Rights in the Indian Constitution Class 11 Political Science
Introduction
- A constitution does more than just define the structure of the different branches of government and their interrelationships.
- It is also a document that restricts government power and guarantees a democratic system where everyone has certain rights.
- Rights are fundamental to ensuring justice and fair treatment in any society.

The Importance of Rights
- When constitutional rights are violated and go unchallenged, it leads to severe injustices.
- Legal intervention is crucial in rectifying these violations and upholding rights, as demonstrated by key cases in India's history.
- The constitutional guarantee of rights such as the right against exploitation and the right to a fair trial highlights their significance in maintaining societal balance and individual dignity.
Two instances where the importance of Rights were highlighted are discussed as follows:
Asian Games Construction (1982)
- The government hired contractors for construction work. These contractors employed poor construction workers in poor working conditions and paid them less than the government-set minimum wage.
- Social scientists petitioned the Supreme Court, arguing that underpayment was a violation of Fundamental Rights against exploitation.
- The court ruled in favor of the workers and directed the government to pay them the prescribed minimum wages.
Case of Machal Lalung:
- Machal Lalung was arrested at 23 for causing grievous injuries and found mentally unstable. He was sent to Lok Priya Gopinath Bordoloi Mental Hospital for treatment.
- Despite being declared fit for trial in 1967 and 1996, authorities ignored this, and he remained in custody for 54 years without a trial.
- The National Human Rights Commission intervened, leading to his release at age 77 in 2005. This case highlighted the right to 'life and liberty' and the necessity for a fair and speedy trial.
Bill of Rights
- Both examples highlight the importance of having rights and their actual implementation in a democracy.
- A democracy must guarantee that individuals have specific rights and that the government will consistently recognize these rights.
- Most democratic countries practice listing the rights of citizens in the constitution itself, known as the ‘bill of rights.’
- A bill of rights prevents the government from violating individual rights and ensures a remedy if those rights are violated.
- The rights of a person can be threatened by another person or organization, which requires government protection.
- It is essential that the government is obligated to protect individual rights.
- The different organs of the government (like the legislature, executive, bureaucracy, or judiciary) may, during their functions, violate individual rights.
Fundamental Rights In the Indian Constitution
- Leaders of the freedom movement understood the importance of rights and demanded that the British respect the rights of the people.
- The Motilal Nehru Committee demanded a bill of rights in 1928.
- After independence, there was unanimous agreement on including and protecting rights in the Constitution, which listed them as 'fundamental rights.'
- Fundamental rights are specially protected by the Constitution, ensuring they are not violated by the government.
- These rights differ from ordinary legal rights, as they are guaranteed by the Constitution and can only be changed by amending it.
- The judiciary has the power to protect fundamental rights and can declare government actions illegal if they violate or unreasonably restrict these rights.
- Fundamental rights are not absolute; the government can impose reasonable restrictions on their exercise.
Bill of rights in the South African Constitution
- The South African Constitution was inaugurated in December 1996.
- The Bill of Rights is considered a cornerstone of democracy in South Africa.
- The Constitution prohibits discrimination on the basis of race, gender, pregnancy, marital status, ethnic or social origin, color, age, disability, religion, conscience, belief, culture, language, and birth.
- It provides a broad range of rights to its citizens.
- A special Constitutional Court is responsible for enforcing the rights enshrined in the Constitution.
The key rights included in the Constitution are:
- Right to Dignity.
- Right to Privacy.
- Right to fair labour practices.
- Right to a healthy environment and protection of the environment.
- Right to adequate housing.
- Right to health care, food, water, and social security.
- Children’s rights.
- Right to basic and higher education.
- Right of cultural, religious, and linguistic communities.
- Right to information.
