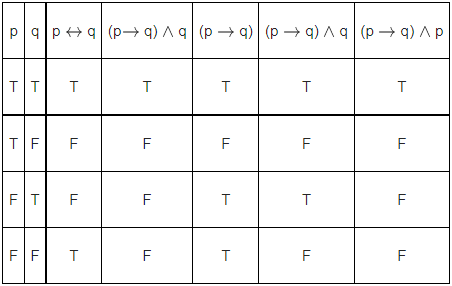
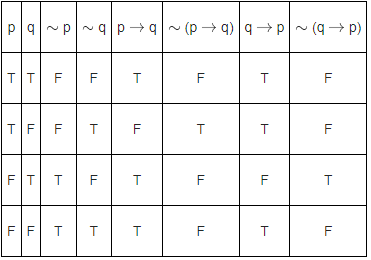
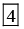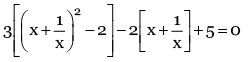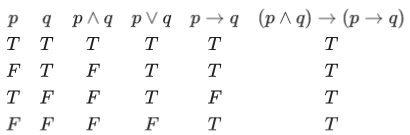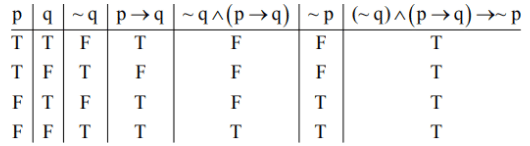Q.1. The compound statement (∼ (P ∧ Q)) ∨ ((∼ P) ∧ Q) ⇒ ((∼ P) ∧ (∼ Q)) is equivalent to (JEE Main 2023)
(a) (∼ Q) ∨ P
(b) ((∼ P) ∨ Q) ∧ (∼ Q)
(c) (∼ P) ∨ Q
(d) ((∼ P) ∨ Q) ∧ ((∼ Q) ∨ P)
Ans. d
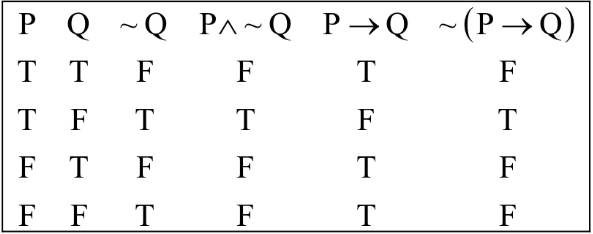
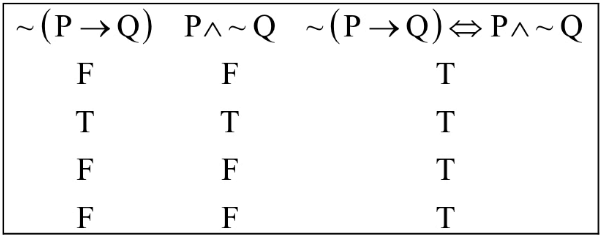
(~ p ∧ q) ∨ (~ p ∧ q)) →~ p∧ ~ q(1 +2 + 4) + 2 ⇒ 4
(1 +2 + 4) ⇒ 4
= ~(1 + 2 +4) + 4
= 3 + 4
Q.2. The number of real solutions of the equation 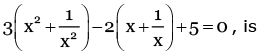 (JEE Main 2023)
(JEE Main 2023)
(a) 0
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 2
Ans. a
3t2 – 2t – 1 = 0
3t2 – 3t + t – 1 = 0
(3t + 1) (t – 1) = 0
t = 1, t = -1/3
Q.3. Let p and q be two statements. Then ∼ (p ∧ (p ⇒∼ q)) is equivalent to (JEE Main 2023)
(1) p ∨ (p ∧ q)
(2) p ∨ (p ∧ (∼ q))
(3) (∼ p) ∨ q
(4) p ∨ ((∼ p) ∧ q)
Ans. c
P ∧ (P ⇒ ~ q) P → q
(P ∧ ~ P∨ ~ q)
∴ Its negation will be
[~ P ∨ P∧ q]
[= ~ P ∨ P] ∧ [~ P ∨ q]
= ~ P ∨ q
Q.4. The statement (p ⇒ q) ∨ (p ⇒ r) is NOT equivalent to (JEE Main 2022)
(a) (p ∧ (∼r)) ⇒ q
(b) (∼q) ⇒ ((∼r) ∨ p)
(c) p ⇒ (q ∨ r)
(d) (p ∧ (∼q)) ⇒ r
Ans. b
(A) (p ∧ (∼r)) ⇒ q
∼ (p∧∼r) ∨ q
≡ (∼ p ∨ r) ∨ q
≡ ∼p ∨ (r ∨ q)
≡ p → ( q ∨ r)
≡(p ⇒ q) ∨ (p ⇒ r)
(C) p ⇒ (q ∨ r)
≡ ∼p ∨ (q ∨ r)
≡ (∼p ∨ q) ∨ (∼p ∨ r)
≡ (p → q) ∨ (p → r)
(D) (p ∧ ∼ q) ⇒ r
≡ p ⇒ (q ∨ r)
≡ (p ⇒ q) ∨ (p ⇒ r)
Q.5. The statement (p ∧ q) ⇒ (p ∧ r) is equivalent to : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) q ⇒ (p ∧ r)
(b) p ⇒ (p ∧ r)
(c) (p ∧ r) ⇒ (p ∧ q)
(d) (p ∧ q) ⇒ r
Ans. d
(p ∧ q) ⇒ (p ∧ r) is equivalent to (p ∧ q) ⇒ r
Q.6. Let
p : Ramesh listens to music.
