UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Post Independence History for UPSC Mains > Linguistic Reorganization of States
Linguistic Reorganization of States | Post Independence History for UPSC Mains PDF Download
Introduction
- In 1917, the Congress Party had committed itself to the creation of linguistic provinces in a Free India.
- After Congress’s Nagpur Session in 1920, the principle was extended and formalized with the creation of provincial Congress Committee by linguistic zones.
- The linguistic reorganization of the Congress was encouraged and supported by Mahatma Gandhi.
First Linguistic Province commission (LPC)
- After the bitter partition on the basis of religion the then PM Nehru was apprehensive of dividing country further on the basis of language, but there was a high demand for it especially from regional congress communities.
- Hence, Constituent Assembly in 1948 appointed Linguistic Provinces Commission, headed by Justice SK Dhar, to enquire into desirability of linguistic provinces.
- The Dhar Commission advised against this at that time reason being it might threaten national unity and also be administratively inconvenient.
- Linguistic Province commission (LPC) headed by Dhar supported reorganization on the basis of administrative convenience rather than on Linguistic basis.
Second Linguistic Province commission (LPC)
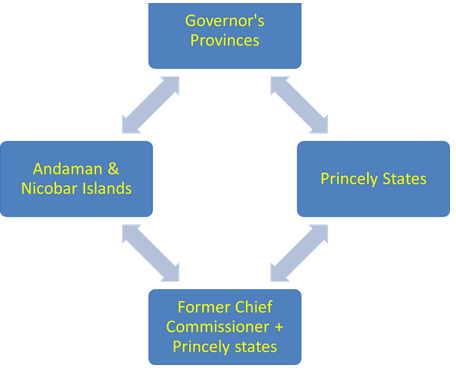
- In Dec, 1948 a second LPC was formed to again verify the report given by Dhar & look into the matter again.
- Members → J.L. Nehru, Vallabh Bhai Patel & Pattabhi sitaramayya
- They gave the same report as given by Dhar, hence on 26th Jan, 1950 division took place as –
Formation of 1st linguistic State
- After Independence, speakers of Telugu asked the congress to implement its old resolution in favour of linguistic states.
- The method they used to advance their causes were petitions, representations, street marches, parts.
- A popular freedom fighter, Potti Sriramulu undertook a fast unto death over the demand for a separate Andhra and expired after fifty-eight days.
- After his death people were agitated and it was followed by rioting, demonstrations, hartals and violence all over Andhra.
- The Vishal-andhra movement turned violent.
- Finally, Nehru announced the formation of a separate state in 1952 State of Andhra Pradesh came into being
States Reorganization Commission 1953
- The formation of Andhra Pradesh spurred the struggle for making of other states on linguistic lines in other parts of the country.
- Hence Nehru appointed states Reorganisation Commission with Justice Fazl Ali, KM Panikkar & H Kunzru as members, to examine the entire question of the reorganization of the states of the Union. They recommended –
- Abolition of 4 fold classification of states
- Recommended creation of 16 states & 3 centrally administered territories
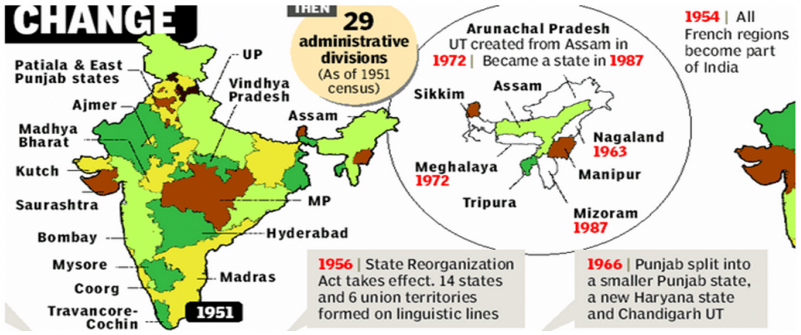
States Reorganization Act: 1956
- It provided for fourteen states and six centrally administered territories.
- SRC opposed the splitting of Bombay & Punjab.