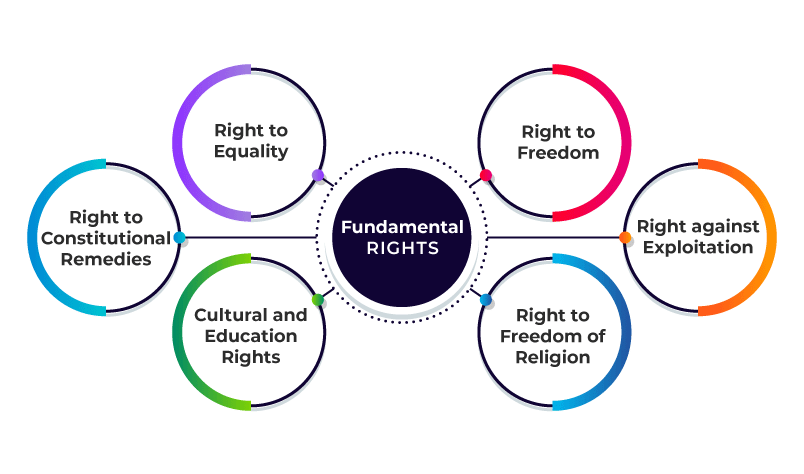
Right to Equality
- Equal Access: Right to Equality ensures equal access to public places without discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
- Non-Discrimination: The right prohibits discrimination in public employment on the grounds of religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
- Abolition of Untouchability: Abolishes untouchability and forbids its practice in any form.
- Title Restriction: Prohibits the state from conferring titles, except for military and academic distinctions.
- Equality of Opportunity: Guarantees equal opportunity for all sections of society, with provisions for affirmative action for disadvantaged groups.
- Judicial Protection: Empowers the judiciary to declare government actions illegal if they violate fundamental rights.
Article 16 (4): Nothing in this article shall prevent the State from making any provision for the reservation of appointments or posts in favour of any backward class of citizens which, in the opinion of the State, is not adequately represented in the services under the State.
Article 21: Protection of life and personal liberty—No person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to procedure established by law.
Right to Freedom
- Equality and liberty are fundamental to a democracy. One cannot exist without the other.
- Liberty includes freedom of thought, expression, and action.
- Liberty does not mean the freedom to do anything one desires.
- Unlimited freedom would prevent many people from enjoying their freedom.
- Freedoms are defined to ensure everyone can enjoy their liberty without threatening others' freedoms or the law and order.
Right to life and personal liberty
- The foremost right among rights to freedom is the right to life and personal liberty.
- No citizen can be denied his or her life except by procedure as laid down under the law.
- No one can be denied his or her personal liberty, meaning no one can be arrested without being told the grounds for such an arrest.
- If arrested, the person has the right to defend himself by a lawyer of his choice.
- It is mandatory for the police to take the arrested person to the nearest magistrate within 24 hours.
- The magistrate, who is not part of the police, will decide whether the arrest is justified or not.
- The right to life and personal liberty includes the right to live with human dignity, which is free from exploitation.
- The Supreme Court has ruled that the right to life includes the right to shelter and livelihood, as no person can live without the means of living.

Preventive Detention
- Ordinarily, a person would be arrested after reportedly committing an offence.
- Exceptions exist where a person can be arrested out of apprehension of likely unlawful activity, known as preventive detention.
- Preventive detention allows the government to detain or arrest a person if they are considered a threat to law and order or national security.
- Preventive detention can be extended only for three months; after this period, the case is reviewed by an advisory board.
- Preventive detention is seen as an effective tool for the government to deal with anti-social elements or subversives.
- However, this provision has often been misused by the government, leading to calls for greater safeguards to prevent unjustified detentions.
- There is a clear tension between the right to life and personal liberty and the provision for preventive detention.
Other freedoms
- Under the right to freedom, there are several other rights, but these are not absolute.
- Each right is subject to restrictions imposed by the government.
- The right to freedom of speech and expression is subject to restrictions such as public order, peace, and morality.
- The freedom to assemble must be exercised peacefully and without arms.
- The government can declare the assembly of five or more persons as unlawful in certain areas.
- Such powers can be misused by the administration, potentially denying genuine protests against government policies.
- Awareness and vigilance by the people regarding their rights can help prevent such misuse.
- Even in the Constituent Assembly, some members expressed dissatisfaction with restrictions on rights.
Rights of the Accused
To ensure a fair trial in courts, the Constitution has provided three rights:
- No person would be punished for the same offence more than once.