q : Ramesh is out of his village.
r : It is Sunday.
s : It is Saturday.
Then the statement "Ramesh listens to music only if he is in his village and it is Sunday or Saturday" can be expressed as (JEE Main 2022)
(a) ((∼q) ∧ (r ∨ s)) ⇒ p
(b) (q ∧ (r ∨ s)) ⇒ p
(c) p ⇒ (q ∧ (r ∨ s))
(d) p ⇒ ((∼q) ∧ (r ∨ s))
Ans. d
p : Ramesh listens to music
q : Ramesh is out of his village
r : It is Sunday
s : It is Saturday
p → q conveys the same p only if q
Statement "Ramesh listens to music only if he is in his village and it is Sunday or Saturday"
p ⇒ ((∼q) ∧ (r ∨ s))
Q.7. Let the operations ∗, ⊙ ∈ {∧, ∨}. If (p ∗ q) ⊙ (p ⊙ ∼ q) is a tautology, then the ordered pair (∗, ⊙) is : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) (∨, ∧)
(b) (∨, ∨)
(c) (∧, ∧)
(d) (∧, ∨)
Ans. b
∗, ⊙ ∈ {∧, ∨}
Now for (p ∗ q) ⊙ (p ⊙ ∼ q) is tautology
(A) (∨, ∧) : (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∧ ∼ q) not a tautology
(B) (∨, ∨) : (p ∨ q) ∨ (p ∨ ∼ q)
= P ∨ T is tautology
(C) (∧, ∧) : (p ∧ q) ∧ (p ∧ ∼ q)
= (p ∧ p) ∧ (q ∧ ∼ q) = p ∧ F not a tautology (Fallasy)
(D) (∧, ∨) : (p ∧ q) ∨ (p ∨ ∼ q) not a tautology.
Q.8. If the truth value of the statement (P ∧ (∼ R)) → ((∼R) ∧ Q) is F, then the truth value of which of the following is F ? (JEE Main 2022)
(a) P ∨ Q → ∼R
(b) R ∨ Q → ∼P
(c) ∼(P ∨ Q) → ∼R
(d) ∼(R ∨ Q) → ∼P
Ans. d
X ⇒ Y is a false
when X is true and Y is false
So, P → T, Q → F, R → F
(a) P ∨ Q → ∼R is T
(b) R ∨ Q → ∼P is T
(c) ∼(P ∨ Q) → ∼R is T
(d) ∼(R ∨ Q) → ∼P is F
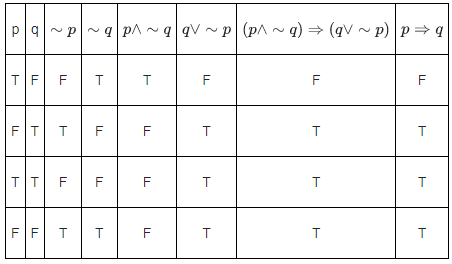
Q.9. (p ∧ r) ⇔ (p ∧ (∼q)) is equivalent to (∼p) when r is (JEE Main 2022)
(a) p
(b) ~p
(c) q
(d) ~q
Ans. c
The truth table
Clearly p ∧ q ⇔ p ∧ ∼ q ≡ ∼ p
∴ r = q
Q.10. Negation of the Boolean expression p ⇔ (q ⇒ p) is (JEE Main 2022)
(a) (∼p) ∧ q
(b) p ∧ (∼q)
(c) (∼p) ∨ (∼q)
(d) (∼p) ∧ (∼q)
Ans. d
p ⇔ (q ⇒ p)
∼ (p ⇔ (q ⇔ p))
≡ p ⇔ ∼(q ⇒ p)
≡ p ⇔ (q ∧ ∼ p)
≡ (p ⇒ (q ∧ ∼ p)) ∧ ((q ∧ ∼ p) ⇒ p))
≡ (∼p ∨ (q ∧ ∼ p)) ∧ ((∼q ∨ p) ∨ p))
