 = 0.03 M
Volume ofused, V2 = 12.5 mL
Using relation,
n2M1V1 = n1M2V2 [n1 and n2 are number of moles of Fe2+ andreacting]
1 × x/25 × 25 = 5 × 0.03 × 12.5 ⇒ x = 1.88
The volume of x is 1.88.
Q.17. In the given chemical reaction, colors of the Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions, are respectively :
5Fe2+ + 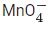 + 8H+ → Mn2+ + 4H2O + 5Fe3+ (JEE Main 2021)
+ 8H+ → Mn2+ + 4H2O + 5Fe3+ (JEE Main 2021)
(a) Yellow, Orange
(b) Yellow, Green
(c) Green, Orange
(d) Green, Yellow
Ans. d
Colour of Fe2+ is observed green and Fe3+ is yellow.
Q.18. Experimentally reducing a functional group cannot be done by which one of the following reagents? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) Pt-C/H2
(b) Na/H2
(c) Pd-C/H2
(d) Zn/H2O
Ans. b
Na in presence of H2, will not release electron which are required for reduction.
H2 gas also not get adsorbed on Na. Hence Na/H2 cannot be used as a reducing agent.
Q.19. In which one of the following sets all species show disproportionation reaction? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 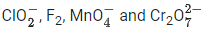
(b) 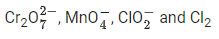
(c) 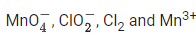
(d) 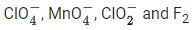
Ans. c
No option contains all species that show disproportionation reaction. So question is bonus.- Cl, Mn, Cr in these anions are present in highest oxidation state. These will not undergo disproportionation.
Q.20. Potassium permanganate on heating at 513 K gives a product which is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) paramagnetic and colourless
(b) diamagnetic and green
(c) diamagnetic and colourless
(d) paramagnetic and green
Ans. d
In K2MnO4, manganese oxidation state is +6 and hence it has one unpaired e−.
Q.21. The nature of oxides V2O3 and CrO is indexed as 'X' and 'Y' type respectively. The correct set of X and Y is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) X = basic, Y = amphoteric
(b) X = amphoteric, Y = basic
(c) X = acidic, Y = acidic
(d) X = basic, Y = basic
Ans. d
V2O3 basic
CrO basic
Q.22. The incorrect statement is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) Cl2 is more reactive than ClF.
(b) F2 is more reactive than ClF.
(c) On hydrolysis ClF forms HOCl and HF.
(d) F2 is a stronger oxidizing agent than Cl2 in aqueous solution.
Ans. a
(i) Reactivity order :
F2 > ClF (inter halogen) > Cl2
(ii) ClF + H2O → HOCl + HF
(iii) Oxidizing power is aqueous solution
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
Q.23. Match List - I with List - II :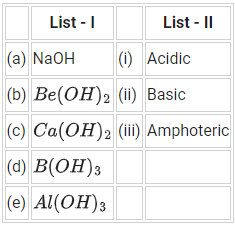
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below (JEE Main 2021)
(a) (a)-(ii), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(ii), (e)-(iii)
(b) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iii), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i), (e)-(iii)
(c) (a)-(ii), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(i), (e)-(iii)
(d) (a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(ii), (d)-(iii), (e)-(iii)
Ans. b
NaOH → Basic
Be(OH)2 → Amphoteric
Ca(OH)2 → Basic
B(OH)3 → Acidic
Al(OH)3 → Amphoteric
Q.24. The oxidation states of 'P' in H4P2O7, H4P2O5 and H4P2O6, respectively, are : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 7, 5 and 6
(b) 5, 4 and 3
(c) 5, 3 and 4
(d) 6, 4 and 5
Ans. c
Oxidation state of P in H4P2O7, H4P2O5 and H4P2O6 is 5, 3 & 4 respectively
H4P2O7
2x + 4(+ 1) + 7 (−2) = 0
x = + 5
2x + 4(+ 1) + 5 (−2) = 0
x = + 3
2x + 4 (+ 1) + 6(−2) = 0
x = +4
Q.25. Identify the process in which change in the oxidation state is five : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) 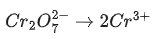
(b) 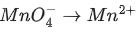
(c) 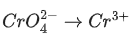
(d) 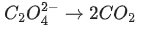
Ans. b
Q.26. The oxidation states of nitrogen in NO, NO2, N2O and 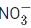 are in the order of : (JEE Main 2021)
are in the order of : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) N2O > NO2 > NO > 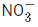
(b) NO > NO2 > N2O > 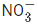
(c) NO2 > 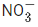 > NO > N2O
> NO > N2O
(d) 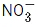 > NO2 > NO > N2O
> NO2 > NO > N2O
Ans. d
The oxidation states of Nitrogen in following molecules are as follows→ +5
NO2 → +4
NO → +2
N2O → +1
Q.27. The set that represents the pair of neutral oxides of nitrogen is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) NO and N2O
(b) N2O and NO2
(c) NO and NO2
(d) N2O and N2O3
Ans. a
NO and N2O are neutral oxides and N2O3 , NO2 and N2O5 are acidic oxides.