- No law shall declare any action as illegal from a backdate, and
- No person shall be asked to give evidence against him or herself.
Right against Exploitation
- Millions of people in our country are underprivileged and deprived, often subjected to exploitation.
- The Constitution prohibits begar or forced labour without payment, which was historically imposed by landlords, moneylenders, and wealthy persons.
- Despite this prohibition, some forms of bonded labour still exist, especially in brick kiln work, but it has been declared a crime and is punishable by law.
- Another form of exploitation, the buying and selling of human beings and using them as slaves, is also prohibited by the Constitution.
- The Constitution forbids the employment of children below the age of 14 years in dangerous jobs like factories and mines.
- With child labour being made illegal and the right to education becoming a fundamental right, the right against exploitation has become more meaningful.
Right to Freedom of Religion
- Everyone enjoys the right to follow the religion of their choice, a hallmark of democracy.
- Historically, rulers often persecuted or forced conversion of those following different religions.
- Democracy incorporates the freedom to follow one's chosen religion as a fundamental principle.

Freedom of Faith and Worship
- In India, everyone is free to choose, practice, profess, follow, and propagate any religion.
- This freedom includes the freedom of conscience, allowing individuals to choose any religion or none at all.
- The government can impose restrictions to protect public order, morality, and health, and to root out social evils. For instance, practices like sati have been banned by the government in the past.
- Restrictions on religious practices often create tensions, especially regarding the propagation and conversion activities.
- The Constitution does not permit forced conversions. It only grants us the right to share information about our religion and, in doing so, attract others to it.
Equality of All Religions
- The government must extend equal treatment to all religions, with no official state religion.
- There is no religious requirement for holding public office.
- The right to equality guarantees no discrimination based on religion in employment and prohibits state-run institutions from favoring any religion.
- These provisions support and nurture the principle of secularism.
Cultural and Educational Rights
- Minorities are groups with a common language or religion that are outnumbered by other social sections in a particular area or the country as a whole.
- The Constitution believes diversity is a strength and includes the right for minorities to maintain their culture.
- Minorities have the right to conserve and develop their own culture, language, and script.
- All minorities, whether religious or linguistic, can set up their own educational institutions to preserve and develop their culture.
- The government will not discriminate against any educational institution managed by a minority community when granting aid to educational institutions.
Right to Constitutional Remedies
- The right to constitutional remedies is the mechanism to achieve the realization and defense of Fundamental Rights.
- Dr. Ambedkar called it the 'heart and soul of the Constitution' because it allows citizens to approach the High Court or the Supreme Court to restore any violated Fundamental Rights.
- The Supreme Court and High Courts can issue orders and directives to the government to enforce these rights.
- The courts can issue various special orders known as writs.
Types of Writs
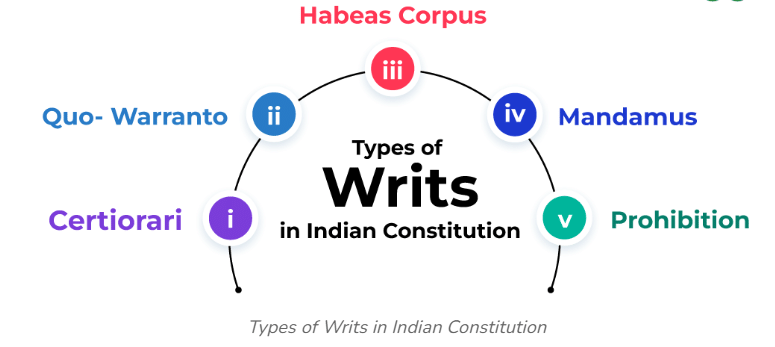
Habeas Corpus
- A writ of habeas corpus is issued by the court to ensure that an arrested person is presented before it.
- If the court finds that the arrest was not lawful or the grounds for arrest were unsatisfactory, it can order the release of the person. This writ protects against unlawful detention.
Example: John is arrested without a warrant and held in custody without being charged. His family petitions the court for a writ of habeas corpus. The court orders the police to bring John before it. After reviewing the case, the court finds no legal basis for his detention and orders his release.