≡ ((∼p ∨ q) ∧ ∼ p) ∧ (∼q ∨ p)
≡ ∼p ∧ (∼ q ∨ p)
≡ (∼p ∧ ∼q)∨( ∼ p ∧ p)
≡ (∼p ∧ ∼q) ∨ c
≡ (∼p ∧ ∼ q)
Q.11. The statement (∼(p ⇔ ∼ q)) ∧ q is : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) a tautology
(b) a contradiction
(c) equivalent to (p ⇒ q) ∧ q
(d) equivalent to (p ⇒ q) ∧ p
Ans. d
∼ (p ⇔ ∼ q) ∧ q
= (p ⇔ q) ∧ q
∴ (∼ (p ⇔ ∼ q)) ∧ q is equivalent to (p ⇒ q) ∧ p.
Q.12. Consider the following statements:
P : Ramu is intelligent.
Q : Ramu is rich.
R : Ramu is not honest.
The negation of the statement "Ramu is intelligent and honest if and only if Ramu is not rich" can be expressed as: (JEE Main 2022)
(a) ((P ∧ (∼R)) ∧ Q) ∧ ((∼Q) ∧ ((∼P) ∨ R))
(b) ((P ∧ R) ∧ Q) ∨ ((∼Q) ∧ ((∼P) ∨ (∼R)))
(c) ((P ∧ R) ∧ Q) ∧ ((∼Q) ∧ ((∼P) ∨ (∼R)))
(d) ((P ∧ (∼R)) ∧ Q) ∨ ((∼Q) ∧ ((∼P) ∨ R))
Ans. d
P : Ramu is intelligent
Q : Ramu is rich
R : Ramu is not honest
Given statement, "Ramu is intelligent and honest if and only if Ramu is not rich"
=(P∧∼R)⇔∼Q
So, negation of the statement is
∼ [(P ∧ ∼ R) ⇔ ∼ Q]
= ∼[{∼(P ∧ ∼ R) ∨ ∼ Q} ∧ {Q ∨ (P ∧ ∼ R)}]
= ((P ∧ ∼ R) ∧ Q) ∨ (∼ Q ∧ (∼ P ∨ R))
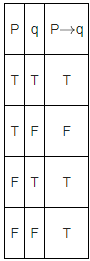
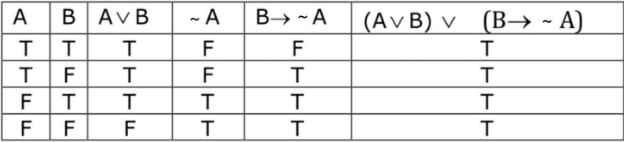
Q.13. Which of the following statements is a tautology ? (JEE Main 2022)
(a) ((∼p) ∨ q) ⇒ p
(b) p ⇒ ((∼p) ∨ q)
(c) ((∼p) ∨ q) ⇒ q
(d) q ⇒ ((∼p) ∨ q)
Ans. d
Truth Table
Q.14. The conditional statement ((p ∧ q) → ((∼p) ∨ r)) ∨ (((∼p) ∨ r) → (p ∧ q)) is : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) a tautology
(b) a contadiction
(c) equivalent to p ∧ q
(d) equivalent to (∼p) ∨ r
Ans. a
∴ Given statement is a tautology.
Q.15. The number of choices for Δ ∈ {∧, ∨, ⇒, ⇔}, such that (p Δ q) ⇒ ((p Δ ∼ q) ∨ ((∼p) Δ q)) is a tautology, is : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans. b
Let x: (p Δ q) ⇒ (p Δ ∼q) ∨ (∼p Δ q)
Case-I
When Δ is same as v
Then (p Δ ∼q) ∨ (∼p Δ q) becomes
(p ∨ ∼q) ∨ (∼p ∨ q) which is always true, so x becomes a tautology.
