Important Formula: LCM and GCD | Quantitative for GMAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Formula |

|
| HCF by Prime Factorization Method |

|
| HCF by Division Method |

|
| LCM by Prime Factorization Method |

|
| LCM by Division Method |

|
| Things to Remember |

|
LCM stands for Least Common Factor.
LCM or least common factor of two numbers 4, 6 is denoted as LCM(4, 6). And the LCM is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 4 and 6, which is 12.
HCF stands for Highest Common Factor
Greated Common Divisor or gcd of two or more positive integers is defined as the largest positive integer that divides the numbers without leaving the remainder.
Formula
1. HCF and LCM Formula
Product of Two numbers = (HCF of the two numbers) x (LCM of the two numbers)
2. How to find HCF
H.C.F. of Two numbers = Product of Two numbers/L.C.M of two numbers
3. How to find LCM
L.C.M of two numbers = Product of Two numbers/H.C.F. of Two numbers
HCF by Prime Factorization Method
- Take an example of finding the highest common factor of 100, 125 and 180.
- Now let us write the prime factors of 100, 125 and 180.
100 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5
125 = 5 × 5 × 5
180 = 3 × 3 × 2 × 2 × 5
The common factors of 100, 125 and 180 are 5
Therefore, HCF (100, 125, 180) = 5
HCF by Division Method
Steps to find the HCF of any given numbers:
- Larger number/ Smaller Number
- The divisor of the above step / Remainder
- The divisor of step 2 / remainder. Keep doing this step till R = 0(Zero).
- The last step’s divisor will be HCF.
- Example:
Let’s take two numbers 120 and 180
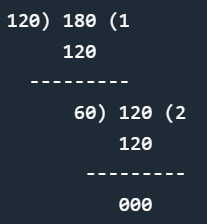
 |
Test: LCM & GCD - 1
|
Start Test |
LCM by Prime Factorization Method
Steps:- Find all the prime factors of the number.
- List all prime numbers discovered, in the order in which they appear most frequently for each number.
- To find the LCM, multiply all of the prime factors together.
- Let a and b be two numbers, then the prime factorization of both a and b is used to compute the LCM(a, b).
- For example, we find the following for LCM(24, 60):
24 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3.
60 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 5
Using all prime factors found in the order in which they occur most frequently, we get 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 = 120, and thus LCM(24, 60) = 120.
LCM by Division Method
- First, separate the given numbers with commas in a horizontal line.
- Then we must divide all the numbers given by the smallest prime number.
- The quotients and undivided numbers must now be written in a new line beneath the previous one.
- Repeat this process until there are no prime factors in common.
- The product of all divisors and the numbers in the last line is LCM.
- Example:
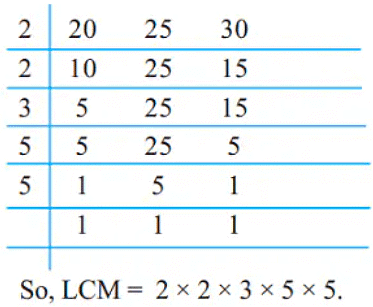
Examples
Q: The greatest possible length which can be used to measure exactly the lengths 7 m, 3 m 85 cm, 12 m 95 cm is:
A. 25 cm
B. 15 cm
C. 35 cm
D. 55 cm
Solution: Required length = H.C.F. of 700 cm, 385 cm and 1295 cm = 35 cm.
Correct Answer: C
Q: Calculate the highest number that will divide 43, 91 and 183 and leaves the same remainder in each case.
A. 4
B. 7
C. 9
D. 13
Solution:
Find the Differences between numbers
Get the HCF ( that differences)
We have here 43, 91 and 183
So differences are
183 – 91 = 92,
183 – 43 = 140,
91 – 43 = 48.
Now, HCF (48, 92 and 140)
48 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3
92 = 2 × 2 × 23
140 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 7
HCF = 2 × 2 = 4
And 4 is the required number.
Correct Answer: A
 |
Download the notes
Important Formula: LCM and GCD
|
Download as PDF |
Things to Remember
1. The product of two numbers' L.C.M. and H.C.F. is the same as the product of the numbers. The L.C.M. of 6 and 12 is 12, and the H.C.F. of 6 and 12 is 6. We see that the product of 6 and 12 is also the product of 6 and 12 L.C.M. and H.C.F.
2. Properties of L.C.M:
- L.C.M is associative.
- L.C.M is commutative.
- L.C.M is distributive.
3. Greatest Common Factor (GCF): It's important to remember what a factor of a number is. A factor is a number that evenly divides another number.
- Here, 1,2,3,4,6,8, 12, and 24 are all possible divisions of 24. As a result, 1,2,3,6, 8,12, and 24 are all factors of 24.
- 1,2,3,4,6,9,12,18, and 36 are all possible divisions of 36. As a result, factors of 36 are 1,2,3,4,6,9,12, and 36.
- As a result, the greatest common factor of 24 and 36 is 12.
4. The LCM (Lowest Common Multiple) of two or more numbers is the smallest of their common multiples. Several methods exist for determining the LCM of two or more numbers. LCM is defined to be zero if either a or b is zero.
|
122 videos|111 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formula: LCM and GCD - Quantitative for GMAT
| 1. What is the Prime Factorization Method for finding HCF? |  |
| 2. How does the Division Method help in finding HCF? |  |
| 3. How can I find LCM using the Prime Factorization Method? |  |
| 4. Explain the Division Method for finding LCM. |  |
| 5. What are some important formulas to remember for LCM and GCD? |  |




