Formation of States till 2014
An opening was through to make more states in India as per the needs of the situation, but only after the decision of parliament. This led to formation of a number of new states in India as shown below:
- Bombay reorganization act, 1960 : Formation of Gujrat
- State of Nagaland act, 1962 : Nagaland as separated state from Assam
- Punjab reorganization act, 1966 : Formation of Haryana
- New state of Himachal Pradesh act , 1970
- North eastern reorganization act, 1971 : Formation of Manipur, Tripura, Meghalaya, Mizoram & Union territories of Arunachal Pradesh & Mizoram
- New state of Sikkim act , 1975
- State of Arunachal Pradesh Act, State of Mizoram act 1986 : Formation of States of Mizoram & Ar. Pradesh
- State of Goa Act, 1987
- P reorganization act, 2000 : Formation of Chhattisgarh
- P reorganization act, 2000 : Formation of Uttarakhand
- Bihar reorganization act, 2000 : Formation of Jharkhand
- Andhra Pradesh reorganization act, 2014 : Formation of Telangana
Pending demands for new states in India
Formation of Telangana created a flame among other separatist movement for creation of new states. There are still long pending demands for state formation on the different basis viz. ethnicity, lack of development, administrative inconvenience.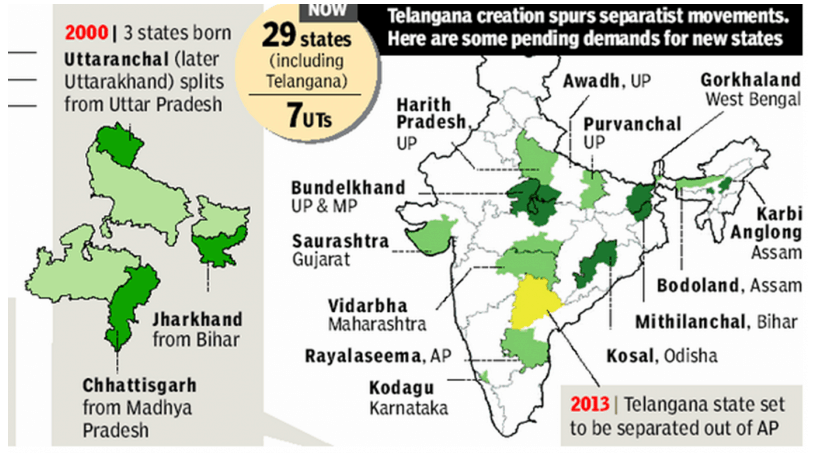
The document Linguistic Reorganization of States | Post Independence History for UPSC Mains is a part of the UPSC Course Post Independence History for UPSC Mains.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
25 videos|44 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Linguistic Reorganization of States - Post Independence History for UPSC Mains
| 1. What is linguistic reorganization of states? |  |
Ans. Linguistic reorganization of states refers to the process of redefining the boundaries of states or creating new states based on linguistic considerations. It involves the division or merger of existing states to accommodate linguistic and cultural differences among various regions.
| 2. What is the significance of linguistic reorganization of states? |  |
Ans. Linguistic reorganization of states is significant as it helps in addressing the linguistic and cultural diversity within a country. It allows for better representation and governance of linguistic communities, enabling them to preserve their language, culture, and identity. It also helps in reducing conflicts and promoting harmony among different linguistic groups.
| 3. How does linguistic reorganization of states impact governance and administration? |  |
Ans. Linguistic reorganization of states impacts governance and administration by allowing for better representation and administration of linguistic communities. It helps in the effective delivery of services and policies tailored to the specific needs of different linguistic groups. It also promotes cultural and linguistic rights, leading to better participation and inclusion of diverse communities in the decision-making process.
| 4. Can linguistic reorganization of states lead to social and economic development? |  |
Ans. Yes, linguistic reorganization of states can lead to social and economic development. By recognizing and empowering linguistic communities, it promotes social cohesion and inclusivity. This, in turn, fosters a sense of belonging and encourages active participation in social and economic activities. Additionally, linguistic reorganization can facilitate the development of region-specific policies and initiatives, promoting economic growth and development in different linguistic regions.
| 5. What are some challenges associated with linguistic reorganization of states? |  |
Ans. Some challenges associated with linguistic reorganization of states include the potential for ethnic tensions and conflicts, administrative complexities, and economic disparities among different linguistic regions. It requires careful consideration of various factors such as language boundaries, resource distribution, and ensuring equal opportunities for all linguistic communities. Balancing the aspirations and interests of different linguistic groups can also be a challenge in the process of linguistic reorganization.
Related Searches
