Case-II
When Δ is same as ∧
Then (p ∧ q) ⇒(p ∧ ∼q) ∨ (∼p ∧ q)
If p ∧ q is T, then (p ∧ ∼q) ∨ (∼p ∧ q) is F
so x cannot be a tautology.
Case-III
When Δ is same as ⇒
Then (p ⇒ ∼ q) ∨ (∼p ⇒ q) is same at (∼p ∨ ∼q) ∨ (p ∨ q), which is always true, so x becomes a tautology.
Case-IV
When Δ is same as ⇔
Then (p ⇔ q) ⇒ (p ⇔ ∼q) ∨ (∼p ⇔ q)
p ⇔ q is true when p and q have same truth values, then p ⇔ ∼q and ∼p ⇔ q both are false. Hence x cannot be a tautology.
So finally x can be ∨ or ⇒.
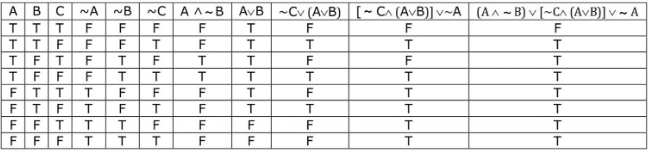
Q.16. Consider the following statements:
A : Rishi is a judge.
B : Rishi is honest.
C : Rishi is not arrogant.
The negation of the statement "if Rishi is a judge and he is not arrogant, then he is honest" is (JEE Main 2022)
(a) B → (A ∨ C)
(b) (∼B) ∧ (A ∧ C)
(c) B → ((∼A) ∨ (∼C))
(d) B → (A ∧ C)
Ans. b
∵ Given statement is
(A ∧ C) → B
Then its negation is
∼ {(A ∧ C) → B}
or ∼ {∼ (A ∧ C) ∨ B}
∴ (A ∧ C) ∧ (∼ B)
or (∼ B) ∧ (A ∧ C)
Q.17. Consider the following two propositions:
P1 : ∼(p → ∼q)
P2 : (p ∧ ∼ q) ∧ ((∼p) ∨q)
If the proposition p → ((∼p) ∨ q) is evaluated as FALSE, then : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) P1 is TRUE and P2 is FALSE
(b) P1 is FALSE and P2 is TRUE
(c) Both P1 and P2 are FALSE
(d) Both P1 and P2 are TRUE
Ans. c
Given p → (∼p ∨ q) is false
⇒ ∼p ∨ q is false and p is true
Now p = True.
∼T ∨ q = F
F ∨ q =F ⇒ q is false
P1 : ∼(T → ∼F) ≡ ∼(T → T) ≡ False.
P2 : (T ∧ ~ F) ∧ (~ T ∨ F) ≡ (T ∧ T) ∧ (F ∨ F)
≡ T ∧ F ≡ False
Q.18. The negation of the Boolean expression ((∼ q) ∧ p) ⇒ ((∼ p) ∨ q) is logically equivalent to:
(a) p ⇒ q
(b) q ⇒ p
(c) ∼(p ⇒ q)
(d) ∼(q ⇒ p)
Ans. c
Let S: ((∼q) ∧ p) ⇒ ((∼p) ∨ q)
⇒ S : ∼((∼q) ∧ p) ∨ ((∼p) ∨ q)
⇒ S : (q ∨ (∼p)) ∨ ((∼p) ∨ q)
⇒ S : (∼p) ∨ q
⇒ S : p ⇒ q
So, negation of S will be ~ (p ⇒ q)
Q.19. Let r ∈ {p, q, ∼p, ∼q} be such that the logical statement
r ∨ (∼p) ⇒ (p ∧ q) ∨ r
is a tautology. Then r is equal to : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) p
(b) q
(c) ~p
(d) ~q
Ans. c
Clearly r must be equal to ∼ p
∵ ∼ p ∨ ∼ p = ∼ p
and (p ∧ q) ∨ ∼ p = p
∴ ∼ p ⇒ p = tautology.
