Important Formulas: Understanding Quadrilaterals | Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
Polygons
A simple closed curve made up of only line segments is called a polygon.

Convex Polygon
We have all the diagonals inside the Polygon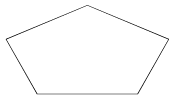
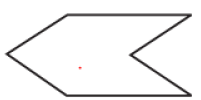
Concave Polygon
We don’t have all the diagonals inside the Polygon
Regular and Irregular Polygons
A regular polygon is both ‘equiangular’ and ‘equilateral’. So all the sides and angles should be same
(a) So square is a regular polygon but rectangle is not
(b) Equilateral triangle is a regular polygon
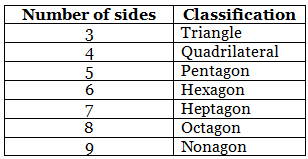
Classification of polygons
We classify polygons according to the number of sides (or vertices)
Terms
1. Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon with four angles. There are many kinds of quadrilaterals. The five most common types are the parallelogram, the rectangle, the square, the trapezoid, and the rhombus.
2. Angle Property of Quadrilateral
- Sum of all the interior angles is 360º
- Sum of all the exterior angles is 360º
3. Parallelogram: A quadrilateral which has both pairs of opposite sides parallel is called a parallelogram.
Its properties are:
- The opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal.
- The opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
- The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
- The adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary.

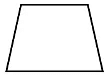
4. Trapezium: A quadrilateral which has one pair of opposite sides parallel is called a trapezium.
5. Kite: It is a quadrilaterals having exactly two distinct consecutive pairs of sides of equal length
Here ABCD is a Kite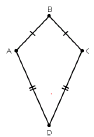
AB=BC
AD=CD
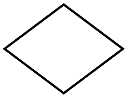
6. Rhombus: Rhombus is a parallelogram in which any pair of adjacent sides is equal.
Properties of a rhombus:
- All sides of a rhombus are equal
- The opposite angles of a rhombus are equal
- The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
7. Rectangles: A parallelogram which has one of its angles a right angle is called a rectangle.
Properties of a rectangle are:
- The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal
- Each angle of a rectangle is a right-angle.
- The diagonals of a rectangle are equal.
- The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other.

8. Square: A quadrilateral, all of whose sides are equal and all of whose angles are right angles.
Properties of square are:
- All the sides of a square are equal.
- Each of the angles measures 90°.
- The diagonals of a square bisect each other at right angles.
- The diagonals of a square are equal.

|
81 videos|423 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Understanding Quadrilaterals - Mathematics (Maths) Class 8
| 1. What are the properties of different types of quadrilaterals? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the area of a quadrilateral? |  |
| 3. What is the sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral? |  |
| 4. How do you determine if a quadrilateral is a parallelogram? |  |
| 5. What are the differences between a rhombus and a rectangle? |  |

