Mandamus
- A writ of mandamus is issued by the court when it finds that a particular office holder is not performing their legal duty, thereby endangering the rights of an individual.
- This writ commands the office holder to fulfill their official duties.
Example: A government official refuses to issue a business license to Maria, despite her meeting all the requirements. Maria files a petition for a writ of mandamus. The court orders the official to perform his legal duty and issue the license.
Prohibition
- A writ of prohibition is issued by a higher court, such as the High Court or the Supreme Court, to prevent a lower court from exceeding its jurisdiction.
- This writ stops the lower court from continuing proceedings in a case that it is not authorized to handle.
Example: A district court is hearing a case that should be under the jurisdiction of the High Court. The High Court issues a writ of prohibition, ordering the district court to stop proceedings because it is exceeding its jurisdiction.
Quo Warranto
- A writ of quo warranto is issued when the court finds that a person is unlawfully holding a public office.
- This writ restricts the person from acting as an office holder, ensuring that only those entitled to hold a position do so.
Example: Peter is appointed as the director of a public institution without having the necessary qualifications. A concerned citizen files for a writ of quo warranto. The court examines the appointment and finds it unlawful, ordering Peter to vacate the office.
Certiorari
- A writ of certiorari is issued by a higher court to a lower court or another authority to transfer a pending matter to the higher court for review.
- This writ ensures that cases are handled by the appropriate level of judicial authority.
Example: A lower court passes a judgment in a complex legal matter. The losing party believes there were significant errors in the judgment and petitions the Supreme Court. The Supreme Court issues a writ of certiorari, ordering the lower court to transfer the case records for review.
National Human Rights Commission
- Background: To protect the vulnerable from exploitation, independent organisations like the People’s Union for Civil Liberties (PUCL) or People’s Union for Democratic Rights (PUDR) have been working as guardians of the implementation of law.
- In this light, the government set up an institution called the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in 1993.
- Composition: The Commission consists of a former Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India, a former Supreme Court judge, a former Chief Justice of a High Court, and two other members with knowledge and practical experience in human rights matters.
- The NHRC plays a crucial role in protecting the rights of individuals from violations by both state and non-state actors.
- The NHRC provides a mechanism for individuals to seek redress in cases of human rights violations, ensuring that their rights are upheld.
- The NHRC monitors and reviews the actions of government bodies, ensuring that they do not infringe upon the fundamental rights of citizens.
- The Commission lacks prosecutorial power; it can only make recommendations to the government or suggest that the courts initiate proceedings based on its inquiries.
Directive Principles of State Policy
- The makers of our Constitution knew that independent India would face many challenges, particularly in achieving equality and well-being for all citizens.
- They believed that certain policy directions were needed to address these issues but did not want to bind future governments to specific policy decisions.
- To balance this, they incorporated guidelines in the Constitution that are not legally enforceable, meaning citizens cannot go to court to compel the government to implement these policies.
- These guidelines are ‘non-justiciable’, indicating that the judiciary cannot enforce them.
- The framers of the Constitution believed the moral force behind these guidelines would prompt the government to take them seriously and that the people would hold the government accountable.
- This separate list of policy guidelines is called the Directive Principles of State Policy.