Q.20. Let Δ, ∇ ∈ {∧, ∨} be such that p ∇ q ⇒ ((p Δ q) ∇ r) is a tautology. Then (p ∇ q) Δ r is logically equivalent to : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) (p Δ r) ∨ q
(b) (p Δ r) ∧ q
(c) (p ∧ r) Δ q
(d) (p ∇ r) ∧ q
Ans. a
Q.21. The boolean expression (∼(p ∧ q)) ∨ q is equivalent to : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) q → (p ∧ q)
(b) p → q
(c) p → (p → q)
(d) p → (p ∨ q)
Ans. d
Making truth table
∴ (∼ (p ∧ q)) ∨ q ≡ p → (p ∨ q)
Q.22. Which of the following statement is a tautology? (JEE Main 2022)
(a) ((∼q) ∧ p) ∧ q
(b) ((∼q) ∧ p) ∧ (p ∧ (∼p))
(c) ((∼q) ∧ p) ∨ (p ∨ (∼p))
(d) (p ∧ q) ∧ (∼p ∧ q))
Ans. c
∵ ((∼ q) ∧ p) ∨ (p ∨ (∼ p))
= (∼ q ∧ p) ∨ t (t is tautology)
≡ t
∴ option (c) is correct.
Q.23. Let p, q, r be three logical statements. Consider the compound statements
S1 : ((∼p) ∨ q) ∨ ((∼p) ∨ r) and
S2 : p → (q ∨ r)
Then, which of the following is NOT true? (JEE Main 2022)
(a) If S2 is True, then S1 is True
(b) If S2 is False, then S1 is False
(c) If S2 is False, then S1 is True
(d) If S1 is False, then S2 is False
Ans. c
S1 : (∼p ∨ q) ∨ (∼p ∨ r)
≅ (∼p ∨ q ∨ r)
S2 : ∼p ∨ (q ∨ r)
Both are same
So, option (C) is incorrect.
Q.24. Negation of the Boolean statement (p ∨ q) ⇒ ((∼ r) ∨ p) is equivalent to (JEE Main 2022)
(a) p ∧ (∼ q) ∧ r
(b) (∼ p) ∧ (∼ q) ∧ r
(c) (∼ p) ∧ q ∧ r
(d) p ∧ q ∧ (∼ r)
Ans. c
Given,
(p ∨ q) ⇒ ((∼ r) ∨ p)
Negation is
∼ ((p ∨ q) ⇒ (∼ r) ∨ p))
= (p ∨ q) ∧ ∼ ((∼ r) ∨ p)
= (p ∨ q) ∧ (r ∧ ∼ p)
[(p ∧ ∼ p) ∨ (q ∧ ∼ p)] ∧ r
= q ∧ ∼ p ∧ r
Q.25. Let Δ ∈ {∧, ∨, ⇒, ⇔} be such that (p ∧ q) Δ ((p ∨ q) ⇒ q) is a tautology. Then Δ is equal to : (JEE Main 2022)
(a) ∧
(b) ∨
(c) ⇒
(d) ⇔
Ans. c
Q.26. The maximum number of compound propositions, out of p ∨ r ∨ s, p ∨ r ∨ ∼s, p ∨ ∼q ∨ s, ∼ p ∨ ∼r ∨ s, ∼p ∨ ∼r ∨ ∼s, ∼p ∨ q ∨ ∼s, q ∨ r ∨∼ s, q ∨ ∼r ∨ ∼s, ∼p ∨ ∼q ∨ ∼s that can be made simultaneously true by an assignment of the truth values to p, q, r and s, is equal to ______. (JEE Main 2022)
Ans. 9
There are total 9 compound propositions, out of which 6 contain ∼s. So if we assign s as false, these 6 propositions will be true.
In remaining 3 compound propositions, two contain p and the third contains ∼r. So if we assign p and r as true and false respectively, these 3 propositions will also be true.
Hence maximum number of propositions that can be true are 9.
