Genetic Load | Anthropology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Concept and Definition
Genetic variability pertains to many advantages and disadvantages, many of the genes maintained by natural selection in a population are disadvantageous to it if their carriers are in homozygous state. The concept of genetic load was given by Haldane (1949) and Muller (1950). It hovers around an idea that the genotypes in a population have a mixture where one is better than the other. Genetic load is the difference between the fitness of an expected optimal genotype with the fitness of observed average genotype in a population. It accompanies with a loss of a portion of individual known as genetic death as there is a probability of an organism failing to reach the reproductive age. This fact is important to study by scientist as the population with too high genetic load will be in danger of going extinct as the organism are unable to survive and reproduce viable offspring. For instance if a gene is deleterious in homozygous state the frequency of homozygotes before and after selection will be as follows
Thus the incurred genetic load by the individuals with aa genotype is sq2 , if there were 100 individuals in the population before selection, 100sq are eliminated because of genetic imperfection.
Haldane’s Dilemma
The value sq2 equals the mutation rate at equilibrium A→a, which is mutation cause by recessive deleterious gene, is equal to the mutation rate. On keeping the mutation rate constant a little difference can be seen in genetic load whether the Darwinian fitness s is small or large. High selection coefficient will lead to rapid elimination of genes (low q) whereas a low selection coefficient will let the gene to remain in the population (high q).
Causes of genetic load
Mutational load
- Genetic loads are affected by mutation, which are negative as more mutations in a genome are deleterious than advantageous. In Crow terms Mutational load can be defined as the extent to which a population is impaired by recurrent mutation. Mutational load is larger in big populations with positive selection because there are more individuals that can be potential carrier of deleterious gene and can pass on the mutation over generations. In positive selection genome undergoes changes and also restores the mutation which is beneficial to the population.
- The mutational load has two components: one produced by deleterious mutation and the other produced by beneficial mutations. Both the components of mutational load arises because an ideal population consist of individual homozygous for both beneficial as well as deleterious gene.
Segregational Load
- The segregational or the balancing load comes into play when heterozygote superiority arises in a population. For a gene with two alleles, segregational load can be computed,
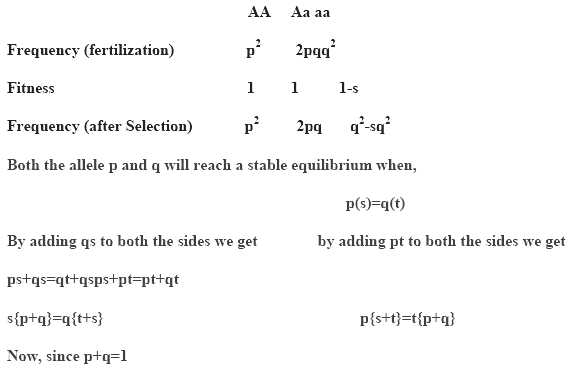
- By substituting the equilibrium frequency for q= s/s+t p=t/s+t is for the equation p2t+q2t is as follows[t/s+1]2s+[s/t+1]2t
=st2+ts2/{s+t}2
=st[s+1]/[s+t]2
=st/s+t
Therefore if s and t both are equal to 1, the segregational load will be 0.05. this value is considered higher for all the mutation rate and demonstrates that in a randomly breeding population genetic load tends to increase by segregational load rather than mutational load.
Inbreeding
- Inbreeding increases the rate of homozygosity, an inbreeding depression will be observed when the offspring’s receive two recessive and deleterious alleles resulting in a lower fitness. A declining population will experience high rate of mutation. An increase in the rate of mutation in alleles will increase the pairing frequency alleles. Due to a decline in population because of higher mutation rate, there is a chance of mating between the remaining organism to breed with their relatives and it will help in pushing out some of the harmful mutations
Sexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction has a direct effect on genetic load, it increases by pairing together of two different deleterious gene, referred to the concealed portion of genetic load. Sexual reproduction can also prevent the spread and maintenance of deleterious gene in a population due to elimination of less fit individuals. Genetic load will increase at a steady rate if mutations spreading to all offspring are slightly deleterious to the point where an individual can survive and reproduce.
Migration
- Migrational load results when an organism non-adaptive to a particular environment comes in contact with individual adapted to that environment. The offspring produced as a result of such mating are not as fit as they would have been if both of their parent where adapted to same environment. The offspring will have a lower variability rate as well as a lower overall fitness and higher will be the genetic load if individuals are from remarkably different environment.
|
209 videos|299 docs
|
