Q.28. Statement I : Sodium hydride can be used as an oxidising agent.
Statement II : The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen in pyridine makes it basic.
Choose the CORRECT answer from the options given below : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) Statement I is false but statement II is true
(b) Both statement I and statement II are true
(c) Statement I is true but statement II is false
(d) Both statement I and statement II are false
Ans. a
NaH is a strong H– (hydride) donor. Hence cannot be used as an oxidising agent.
In Pyridine, the lone pair of ‘N’ is localised, makes it basic.
Q.29. Compound A used as a strong oxidizing agent is amphoteric in nature. It is the part of lead storage batteries. Compound A is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) PbO
(b) PbO2
(c) PbSO4
(d) Pb3O4
Ans. b
PbO2 is strong oxidizing agent because Pb+4 is not stable and can be easily reduced to Pb+2.
PbO2 is used in lead storage batteries. It is also amphoteric in nature.
Q.30. Which of the following equation depicts the oxidizing nature of H2O2? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) CL2 + H2O2 → 2HCl + O2
(b) KIO4 + H2O2 → KIO3 + H2O + O2
(c) 2I− + H2O2 + 2H+ → I2 + 2H2O
(d) I2 + H2O2 + 2OH− → 2I− + 2H2O + O2
Ans. c
2I− + H2O2 + 2H+ → I2 + 2H2O
Oxygen reduces from –1 to –2.
So, its reduction will takes place. Hence it will behave as oxidising agent or it shows oxidising nature.
While in other option it change from (–1) to 0.
Q.31. The incorrect statement among the following is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) RuO4 is an oxidizing agent
(b) Cr2O3 is an amphoteric oxide.
(c) VOSO4 is a reducing agent
(d) Red colour of ruby is due to the presence of Co3+
Ans. d
Red colour of ruby is due to presence of Cr3+ ions in Al2O3. Chromium is the trace element that causes ruby’s red colour, which ranges from an orange red to a publish red. The strength of ruby’s red depends on how much chromium is present.
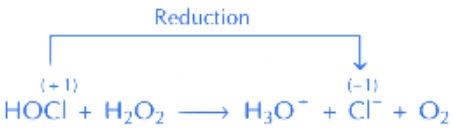
Q.32. (A) HOCI + H2O2 → H3O+ + Cl- + O2
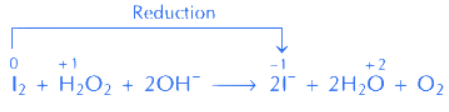
(B) I2 + H2O2 + 2OH- → 2I- + 2H2O + O2
Choose the correct option. (JEE Main 2021)
(a) H2O2 acts as reducing and oxidising agent respectively in equations (A) and (B).
(b) H2O2 act as oxidizing and reducing agent respectively in equations (A) and (B).
(c) H2O2 acts as oxidising agent in equations (A) and (B).
(d) H2O2 acts as reducing agent in equations (A) and (B).
Ans. d
In equation (A), HOCl undergoes reduction in presence of H2O2.Here, oxidation state of Cl changes from +1 to –1 (i.e. reduces)
∴ H2O2 act as reducing agent I2 reduces to I- in presence of H2O2.
In equation (B),
Here oxidation state of iodine decreases (from 0 to –1)
∴ H2O2 act as reducing agent in both the equations.