Polygenic Inheritance | Anthropology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Polygenic inheritance is a phenomenon where numerous genes found in different locations, called loci, contribute to a single characteristic or trait in plants and animals. Examples of such traits include height, skin pigmentation, eye and hair color, and milk and egg production. In this form of inheritance, many alleles (variations of a gene) work together to influence a single trait.
- In the case of human height and skin pigmentation, we can observe a wide range of variations instead of just two categories, such as "tall" and "short" or "dark" and "light." This continuous variation is due to the fact that multiple genes control these traits. For instance, around 400 genes are involved in determining height, leading to the diverse range of heights in the human population.
Polygenic Inheritance Definition
“Polygenic inheritance is defined as quantitative inheritance, where multiple independent genes have an additive or similar effect on a single quantitative trait.”
Polygenic inheritance is also known as multiple gene inheritance or multiple factor inheritance.
Polygenic Inheritance characteristics
- Polygenic inheritance refers to the process by which multiple genes, each with a small effect, work together to influence a particular trait or phenotype. This type of inheritance is complex because the individual effect of each gene is too small to be easily detected, and the genes often work together to produce a cumulative or additive effect.
- In contrast to multiple alleles, where three or more alleles are present in the same genetic location (locus) and any two alleles can be present in an organism, polygenic inheritance involves multiple genes that each contribute to the expression of a trait. For example, the ABO blood group system is controlled by three alleles, whereas polygenic traits involve multiple genes working together.
- Polygenic inheritance does not involve epistasis, which is the masking of the expression of an allele at a different locus. Additionally, there is no linkage or dominance in polygenic inheritance. Instead, there are contributing (active) and non-contributing (null) alleles that work together to influence the phenotype of a trait.
- One of the main characteristics of polygenic inheritance is the continuous variation of a trait's phenotype. This means that the expression of the trait can range widely, making it difficult to predict an individual's phenotype based on their genetic makeup.
- However, statistical analysis can be used to estimate population parameters and better understand the distribution of polygenic traits in a population. Overall, polygenic inheritance is a complex and intricate process that plays a significant role in the expression of many traits and phenotypes.
Polygenic Inheritance Examples
- Polygenic inheritance is a type of genetic inheritance that involves multiple genes contributing to the expression of a particular characteristic or trait in humans. Some examples of traits showing polygenic inheritance include skin and hair color, height, eye color, susceptibility to diseases, intelligence, blood pressure, bipolar disorder, autism, longevity, and more.
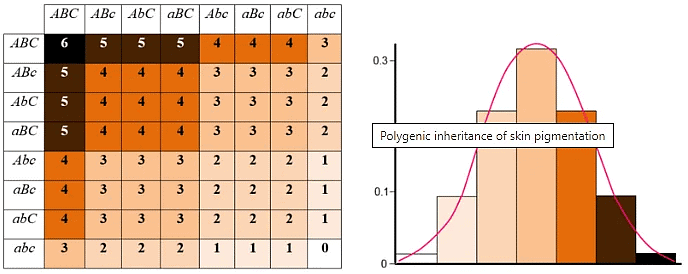
- One example of polygenic inheritance is skin pigmentation. The inheritance of skin color is determined by around 60 genetic loci, each contributing to the overall expression of this trait. For instance, consider three different pairs of alleles (alternative forms of a gene) at three unlinked loci, represented by A and a, B and b, C and c. The capital letters (A, B, C) represent the incompletely dominant alleles for darker skin color. The more capital letters present, the darker the skin color, while the more lowercase letters (a, b, c) present, the lighter the skin color.
- In a mating event between parents with genotypes AABBCC (dark skin) and aabbcc (light skin), their offspring will have an intermediate skin color with a genotype of AaBbCc. When two offspring with this genotype (AaBbCc) mate, their children will exhibit a range of skin colors, from very dark to very light, following a ratio of 1:6:15:20:15:6:1. This illustrates the complex inheritance pattern of polygenic traits, with multiple genes contributing to the overall expression of a characteristic.
 Punnett square showing F2 generation off springs continuous variation
Punnett square showing F2 generation off springs continuous variation
From light to dark→
- Height There are around 400 genes responsible for the phenotype and environment greatly influences the expression of genes.
- Eye colour The colour of the eye is determined by polygenes. At least 9 colours of eye colour are recognised in humans. There are two major eye colour genes and 14 more genes that determine the expression of the phenotype. A different number of alleles contribute to each colour. These are found to be X-linked.
Polygenic Inheritance in Plants
Polygenic inheritance in plants includes the colour and shape of the stem, pollen, flower, yield, oil content, size of a seed, time to mature or flower, etc.
Brief description of some of the traits
- Kernel colour of the wheat: The three independent pairs of alleles are involved in the expression of kernel colour of wheat. They show independent assortment. When dark red wheat kernel (AABBCC) is crossed with the white wheat kernel (aabbcc) the F1 generation has an intermediate red colour kernel (AaBbCc). When F1 generation is crossbred, F2 generation has 63 red kernel plants having different shades of red and 1 white kernel.

63 Red (many shades):1 (white)
- Length of the corolla in tobacco There are around 5 genes involved in the expression of phenotype for corolla length of tobacco. There is a wide variety in the length of the corolla in tobacco due to polygenic inheritance.
Effect of environment on Polygenic Inheritance
- The expression of polygenes, which are multiple genes that contribute to a particular trait, can be significantly impacted by environmental factors. While the genotype provides a range of potential outcomes for a quantitative trait, it is the environmental conditions that ultimately determine the specific phenotype within its genetic boundaries. In other words, genes may function differently depending on the environment they are in, as the environment can regulate the activity of certain genes by turning them on or off.
- The term 'norm of reaction' refers to the range of possible phenotypes that can occur under various environmental conditions for a single genotype. Some genotypes have a narrow norm of reaction, while others, such as those involved in determining human height, have a much broader range of potential outcomes.
- This concept is exemplified by identical twins who are raised in different environments. They may have the same genetic potential or vulnerability, but the environmental conditions they are exposed to can greatly influence how their genotype is expressed. Many human traits, including intelligence, depression, height, skin color, and schizophrenia, demonstrate the impact of the environment on gene expression. Thus, phenotypic expression is dependent on a combination of both genetic and environmental factors, or nature and nurture.
Examples
- A person's height is significantly impacted by their diet and overall health.
- The color of a Hydrangea shrub's flowers is determined by the amount of aluminum present in the soil in which it grows.
- The skin color of Himalayan rabbits is influenced by the temperature of their environment.
Conclusion
Polygenic inheritance is a complex process that involves multiple genes contributing to the expression of a single trait or characteristic. This type of inheritance results in a continuous variation of phenotypes, making it difficult to predict an individual's phenotype based solely on their genetic makeup. Examples of polygenic traits include human height, skin pigmentation, eye color, and various traits in plants. Environmental factors play a significant role in the expression of polygenes, as they can influence how genes function and interact with each other. Overall, polygenic inheritance is an intricate and essential aspect of genetics that helps to explain the vast diversity in phenotypes observed in both plants and animals.
|
209 videos|299 docs
|
















