Active and Passive Voice Rules | English Language Preparation for CUET UG PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Uses of Passive Voice |

|
| The Form of Active Voice and Passive Voice in Tenses |

|
| The following tenses cannot be changed into passive voice. |

|
| Imperative Sentences |

|
In English, the verb form which indicates whether the subject (person or object) of a sentence do something or something has been done on the subject called the voice. A sentence that begin with the subject or the object to determine whether the sentence was categorized as active or passive voice sentences.
For example, when a sentence has one auxiliary verb, such as am, are, is, been, being, be, and past participle of verbs like written, driven, drawn, known, learnt, broken, discovered; the sentence is a passive voice.
Uses of Passive Voice
- “By” is used in the passive voice when the actor needs to know the job.
Example: “Love addicted” was sung by Vamps. - Passive voice is used if it doesn’t need to know the perpetrator work.
Example: the streets are cleaned everyday - Passive voice is used if we don’t know or forget who the perpetrator work.
Example: The police was murdered. - Passive voice is used if we are more interested in the job than the actors who work.
Example: A new departmental store is being built. - Passive voice is used to avoid an awkward sentence or inappropriate with grammar.
Example: When she arrived home a police arrested her — it‟s better: when she arrived home she was arrested (by a police).
The Rules to Change the Sentences from Active to Passive Form
- The sentence must have objects (transitive verb). If there is no object then there must be question word who asks the object.
- Object active sentence became the subject of passive sentences.
- Subject or active sentences into passive sentences that preceded the object word "by”.
- The verb used is verb III (past participle) which preceded by to be.
- The adjusted sentence structure by tenses.
Fundamental Rules
- The places of subject and object are interchanged i.e. the object shifts to the place of subject and subject shifts to the place of object in passive voice.
Example:
Active voice: I write a letter.
Passive voice: I letter is written by me.
Subject (I) of sentence shifted to the place of object (letter) and object (letter) shifted to the place of subject (I) in passive voice. - Sometimes subject of sentence is not used in passive voice. Subject of sentence can be omitted in passive voice, if without subject it can give enough meaning in passive voice.
Example: Passive voice: cloth is sold in yards - 3rd form of verb (past participle) is always used as main verb in sentences of passive voice for all tenses. Base form of verb or present participle will be never used in passive voice.
The word "by” is used before subject in sentences in passive voice.
Example:
Active voice: He sings a song.
Passive voice: A song is sung by him. - The word "by” is not always used before subject in passive voice. Sometimes words "with, to, etc” may also be used before subject in passive voice.
Examples:
(i) Active voice: The water fills the tub.
(ii) Passive voice: The tub is filled with water.
Active voice: He knows me.
Passive voice: I am known to him. - Auxiliary verbs are used passive voice according to the tense of sentence.
Changes of Pronouns

The Form of Active Voice and Passive Voice in Tenses
Passive voice in Simple Present Tense
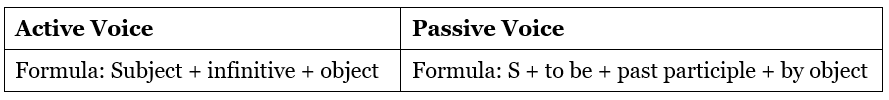
Examples:

Passive voice in Present Continuous Tense
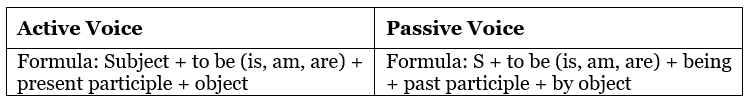
Examples: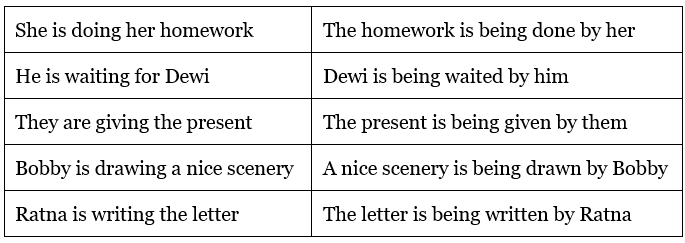
Passive voice in Simple Past Tense
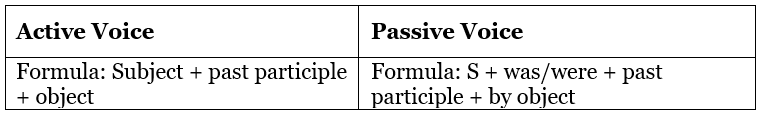
Examples: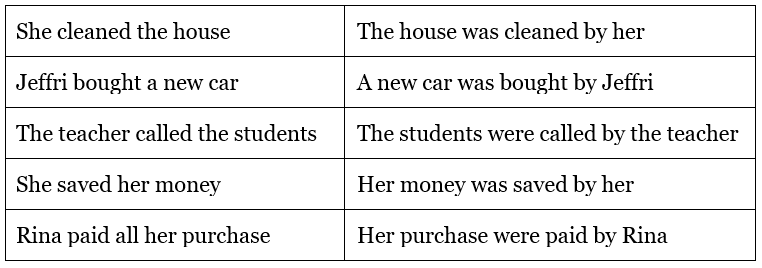
Passive voice in Past Continuous Tense