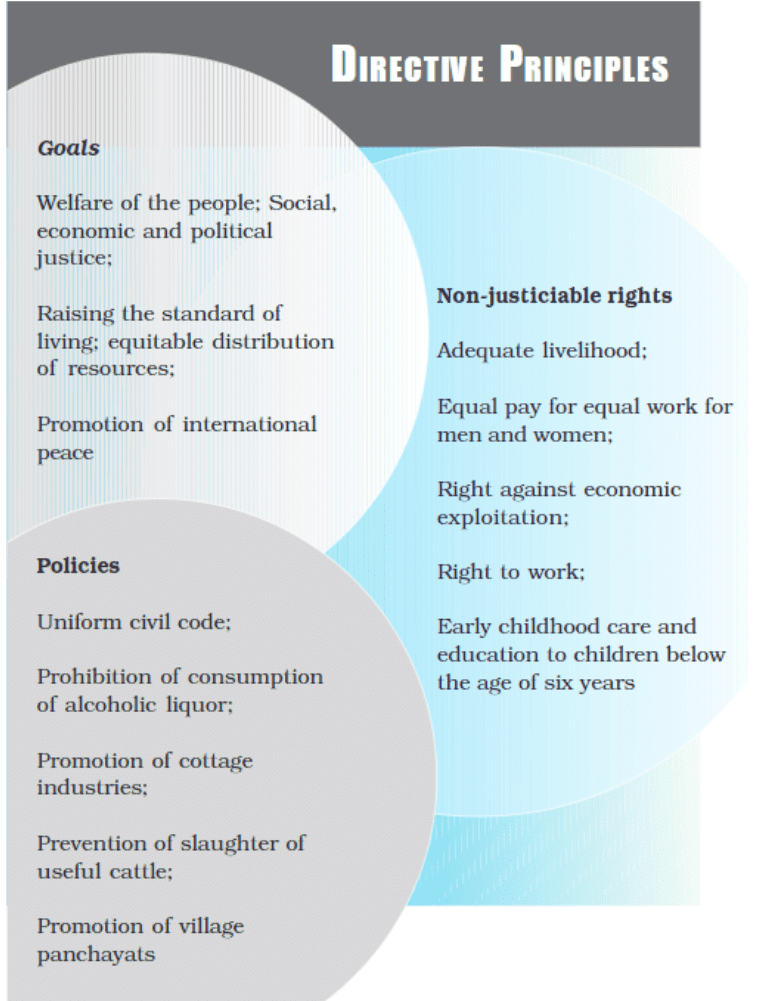
What do the Directive Principles contain?
The chapter on Directive Principles covers three main things:
- The goals and objectives that society should aim for.
- Additional rights people should have besides the Fundamental Rights.
- Policies that the government should follow.
Examples of implementation include zamindari abolition bills, nationalization of banks, factory laws, minimum wage laws, and promotion of cottage and small industries. Additional efforts include reservation provisions for scheduled castes and tribes, the right to education, panchayati raj institutions, the employment guarantee programme, and the mid-day meal scheme.
 Directive Principles of State Policy
Directive Principles of State Policy
Fundamental Duties of citizens
- In 1976, the 42nd amendment to the Constitution introduced a list of Fundamental Duties for citizens.
- Ten Fundamental Duties were enumerated by this amendment.
- The Constitution does not specify how these duties are to be enforced.
- Citizens are required to abide by the Constitution, defend the country, promote harmony among all citizens, and protect the environment.
- The enjoyment of fundamental rights is not conditional upon the fulfillment of these duties.
- The inclusion of Fundamental Duties has not changed the status of fundamental rights.
Relationship Between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles
- Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles are complementary, with Fundamental Rights restraining the government and Directive Principles exhorting it to act for societal well-being.
- Fundamental Rights protect individual rights, while Directive Principles ensure the well-being of society.
- Conflicts can arise when implementing Directive Principles infringes on Fundamental Rights, such as the abolition of the zamindari system, which was opposed due to the right to property.
- The government argued that rights could be abridged to implement Directive Principles, viewing them as essential for societal welfare.
- The judiciary maintained that Fundamental Rights are sacred and cannot be limited, even for implementing Directive Principles.
- Kesavananda Bharati Case: This case resolved the debate, with the Supreme Court ruling that certain basic features of the Constitution, including Fundamental Rights, cannot be changed by Parliament.
 Right to Property
Right to Property
Conclusion
The inclusion and protection of rights in the Constitution aim to build a just and equitable society. Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles work together to ensure individual freedoms and societal well-being. Legal mechanisms empower citizens to defend their rights, reinforcing the importance of balancing individual rights with societal needs for the healthy functioning of democracy.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Rights in the Indian Constitution Class 11 Political Science
| 1. What are the fundamental rights guaranteed in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the right to equality in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 3. How does the Indian Constitution protect the right to freedom of religion? |  |
| 4. What are cultural and educational rights in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 5. What are the types of writs available for enforcing fundamental rights in India? |  |

