Q.27. Which of the following is equivalent to the Boolean expression p ∧ ∼ q ? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) ∼ (q → p)
(b) ∼ p → ∼ q
(c) ∼ (p → ∼ q)
(d) ∼ (p → q)
Ans. d
p ∧ ∼ q ≡ ∼ (p → q)
Option (d)
Q.28. Negation of the statement (p ∨ r) ⇒ (q ∨ r) is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) p ∧ ∼ q ∧ ∼ r
(b) ∼ p ∧ q ∧ ∼ 4
(c) ∼ p ∧ q ∧ r
(d) p ∧ q ∧ r
Ans. a
Negative of (p ∨ r) ⇒ (q ∨ r)
≡ ∼ ((p ∨ r) ⇒ (q ∨ r)) ≡ (p ∨ r) ∧ (∼ (q ∨ r))
≡ (p ∨ r) ∧ (∼ q ∧ ∼ r) ≡ (p ∨ r) ∧ ∼ r) ∧ ∼ q
≡ ((p ∧ ∼ r)) ∨ (r ∧ ∼ r) ∧ ∼ q ≡ (p ∧ ∼ r) ∧ f) ∧ ∼ q
≡ (p ∧ ∼ r) ∧ (∼ q) ≡ p ∧ ∼ q ∧ ∼ r
Q.29. Let *, ▢ ∈{∧, ∨} be such that the Boolean expression (p * ∼ q) ⇒ (p ▢ q) is a tautology. Then : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) * = ∨, ▢ = ∨
(b) * = ∧, ▢ = ∧
(c) * = ∧, ▢ = ∨
(d) * = ∨, ▢ = ∧
Ans. c
(p ∧ ∼ q) → (p ∨ q) is tautology
Q.30. The Boolean expression (p ∧ q) ⇒ ((r ∧ q) ∧ p) is equivalent to : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) (p ∧ q) ⇒ (r ∧ q)
(b) (q ∧ r) ⇒ (p ∧ q)
(c) (p ∧ q) ⇒ (r ∨ q)
(d) (p ∧ r) ⇒ (p ∧ q)
Ans. a
given statement says
"if p and q both happen then p and q and r will happen"
it simply implies "If p and q both happen then 'r' too will happen"
i.e.
"if p and q both happen then r and p too will happen
i.e.
(p ∧ q) ⇒ (r ∧ p)
Q.31. The statement (p ∧ (p → q) ∧ (q → r)) → r is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) a tautology
(b) equivalent to p → ∼ r
(c) a fallacy
(d) equivalent to q → ∼ r
Ans. a
(p ∧ (p → q) ∧ (q → r)) → r
≡ (p ∧ (∼ p ∨ q) ∨ (∼ q ∨ r)) → r
≡ ((p ∧ q) ∧ (∼ p ∨ r)) → r
≡ (p ∧ q ∧ r) → r
≡ ∼ (p ∧ q ∧ r) ∨ r
≡ (∼ p) ∨ (∼ q) ∨ (∼ r) ∨ r
⇒ tautology
Q.32. Consider the two statements :
(S1) : (p → q) ∨ (∼ q → p) is a tautology .
(S2) : (p ∧ ∼ q) ∧ (∼ p ∧ q) is a fallacy.
Then : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) only (S1) is true.
(b) both (S1) and (S2) are false.
(c) both (S1) and (S2) are true.
(d) only (S2) is true.
Ans. c
S1 : (∼ p ∨ q) ∨ (q ∨ p) = (q ∨ ∼ p) ∨ (q ∨ p)
S1 = q ∨ (∼ p ∨ p) = qvt = t = tautology
S2 : (p ∧ ∼ q) ∧ (∼ p ∨ q) = (p ∧ ∼ q) ∧ ∼ (p ∧ ∼ q) = C = fallacy
Q.33. If the truth value of the Boolean expression ((p ∨ q) ∧ (q → r) ∧ (∼ r)) → (p ∧ q) is false, then the truth values of the statements p, q, r respectively can be : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) T F T
(b) F F T
(c) T F F
(d) F T F
Ans. c
Q.34. The compound statement (P ∨ Q) ∧ (∼P) ⇒ Q is equivalent to : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) P ∨ Q
(b) P ∧ ∼ Q
(c) ∼(P ⇒ Q)
(d) ∼(P ⇒ Q) ⇔ P ∧ ∼ Q
Ans. d
Using Truth Table :
Q.35. Consider the statement "The match will be played only if the weather is good and ground is not wet". Select the correct negation from the following : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) The match will not be played and weather is not good and ground is wet.
(b) If the match will not be played, then either weather is not good or ground is wet.
(c) The match will be played and weather is not good or ground is wet.
(d) The match will not be played or weather is good and ground is not wet.
