Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Notes > Communication System > Detailed Notes: Phase Modulation
Detailed Notes: Phase Modulation | Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Introduction
Phase modulation is defined as the process of varying the phase of the carrier signal linearly with the instantaneous value of the message signal. The waveforms of a message signal and the phase-modulated signal are shown below:
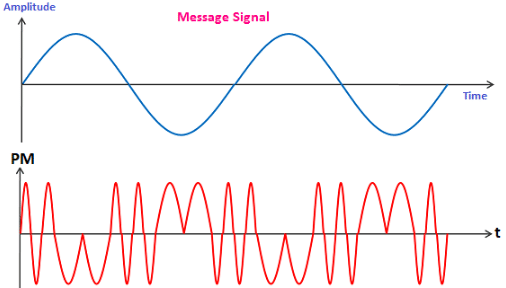 The equation of a PM signal is represented by:
The equation of a PM signal is represented by:V(t) = A cos [ωct + ϕ (t)]
Where,
ωc is the carrier frequency constant
A is the amplitude constant
ϕ (t) is the phase angle, which is not constant. It is a function of the baseband signal.
Let's first discuss the message signal and the carrier signal.
Message signal
- A message signal contains information or a message. It is the original signal that needs to be transmitted from the transmitter to the receiver. The transmitter converts the signal into a suitable form and sends it through the communication channel to the receiver. The communication channel is a medium for the signal to travel from one end to the other. The receiver perceives the signal, which is converted back to its original form.
- A message signal suffers from attenuation and various noise factors. It is essential to modulate the message signal to remove the noise. It also helps in improving the efficiency of the signal. Hence, a message signal is often known as a modulated signal. Another name of the message signal is the baseband signal.
Carrier signal
- Carrier signal is the same sinusoidal waveform signal like message signal with greater frequency. It means that the frequency of the carrier signal is higher than the message signal. The Carrier signal is sent with the message signal on the same communication channel during the modulation process. When sent with the message signal, the high-frequency carrier signal increases the frequency of the message signal. It is used in applications where the incoming message signal is low frequency, and the required output signal is high frequency.
Phase Modulators
- Modulation refers to converting the information signal to a suitable form of transmission. Here, the incoming message signal is converted to radio waves, which is a suitable mode of transmission for the communication system.
- The modulation process of PM is similar to the FM modulation process except for the integrator. FM requires an integrator before the modulated signal is applied to the balanced modulator. The integrator block in FM is present before the balance modulator block. But in PM modulation, no integrator block is required. The block diagram of the PM modulator is shown below:
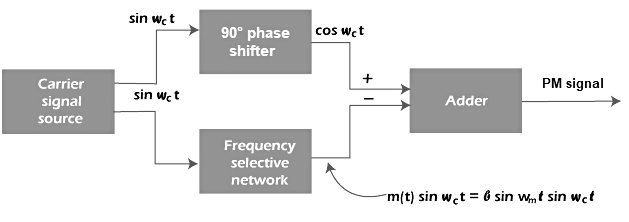
- The circuit consists of a carrier signal source, balance modulator, adder, and a 90 degree phase shifter. The carrier signal source generates a carrier sinωct with the carrier frequency ωc. The 90 degree phase shifter converts the carrier signal sinωct to cosωct, which is the carrier with a phase shift of 90 °. A balance modulator generates a double sideband amplitude modulated signal by superimposing the message and the carrier signal sinωct. The output signal is generally a suppressed carrier signal. The output of the balance modulator and the output of the phase shifter are sent to the adder, which adds these two outputs. The carrier shifted by a phase of 90° when added to the output of the balanced modulator forms a phase modulated signal.
We can also use a frequency modulator as a phase modulator by passing the FM signal through a differentiator and an FM modulator.
The block diagram is shown below: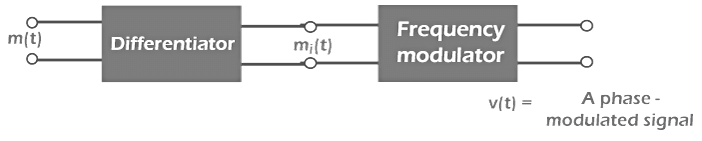 Where,
Where,
m(t) is the modulated signal
mi(t) is the instantaneous modulated signal, which is the output of the differentiator.
v(t) is the phase modulated signal, output of the frequency modulator.
Phase Demodulators
Demodulation is a process to recover the original signal. It is function at the receiving end. It converts the signal into its original form. Demodulation of PM is also related to the demodulation of FM. Let the output of the FM demodulator be y(t). The modulated signal is directly proportional to the output of the FM demodulator.
m(t) ∝ y(t)
Where,
m(t) is the modulated signal
m(t) ∝ θ(t)
The message is also proportional to the phase angle of the modulating system. It is the condition for the phase modulated signal.
y(t) ∝ dθ(t)/dt
y(t) = kdθ(t)/dt
A constant is always substituted in place of the proportionality symbol.
Where,
K is the proportionality constant
Thus, we get a recovered message signal from the phase modulated input by placing the integrators after the frequency discriminator or frequency demodulators in FM.
 |
Download the notes
Detailed Notes: Phase Modulation
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Applications of Phase Modulation
The applications of Phase Modulation are listed as follows:
- Sound Synthesis
PM is less susceptible to noise interference and popping sounds than AM. Hence, it is suitable for sound broadcasting, commonly referred to as sound synthesis. - Digital Synthesizers
PM is used in digital synthesizers for the generation of signals and waveform. - Telephone communication
PM is widely used in telephone communication due to its high-speed transmission.
Advantages of Phase Modulation
The advantages of Phase Modulation are as follows:
- High speed
- Phase modulation is considered as one the fastest modulation technique. It is due to the pulse generation at high speed.
- Low signal power consumption
PM requires low signal power consumption due to its better efficiency and fast speed. - Simple circuit design
The components required in the phase modulated circuit are less as compared to FM. Hence, it has a simple circuit design. - Easy modulation and demodulation
Phase modulation and demodulation is easy as compared to PM due to its simple circuit design.
Disadvantages of Phase Modulation
The disadvantages of Phase Modulation are as follows:
- Low noise immunity
PM has less noise immunity than FM. It is because the frequencies are less affected by external disturbances than phase. Hence, PM has low noise immunity than FM. - Complex circuitry during conversion from FM to PM
The conversion process from frequency modulation to phase modulation is complex. It is due to the additional components required for the conversion. - Low signal to noise ratio
PM has a low signal to noise ratio than FM. It is due to the higher bandwidth of FM.
The document Detailed Notes: Phase Modulation | Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) is a part of the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Course Communication System.
All you need of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) at this link: Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
|
13 videos|39 docs|30 tests
|
Related Searches


















