GS - 2 | UPSC Mains Answer Writing: Practice PDF Download
- GS-2 is tricky in the sense that it’s easy to find the sources and prepare from them, yet for many aspirants, scoring above 100 feels like an uphill task. In this chapter, we will break down the syllabus, examine each segment in detail, and discuss what changes you can bring in your preparation and answer writing to improve your scores.
- Syllabus under GS-2 can be classified into two segments:
- A mistake many aspirants commit while preparing for this paper is to put too much focus on the current affairs part, at the cost of the equally important static portion. Questions from this topic pertain to Constitution, Government schemes, laws, governance and development sector etc, linking them all to some current affair issue. But, it’s not enough to just know about the issue, you need to also connect it to the theory part of the syllabus.
- In the following sections, I lay out some fundamental guidelines for answering GS-2 questions.
Polity, Governance & Social Justice
Begin with Constitutional Articles
You can start the answer as follows:
A: 73rd and 74th amendments to the Constitution established local self government in India. Some important articles pertaining to local government are 243A (Gram Sabha), 243B (Panchayats), 243G & 243W(Powers and responsibilities of Panchayats and Municipalities), 243 ZD & ZE (District and Metropolitan Planning Committee).
- This is a simple rule of thumb for Polity related questions, but works remarkably well. Whenever you read a question that has some Constitutional relevance, simply start it with the article number.
- Mentioning the article number will convey to the examiner that you have an idea about the fundamental principles of the Constitution and how it operates. Also, memorising them serves another useful purpose.
- Sometimes, questions are based on the Constitutional articles themselves without revealing other details. If you can’t figure out what that Article is about, you will be in no position to attempt that question. For instance, consider the following question:
“The Supreme Court’s use of its vast powers under Article 142 may have done tremendous good. However, it’s time to have some checks and balances.” Critically analyse the statement citing recent judgements.
- If you don’t know what Article 142 refers to, you’ll be left clueless.
- Hence, it’s critical that you remember them like the back of your hand. At first, it might seem difficult to memorise so many, but with enough revisions, it isn’t that hard. Knowing Constitutional articles will help you across every stage and paper of the exam— Prelims, Essay, GS and even the interview.
Present Both Sides of the Issue
- In GS 2, questions are usually asked on contentious topics where there is a possibility to take more than one view. In such questions, it helps to mention both sides of the argument even if not explicitly asked in the question and club them under relevant subheadings (arguments for/ arguments against) to mark a clear distinction between both. To illustrate, consider this question: “Simultaneous election to the Lok Sabha and the State Assemblies will limit the amount of time and money spent in electioneering but it will reduce the government’s accountability to the people. Discuss.”
- This is a debatable topic and one may agree or disagree with the statement. A common mistake aspirants commit is to take a side in the introduction itself and use rest of the answer to justify it repeatedly. A better approach is to present both sides of the topic with substantiation (data, facts, reasoning) and conclude the answer with what you think is right.
Use Subheadings
Adding subheadings in the main body of the answer helps in two ways:
- One, it will help you break down the question into smaller, manageable chunks
- and two, it will help you stay close to the topic that’s being asked. It will convey to the examiner that you are precisely answering the question.
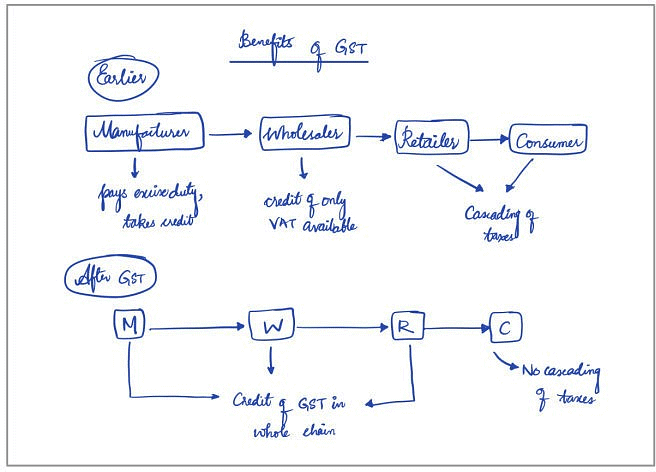
For the question: Explain the salient features of the constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act, 2016. Do you think it is efficacious enough ‘to remove cascading effect of taxes and provide for common national market for goods and services’?
Subheadings for this question would be:
- Salient Features of the Act
- GST and Cascading of Taxes
- GST and Common National Market in the current Act
- Way Forward/Suggestions
These subheadings closely align with the terms used in the question and make your answer easier for the examiner to understand.
Add Data and Statistics
- GS-2 is mostly analysis based paper with questions asking for your opinion. Merely writing arguments without facts and data would make your answers sound shallow.
- You must be armed with data and facts and mention them wherever apt. They make your arguments credible. If you want to say that India is struggling under the burden of NPAs— mention by how much, and what’s the trend of such NPA figures— is it increasing or decreasing? If you want to argue how India’s public health is in bad shape, back it up with numbers like IMR, high percentage out of pocket expenditure, MMR, scarcity of doctors, WHO standards etc.,
Further, you can also cite authentic reports from reputed international and national organisations to drive home your point. For instance, Transparency International report findings on corruption, ASER on education etc.
