Biological Mutation | Anthropology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Mutation Definition
Mutations refer to alterations in an organism's DNA sequence, which can be caused by various environmental factors such as UV light or errors during DNA replication. These changes in the base-pair sequence can lead to modifications in the proteins produced by the DNA. Typically, cells are able to detect and repair any damage caused by mutations before they become permanent.
A mutation is a sudden, inheritable change in an organism's characteristics. An individual with these inheritable changes is known as a mutant. In most cases, mutations result in the formation of recessive genes.
Classification & Types of Mutations
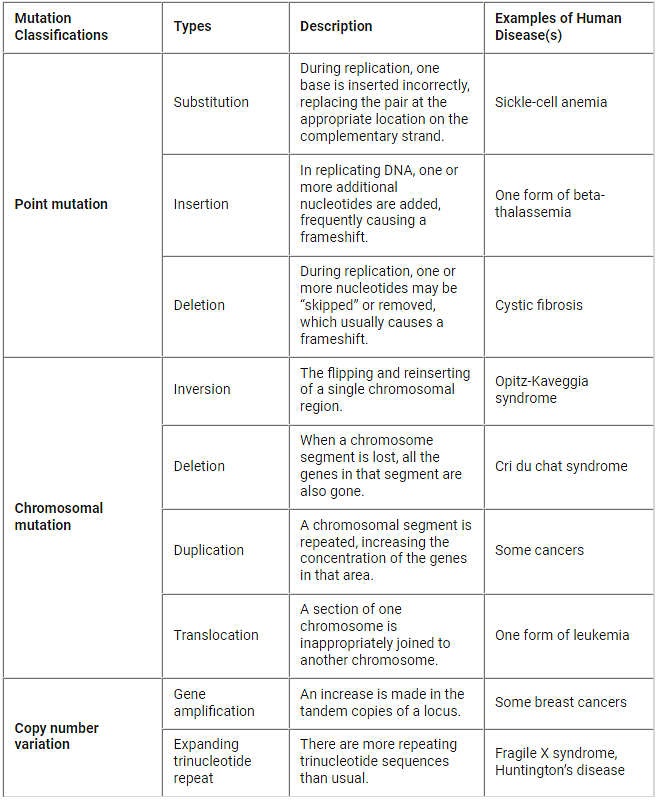
Causes of Mutations
Mutation is a process that results in genetic variations within species. These genetic changes can lead to both positive and negative consequences, with some mutations being passed down through generations. For example, a mutation in the gene responsible for producing hemoglobin can cause sickle cell anemia, a condition where red blood cells adopt a sickle shape. However, this mutation can also provide protection against malaria in certain populations, such as those in Africa.
Another example of a mutation with negative consequences is one that affects the gene controlling cell division, potentially leading to cancer. In summary, mutations are responsible for the genetic diversity seen within species and can have both beneficial and detrimental effects on the organisms that carry them.
Mutations can arise from internal or external factors.
Internal Causes
- Internal factors mainly involve errors in DNA replication. During the process of cell division, DNA must create a copy of itself. Occasionally, this copy may not be an exact replica of the original DNA, leading to a mutation. These mutations contribute to the process of evolution.
External Causes
- External factors include exposure to specific chemicals or radiation, which can cause DNA damage. For example, ultraviolet radiation can break thymine dimers, resulting in a mutated DNA sequence.
Effects of Mutation
Some mutations cannot be inherited by offspring, as they occur in somatic cells, and are known as somatic mutations. On the other hand, germline mutations happen in reproductive cells and can be passed on to future generations.
Let's examine some of the impacts of mutations:
Positive Effects of Mutation
- Certain mutations lead to new protein variants, enabling organisms to adapt to environmental changes and contributing to evolution. Some mutations in bacteria create antibiotic-resistant strains, allowing them to survive in the presence of antibiotics. A specific mutation found in an Italian population protects them from atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty materials accumulate in blood vessels.
Effects of Mutations
- Mutations refer to the alteration of genetic information within one or more genes, which can lead to the development of various genetic disorders. One well-known genetic disorder resulting from such mutations is cystic fibrosis, where the affected genes cause complications in the respiratory and digestive systems.
- Another serious health condition arising from gene mutations is cancer. In this case, the mutations occur in specific genes responsible for controlling the cell cycle. As a result, cells divide uncontrollably, eventually forming tumors and potentially spreading to other parts of the body.
Conclusion
Mutations are alterations in an organism's DNA sequence that can be caused by internal or external factors. They can have both positive and negative effects on the organisms carrying them, contributing to genetic diversity and evolution. While some mutations lead to beneficial adaptations or protection against diseases, others can cause genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis or cancer. Overall, mutations play a significant role in the development, adaptation, and health of living organisms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for Biological Mutation
What is a mutation and how is it caused?
A mutation is an alteration in an organism's DNA sequence, which can be caused by various internal factors, such as errors during DNA replication, or external factors, such as exposure to chemicals or radiation. Mutations can lead to changes in the proteins produced by the DNA and contribute to genetic diversity within species.
What are the different types of mutations?
There are two main types of mutations: somatic mutations, which occur in non-reproductive cells and cannot be inherited by offspring, and germline mutations, which occur in reproductive cells and can be passed on to future generations.
Can mutations have positive effects on an organism?
Yes, certain mutations can have positive effects, leading to new protein variants that enable organisms to adapt to environmental changes and contributing to evolution. For example, some mutations in bacteria create antibiotic-resistant strains, allowing them to survive in the presence of antibiotics.
What are some examples of genetic disorders caused by mutations?
Some genetic disorders caused by mutations include cystic fibrosis, where affected genes cause complications in the respiratory and digestive systems, and cancer, which results from mutations in specific genes responsible for controlling the cell cycle, leading to uncontrolled cell division and the formation of tumors.
|
209 videos|299 docs
|

















