Types of Transmission media | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Transmission Media? |

|
| Guided Media |

|
| Unguided Media |

|
Introduction
Transmission media refer to the physical pathways through which data is transmitted from one device to another within a network. These pathways can be wired or wireless. The choice of medium depends on factors like distance, speed, and interference. In this article, we will discuss the transmission media.
What is Transmission Media?
A transmission medium is a physical path between the transmitter and the receiver i.e. it is the channel through which data is sent from one place to another. Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types:
Guided Media
It is also referred to as Wired or Bounded transmission media. Signals being transmitted are directed and confined in a narrow pathway by using physical links.
Features:
- High Speed
- Secure
- Used for comparatively shorter distances
There are 3 major types of Guided Media:
1. Twisted Pair Cable
It consists of 2 separately insulated conductor wires wound about each other. Generally, several such pairs are bundled together in a protective sheath. They are the most widely used Transmission Media. Twisted Pair is of two types:
(i) Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
UTP consists of two insulated copper wires twisted around one another. This type of cable has the ability to block interference and does not depend on a physical shield for this purpose. It is used for telephonic applications.

Advantages
- Least expensive
- Easy to install
- High-speed capacity
Disadvantages
- Susceptible to external interference
- Lower capacity and performance in comparison to STP
- Short distance transmission due to attenuation
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
This type of cable consists of a special jacket (a copper braid covering or a foil shield) to block external interference. It is used in fast-data-rate Ethernet and in voice and data channels of telephone lines.
Advantages
- Better performance at a higher data rate in comparison to UTP
- Eliminates crosstalk
- Comparatively faster
Disadvantages
- Comparatively difficult to install and manufacture
- More expensive
- Bulky
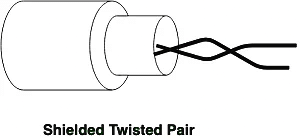
(ii) Coaxial Cable
It has an outer plastic covering containing an insulation layer made of PVC or Teflon and 2 parallel conductors each having a separate insulated protection cover. The coaxial cable transmits information in two modes: Baseband mode(dedicated cable bandwidth) and Broadband mode(cable bandwidth is split into separate ranges). Cable TVs and analog television networks widely use Coaxial cables.
Advantages
- High Bandwidth
- Better noise Immunity
- Easy to install and expand
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages
- Single cable failure can disrupt the entire network
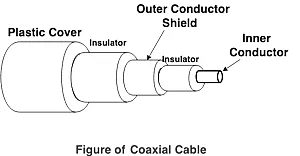
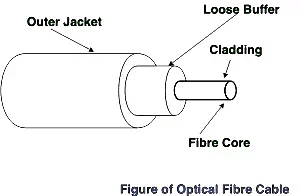
(iii) Optical Fiber Cable
- It uses the concept of refraction of light through a core made up of glass or plastic. The core is surrounded by a less dense glass or plastic covering called the cladding. It is used for the transmission of large volumes of data.
- The cable can be unidirectional or bidirectional. The WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer) supports two modes, namely unidirectional and bidirectional mode.
Advantages:
- Increased capacity and bandwidth
- Lightweight
- Less signal attenuation
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference
- Resistance to corrosive materials
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to install and maintain
- High cost
- Fragile
(iv) Stripline
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest form of the planar transmission line. It uses a conducting material to transmit high-frequency waves it is also called a waveguide. This conducting material is sandwiched between two layers of the ground plane which are usually shorted to provide EMI immunity.
(v) Microstripline
In this, the conducting material is separated from the ground plane by a layer of dielectric.
Unguided Media
It is also referred to as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media. No physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic signals.
Features:
- The signal is broadcasted through air
- Less Secure
- Used for larger distances
There are 3 types of Signals transmitted through unguided media:
(i) Radio waves: These are easy to generate and can penetrate through buildings. The sending and receiving antennas need not be aligned.
- Frequency Range: 3KHz – 1GHz. AM and FM radios and cordless phones use Radio waves for transmission.
 Further Categorized as (i) Terrestrial and (ii) Satellite.
Further Categorized as (i) Terrestrial and (ii) Satellite.
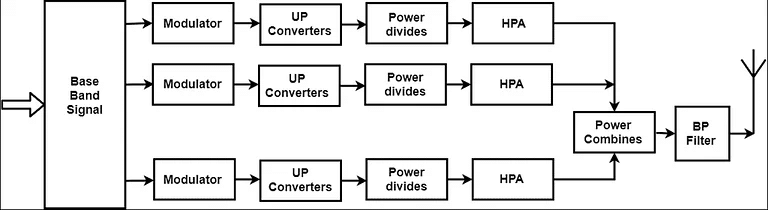
(ii) Microwaves: It is a line of sight transmission i.e. the sending and receiving antennas need to be properly aligned with each other. The distance covered by the signal is directly proportional to the height of the antenna.
- Frequency Range: 1GHz – 300GHz. These are majorly used for mobile phone communication and television distribution.
(iii) Infrared: Infrared waves are used for very short distance communication. They cannot penetrate through obstacles. This prevents interference between systems.
- Frequency Range: 300GHz – 400THz. It is used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, keyboard, printer, etc.
|
21 videos|145 docs|66 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Transmission media - Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What are the different types of transmission media used in computer science engineering? |  |
| 2. How does twisted pair transmission media work? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using fiber optic cable as a transmission medium? |  |
| 4. What is the role of transmission media in computer network communication? |  |
| 5. How does radio wave transmission media work in wireless communication? |  |