Mention Supreme Court Judgments
These add incredible value and authority to your arguments. In Mains, it’s always the opinion of the experts that matter. We merely convey those expert opinions. Since Supreme Court is the ultimate interpreter of laws and the Constitution, we must know about the landmark judgments of the Apex court and use them wherever relevant. Below are some of the important judgments in independent India’s history. These are by no means exhaustive. If you think I have missed some important judgements, please add and memorize this list.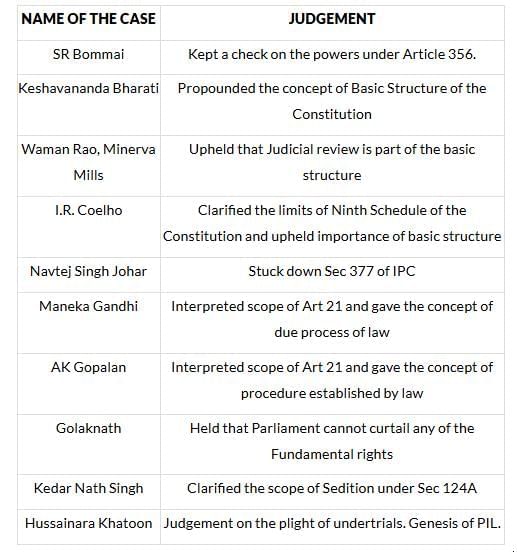
Recommendations of the Committees and Commissions
For this paper, every committee that’s in news is important. But apart from these current affairs related ones, there are a few core committees of the past whose observations and recommendations have remained timeless. You can quote them in your answers to substantiate your opinion, especially in the conclusion. The following list is not exhaustive
- 1st ARC
- 2nd ARC
- Sarkaria Commission
- Punchhi Commission Law Commission Reports NCRWC
Illustrations
Illustrations and diagrams should be drawn when it meets two conditions: one, when it helps you express more content concisely and in less time. Two, it adds value and illuminates your answer by way of introducing or explaining a concept simply; conveying geographical spread on a map etc.
International Relations
Mastering IR is about grasping a few fundamentals and applying them in your answers. Below is a list of such basics that you need to cover while preparing for this section.
Historical Backdrop
With respect to every major bilateral relationship, you must know about the history and all the important agreements/treaties we had signed with those countries. For instance, Indo-Nepal treaty of Friendship, Kyoto protocol, Indo-Sri Lanka accord etc. might be dated agreements, but you must have a fair idea about them. List 4-5 core points of each agreement, and understand them. Adding these will add authority to your answers.
Key Points to Understand for Each Agreement
- Identify the main objectives of the treaty.
- Recognize the countries involved and their roles.
- Understand the implications of the agreement on current relations.
- Note any significant outcomes or results from the treaty.
- Be aware of any amendments or changes made to the agreement over time.
Factual Details about a Current Issue
For every current affair issue, have thorough factual knowledge related to it. Example: If International Court of Justice is in news, you must know about ICJ, its structure and mandate, how cases are referred to it etc., It will help you write better answers.
Multi-Dimensional Perspectivyojae
Understand the holistic relation that India shares with important countries such as US, UK, and other neighbouring countries. It can be categorised in the following way.
- Technological: Includes all the scientific and tech related relationship. For example, India-US collaborates to address tech initiative.
- Economic: Trade and investment aspect of the bilateral relationship Global fora: How India is cooperating with that particular country in various international groupings. For example, India - Japan relationship you can mention how we are working together in ASEAN, UNSC status, how Japan is helping us at Nuclear Suppliers Group etc.,
- Strategic & Defence: In your answers, give specific names when you write about nuclear or defence cooperation. Mention the name of the equipment such as BARAK (Israel), Apache Helicopter (US), S-400 (Russia) etc. or various military exercises (SIMBEX, MILAN, Varun etc).
- Educational and Cultural: Any student exchange, tourism, establishment of universities, people to people contact initiatives etc.,
Sample Answer
In the context of the proposed amendment, it is crucial to advocate for a single, permanent tribunal to replace the existing tribunals for resolving inter-state water disputes.
Ans: Article 262 of the constitution deals with the resolution of inter-state water disputes. It envisages that:
1. Parliament may provide for adjudication of inter-state water disputes
2. Takes away powers of Supreme Court and other courts to entertain appeals against the tribunal award.
Issues with current system and need for a single tribunal
1. Membership : Current system doesn't specify term limits tribunal members.
2. Award : 8 tribunals have been established so far, but out of them, only 3 gave final awards accepted by States.
3. Delay in implementation : Many awards are appealed against in courts via PIL.
4. Non-Publication of awards in gazette leading to festering of disputes
5. Institutional problems such as no River Board established as per the River Board Act,1953 Eg : Kaveri award was given in 2007, but not implemented because of court litigation
How the new amendment speeds up settlement of water disputes
- The proposed new amendment Bill subsume existing tribunals to establish a single, permanent tribunal.
- Time limits have been specified for awards (2 years, extendable by 1 year).
- Qualification of members, term limits are outlined clearly.
- Experts from hydrology, geology etc will provide technical inputs.
- Need for Gazelle publication is removed to expedite implementation.
- A dispute resolution committee (DRC) will help in setting disputes amicably without going to tribunal (time limit - 1 year)
Way Forward
Government must implement Mihir shah committee recommendations and establish a National water commission, subsuming Central ground water commission. Also, fora like Inter-state council, zonal council, NITI Aayog etc must be harnessed for better coordination and integrated water management.
|
8 videos|605 docs
|
FAQs on GS - 2 - UPSC Mains Answer Writing: Practice
| 1. What are the key features of the Indian polity and governance system? |  |
| 2. How does the Supreme Court of India influence social justice? |  |
| 3. What recommendations have been made by committees and commissions regarding governance and social justice in India? |  |
| 4. What is the historical backdrop of social justice movements in India? |  |
| 5. How do international relations impact India's governance and social justice initiatives? |  |

