Ans. c
p : weather is good
q : ground is not wet
∼ (p ∧ q) ≡ ∼ p ∨ ∼ q
≡ weather is not good or ground is wet
Q.36. Which of the following is the negation of the statement "for all M > 0, there exists x ∈ S such that x ≥ M" ? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) there exists M > 0, such that x < M for all x ∈ S
(b) there exists M > 0, there exists x ∈ S such that x ≥ M
(c) there exists M > 0, there exists x ∈ S such that x < M
(d) there exists M > 0, such that x ≥ M for all x ∈ S
Ans. a
P : for all M > 0, there exists x ∈ S such that x ≥ M.
∼ P : there exists M > 0, for all x ∈ S
Such that x < M
Negation of 'there exists' is 'for all'.
Q.37. The Boolean expression (p ⇒ q) ∧ (q ⇒ ∼p) is equivalent to : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) ~q
(b) q
(c) p
(d) ~p
Ans. d
(p → q) ∧ (q → ∼p)
≡ (∼p ∨ q) ∧ (∼q ∨ ∼p){p → q ≡ ∼p ∨ q}
≡ (∼p ∨ q) ∧ (∼p ∨ q) {commutative property}
≡ ∼p ∨ (q ∧ ∼q) {distributive property}
≡ ∼p
Q.38. Which of the following Boolean expressions is not a tautology? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) (p ⇒ q) ∨ (∼ q ⇒ p)
(b) (q ⇒ p) ∨ (∼ q ⇒ p)
(c) (p ⇒ ∼ q) ∨ (∼ q ⇒ p)
(d) (∼ p ⇒ q) ∨ (∼ q ⇒ p)
Ans. d
(1) (p → q) ∨ (∼ q → p)
= (∼ p ∨ q) ∨ (q ∨ p)
= (∼ p ∨ p) ∨ q
= t ∨ q = t
(2) (q → p) ∨ (∼ q → p)
= (∼ q ∨ p) ∨ (q ∨ p)
= (∼ q ∨ q) ∨ p
= t ∨ p = t
(3) (p → ∼ q) ∨ (∼ q → p)
= (∼ p ∨ ∼ p) ∨ (q ∨ p)
= (∼ p ∨ p) ∨ (∼ q ∨ q)
= t ∨ t = t
(4) (∼ q → q) ∨ (∼ q → p)
= (p ∨ q) ∨ (q ∨ p)
= (p ∨ p) ∨ (q ∨ p)
= p ∨ q
Which is not a tautology.
Q.39. Consider the following three statements :
(A) If 3 + 3 = 7 then 4 + 3 = 8
(B) If 5 + 3 = 8 then earth is flat.
(C) If both (A) and (B) are true then 5 + 6 = 17.
Then, which of the following statements is correct? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) (A) is false, but (B) and (C) re true
(b) (A) and (C) are true while (B) is false
(c) (A) is true while (B) and (C) are false
(d) (A) and (B) are false while (C) is true
Ans. b
Truth Table
Q.40. The Boolean expression (p ∧ ∼q) ⇒ (q ∨ ∼p) is equivalent to : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) q ⇒ p
(b) p ⇒ q
(c) ∼q ⇒ p
(d) p ⇒ ∼q
Ans. b
∴ (p ∧ ∼q) ⇒ (q ∨ ∼p)
≡ p ⇒ q
So, option (2) is correct
Q.41. If P and Q are two statements, then which of the following compound statement is a tautology? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) ((P ⇒ Q) ∧ ∼ Q) ⇒ (P ∧ Q)
(b) ((P ⇒ Q) ∧ ∼ Q) ⇒ Q
(c) ((P ⇒ Q) ∧ ∼ Q) ⇒ P
(d) ((P ⇒ Q) ∧ ∼ Q) ⇒ ∼ P
Ans. d
LHS of all the options are same i.e.
