Class 10 Physics All Formulas - PDF Download PDF Download
Physics Formulas – List of all Physics Formulas
Physics is that branch of science that basically deals with the prime constituents of matter, its characteristics and behaviour and different related elements of force and energy. Physics formulas are not meant to be memorised but conveyed in real-time and space. The application of the formulas of physics includes the concepts of mathematics and its formulas.
It is also important to remember that if one is unable to crack the theoretical part of physics, that is, understanding the theories properly, one can never find any relation between the formulas. In order to make the understanding easier, it is also recommended to know the S.I. units of Physics well.
List of All Physics Formulas
Given below is the list of all Physics formulas:
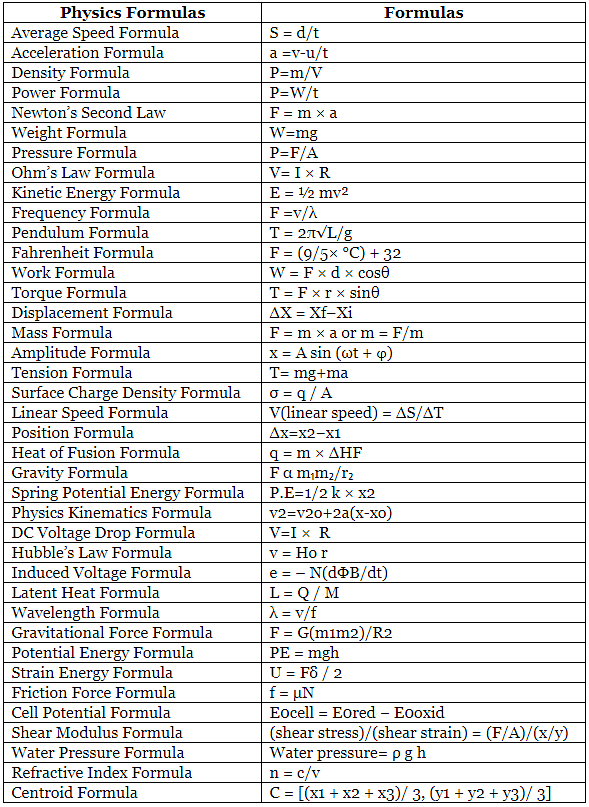
Important Physics Formulas
Given below is the most important Physics formulae list:
- Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10−34 J.s = 4.136 × 10-15 eV.s
- Gravitation constant G = 6.67×10−11 m3 kg−1 s−2
- Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 × 10−23 J/K
- Molar gas constant R = 8.314 J/(mol K)
- Avogadro’s number NA = 6.023 × 1023 mol−1
- Charge of electron e = 1.602 × 10−19 C
- Permittivity of vacuum 0 = 8.85 × 10−12 F/m
- Coulomb constant 1/4πε0 = 8.9875517923(14) × 109 N m2/C2
- Faraday constant F = 96485 C/mol
- Mass of electron me = 9.1 × 10−31 kg
- Mass of proton mp = 1.6726 × 10−27 kg
- Mass of neutron mn = 1.6749 × 10−27 kg
- Stefan-Boltzmann constant σ = 5.67 × 10−8 W/(m2 K4)
- Rydberg constant R∞ = 1.097 × 107 m−1
- Bohr magneton µB = 9.27 × 10−24 J/T
- Bohr radius a0 = 0.529 × 10−10 m
- Standard atmosphere atm = 1.01325 × 105 Pa
- Wien displacement constant b = 2.9 × 10−3 m K .
- Wave = ∆x ∆t wave = average velocity ∆x = displacement ∆t = elapsed time.
Vavg = (vi + vf*)2
- Vavg = The average velocity
- vi = initial velocity
- vf = final velocity
a = ∆v ∆t,
- a = acceleration
- ∆v = change in velocity
- ∆t = elapsed time.
∆x = vi∆t + 1/2 a(∆t)2
- ∆x = the displacement
- vi = the initial velocity
- ∆t = the elapsed time
- a = the acceleration
∆x = vf∆t − 1/2 a(∆t)2
- ∆x = displacement
- vf = is the final velocity
- ∆t = elapsed time
- a = acceleration
F = ma
- F = force
- m = mass
- a = acceleration
W = mg
- W = weight
- m = mass
- g = acceleration which is due to gravity.
f = µN
- f = friction force
- µ = coefficient of friction
- N = normal force
p = mv
W = F d cos θ or W = F!d
- W = work t
- F = force
- d = distance
- θ = angle between F and the direction of motion
KE = 1/2 mv2 K
- KE = kinetic energy
- m = mass
- v = velocity
PE = mgh
- PE = potential energy
- m = mass
- g = acceleration due to gravity
- h = height
W = ∆(KE)
- W = work done
- KE = kinetic energy.
P = W ∆t
- P = power
- W = work
- ∆t = elapsed time
FAQs on Class 10 Physics All Formulas - PDF Download
| 1. What are vectors and why are they important in physics? |  |
| 2. Can you explain the concept of projectile motion? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between work, power, and energy? |  |
| 4. How does gravity affect the motion of objects? |  |
| 5. What are the laws of reflection and refraction of light? |  |