UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Anthropology Optional for UPSC > Types of Marriage
Types of Marriage | Anthropology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Marriage? |

|
| Types of Marriage |

|
| Other Types of Marriage |

|
| Conclusion |

|
What is a Marriage?
Marriage is a legally acknowledged and binding relationship between two people, usually marked by a public or private ceremony where they pledge to share their lives and provide mutual emotional, financial, and social support. The specific definition of marriage can differ based on cultural, religious, and legal frameworks.
Types of Marriage
Marriage is a union of two individuals belonging to different sex with the approval of the society.
However, the degree and approach to marriage differs from society or from community to community.
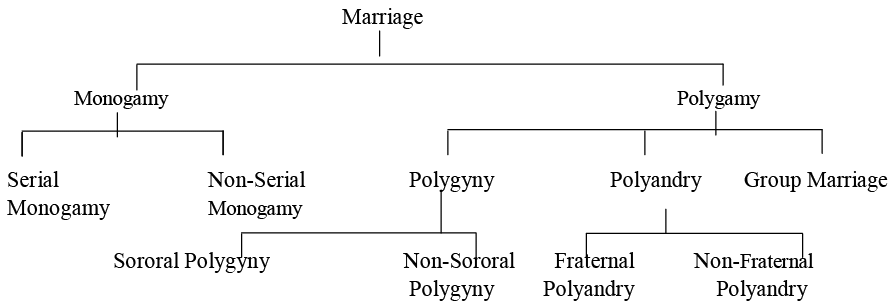
Monogamy
- Monogamy refers to a type of marriage or relationship where an individual has only one spouse or romantic partner at a time. In these relationships, both parties agree to be sexually and romantically exclusive to each other, meaning they do not engage in intimate relationships with anyone else while being together. Monogamy is often seen as a representation of commitment, loyalty, and trust between partners.
- Although monogamy is the standard in many cultures, it is not the only form of relationship that exists. Some individuals may opt for polygamous relationships, open relationships, or other forms of non-monogamous arrangements. Ultimately, the decision to engage in monogamous or non-monogamous relationships is a personal one, varying based on individual beliefs, values, and preferences.
Serial Monogamy
- Serial monogamy is a type of monogamous relationship where an individual has a series of monogamous partners over time, rather than having multiple partners at the same time. In this pattern, a person may enter into a new monogamous relationship after the previous one ends. Serial monogamy is a common relationship pattern in many cultures and societies and is often viewed as a socially acceptable way to pursue long-term relationships with different partners over time.
Straight Monogamy
- Straight monogamy is a type of monogamous relationship involving two individuals of different genders, typically a man and a woman, who are exclusively committed to each other. This form of monogamy is the most prevalent in many cultures and is often considered the normative relationship model. In straight monogamous relationships, partners may share responsibilities related to marriage, family, and household duties.
Polygamy
- Polygamy is a type of marriage where an individual has multiple spouses simultaneously. It is often linked to certain cultures and religions that permit or encourage such practices, like some Muslim and Mormon communities. There are two main types of polygamy:
Polygyny
- Polygyny is a form of polygamy where one man has multiple wives. This is the most common type of polygamy and is practiced in various cultures worldwide.
- Sororal polygyny is a subtype of polygyny where a man marries multiple sisters. This practice is often found in cultures that highly value kinship ties and family relationships.
- Non-sororal polygyny involves a man marrying multiple women who are not sisters. This form of polygyny is prevalent in many cultures, particularly in parts of Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia.
Polyandry
- Polyandry is a type of marriage where one woman is married to multiple men simultaneously. This practice is much less common than polygyny and is found in only a few cultures, such as certain regions of Tibet, Nepal, and India.
- Fraternal polyandry is a subtype of polyandry where a woman is married to multiple brothers at the same time. This practice is seen in some parts of Tibet and Nepal and is often a means to preserve family property and resources. The brothers typically share marital and familial responsibilities and have equal rights within the marriage.
- Non-fraternal polyandry involves a woman marrying multiple men who are not brothers. This type of polyandry is rarer than fraternal polyandry and is practiced in a few societies, mainly in parts of India. The men may or may not have a relationship with each other and share marital and familial responsibilities. Non-fraternal polyandry is sometimes viewed as a strategy to control population growth and ensure the economic stability of the family unit.
Question for Types of MarriageTry yourself: What is monogamy?View Solution
Other Types of Marriage
- Arranged Marriage: In an arranged marriage, the partners are chosen by the parents or family members of the individuals involved.
- Love Marriage:. love marriage is based on the mutual feelings and consent of the individuals involved, without external influence.
- Interfaith Marriage: This type of marriage occurs between individuals belonging to different religious backgrounds.
- Same-sex Marriage: Same-sex marriage involves a union between individuals of the same gender.
- Common-law Marriage: In a common-law marriage, individuals who have lived together for a certain period are considered married, even without a formal ceremony.
- Group Marriage: Group marriage involves a union between multiple individuals who have chosen to live together and share their lives with one another.
Conclusion
- Marriage is a social institution that unites individuals and is recognized by society.
- There are various types of marriages, including monogamy, polygamy (polygyny and polyandry), endogamy, exogamy, and group marriage.
- Monogamy is the most common and widely accepted form of marriage, where one man marries one woman.
- Polygamy, although less common, involves one individual marrying multiple partners.
- Endogamy and exogamy refer to marriages within and outside one's social group, respectively.
- Group marriage, a rare form of marriage, involves a group of men and women marrying each other.
- Each type of marriage has its unique cultural, social, and economic implications, and the choice of marriage type often depends on various factors such as tradition, religion, and societal norms.
The document Types of Marriage | Anthropology Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Anthropology Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
209 videos|299 docs
|
FAQs on Types of Marriage - Anthropology Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the definition of marriage? |  |
Ans.Marriage is a legally and socially recognized union between individuals that establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children. It often involves a formal ceremony and is governed by laws and cultural practices.
| 2. What are the different types of marriages recognized around the world? |  |
Ans.Different types of marriages include monogamy (one spouse), polygamy (multiple spouses), polyandry (one woman, multiple men), and group marriage (multiple individuals in a single marriage). Each type varies in legal recognition and cultural significance across societies.
| 3. How does marriage differ across cultures? |  |
Ans.Marriage differs significantly across cultures in terms of customs, ceremonies, and legal implications. Some cultures emphasize arranged marriages, while others prioritize love matches. Additionally, the rights and roles of spouses can vary widely.
| 4. What is the significance of marriage in society? |  |
Ans.Marriage plays a crucial role in society by establishing family units, providing social stability, and creating networks of support. It also has implications for inheritance, property rights, and societal norms regarding relationships.
| 5. How does the legal framework surrounding marriage vary by country? |  |
Ans.The legal framework surrounding marriage varies by country, influencing age of consent, registration processes, divorce laws, and recognition of same-sex marriages. Each jurisdiction has its own regulations that reflect its cultural and social values.
Related Searches