((P → Q) ∧ ∼Q)
≡ (∼P ∨ Q) ∧ ∼Q
≡ (∼P ∧ ∼Q) ∨ (Q ∧ ∼Q)
≡ ∼P ∧ ∼Q
(A) (∼P ∧ ∼Q) → Q
≡ ∼(∼P ∧ ∼Q) ∨ Q
≡ (P ∨ Q) ∨ Q ≠ Tautology
(B) (∼P ∧ ∼Q) → P
≡ ∼(∼P ∧ ∼Q) ∨ ∼P
≡ (P ∨ Q)∨∼P
(C) (∼P ∧ ∼ Q) → P ≡ (P ∧ Q) ∧ P ≠ Tautology
(D) (∼P ∧ ∼Q) → (P ∨ Q)
≡ (P ∧ Q) ∧ (P ∨ Q) ≠ Tautology
Q.42. If the Boolean expression (p ∧ q) ⊙ (p ⊗ q) is a tautology, then ⊙ and ⊗ are respectively given by : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) ∨, →
(b) →, →
(c) ∧, ∨
(d) ∧, →
Ans. b
(p ∧ q) → (p → q)
(p ∧ q) → (∼p ∨ q)
(∼p ∨ ∼q) ∨ (∼p ∨ q)
∼p ∨ (∼q ∨ q) ⇒ Tautology
⇒ ⊙ ⇒ →
⊗ ⇒ →
Q.43. If the Boolean expression (p ⇒ q) ⇔ (q * (∼q) is a tautology, then the boolean expression p * (∼q) is equivalent to : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) q ⇒ p
(b) p ⇒ q
(c) p ⇒ ∼ q
(d) ∼q ⇒ p
Ans. a
∵ p → q ≡ ∼ p ∨ q
So, * ≡ ∨
Thus, p * (∼ q) ≡ p ∨ (∼ q)
≡ q → p
Q.44. Which of the following Boolean expression is a tautology? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) (p ∧ q) ∨ (p → q)
(b) (p ∧ q) ∨ (p ∨ q)
(c) (p ∧ q) → (p → q)
(d) (p ∧ q) ∧ (p → q)
Ans. c
Q.45. Let F1(A, B, C) = (A ∧ ∼ B) ∨ [∼C ∧ (A ∨ B)] ∨ ∼ A and
F2(A, B) = (A ∨ B) ∨ (B → ∼A) be two logical expressions. Then : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) Both F1 and F2 are not tautologies
(b) F1 and F2 both are tautologies
(c) F1 is not a tautology but F2 is a tautology
(d) F1 is a tautology but F2 is not a tautology
Ans. c
Truth table for F1 :
∴ F1 is not a tautology.
Truth table for F2 :
∴ F2 is a tautology.
Q.46. The contrapositive of the statement "If you will work, you will earn money" is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) If you will not earn money, you will not work
(b) If you will earn money, you will work
(c) You will earn money, if you will not work
(d) To earn money, you need to work
Ans. a
Contrapositive of p → q is ~q → ~p
p : you will work
q : you will earn money
~q : you will not earn money
~p : you will not work
∴ ~q → ~p : If you will not earn money, you will not work
Q.47. The statement A → (B → A) is equivalent to : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) A → (A ⟷ B)
(b) A → (A ∨ B)
(c) A → (A ∧ B)
(d) A → (A → B)
Ans. b
A → (B → A)
⇒ A → (∼B ∨ A)
⇒ ∼A ∨ (∼B ∨ A)
⇒ ∼B ∨ (∼A ∨ A)
⇒ ∼B∨t
= t (tantology)
From options :
(B) A → (A ∨ B)
⇒ ∼A ∨ (A ∨ B)
⇒ (∼A ∨ A) ∨ B
⇒ t ∨ B
⇒ t
Q.48. For the statements p and q, consider the following compound statements :
(a) (∼q ∧ (p → q)) → ∼p
(b) ((p ∨ q) ∧ ∼p) → q
Then which of the following statements is correct? (JEE Main 2021)
(a) (b) is a tautology but not (a).
(b) (a) and (b) both are not tautologies.
(c) (a) and (b) both are tautologies.
(d) (a) is a tautology but not (b).
Ans. c
(a)
(a) is tautologies
(b)
(b) is tautologies
∴ a & b are both tautologies.
Q.49. The negation of the statement
∼p ∧ (p ∨ q) is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) p ∨ ∼q
(b) ∼p ∨ q
(c) ∼p ∧ q
(d) p ∧ ∼q
Ans. a
∴ ∼ p ∧ (p ∨ q) ≡ p ∨ ∼ q
Q.50. The statement among the following that is a tautology is : (JEE Main 2021)
(a) B →[A ∧ (A → B)]
(b) [A ∧(A → B)] → B
(c) [A ∧ (A ∨ B)]
(d) [A ∨ (A ∧ B)]
Ans. b
Given, [A ∧ (A → B)] → B
= A ∧ (∼A ∨ B) → B
= [(A ∧ ∼A) ∨ (A ∧ B)] → B
= (A ∧ B) → B
= ∼A ∨ ∼B ∨ B
= t
Hence, [A ∧ (A → B)] → B is a tautology.