Examples:
Passive voice in Past Perfect Tense
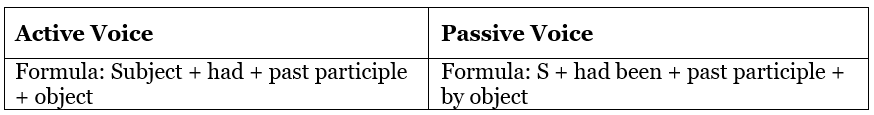
Examples: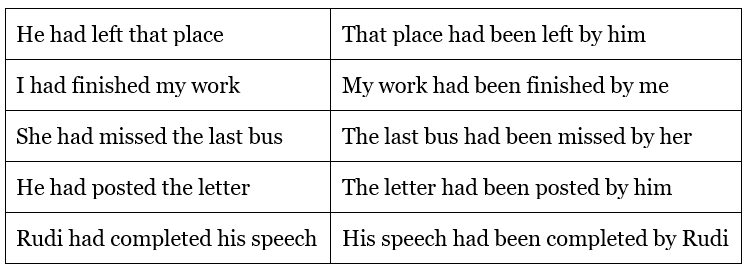
Passive voice in Simple Future Tense

Examples:
Passive voice in Future Continuous Tense
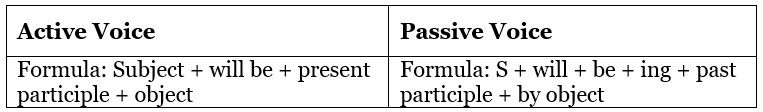
Examples: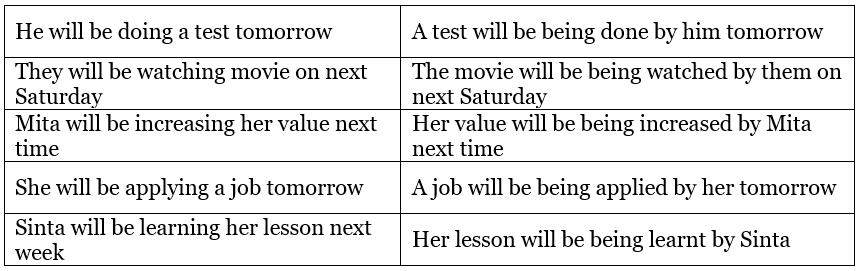
Passive voice in Past Future Tense

Examples:
The following tenses cannot be changed into passive voice.
- Present perfect continuous tense
- Past perfect continuous tense
- Future perfect continuous tense
Active and Passive voice using Modals
Active and Passive voice using Can
This modal applies to all subjects. The sentence patterns are: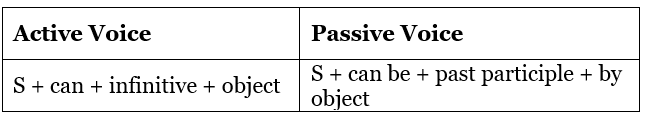
Examples:
To change the above sentence into a negative sentence, then place the word not after can. The sentence patterns are:
Active and Passive voice using May
This modal applies to all subjects. The sentence patterns are:

Examples:
To change the above sentence into a negative sentence, then place the word not after may.
Active and Passive voice using Must
This modal applies to all subjects. The sentence patterns are: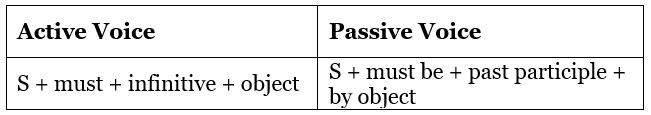
Examples: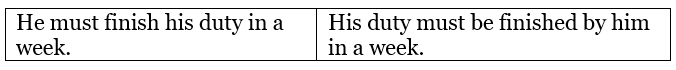
To change the above sentence into a negative sentence, then place the word not after must.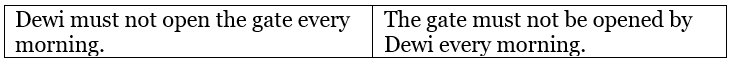
Active and Passive voice using Might
This modal applies to all subjects. The sentence patterns are: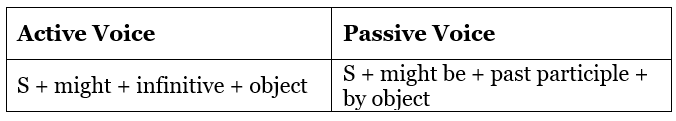
Examples:
To change the above sentence into a negative sentence, then place the word not after might.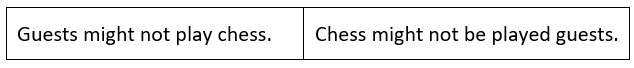
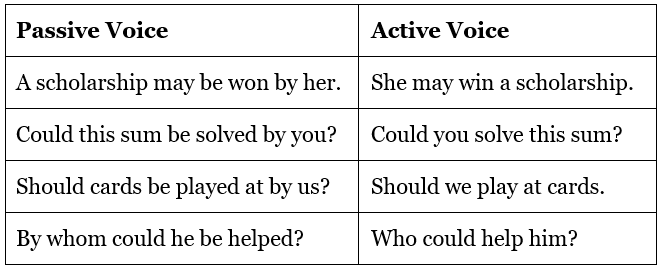
Passive voice for “May Have, Might Have, Should Have, Must Have, Ought To Have”
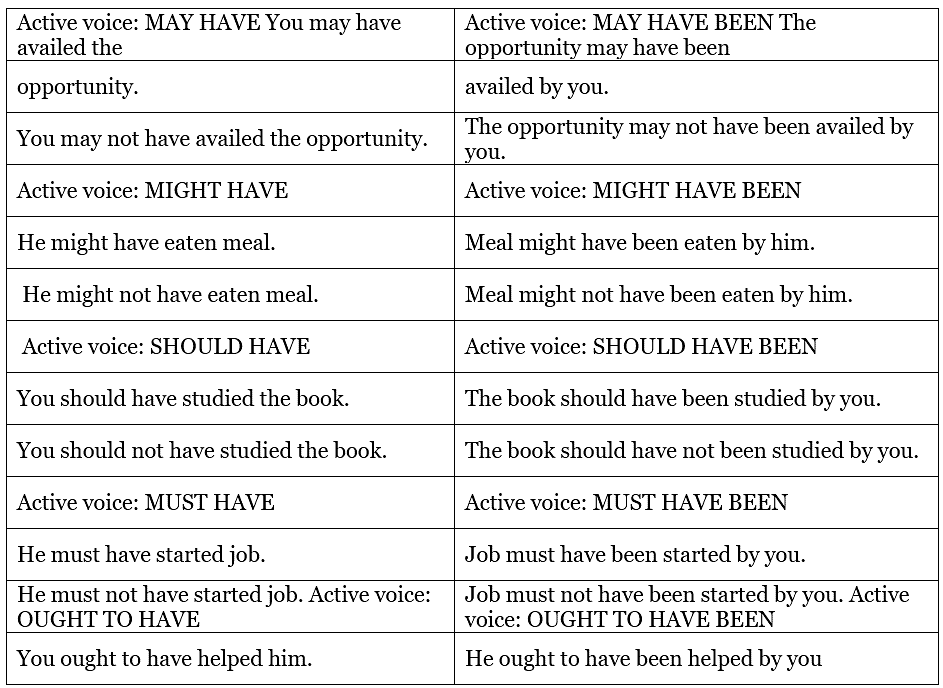
Verbs Followed by Modals (Can, could, may, might, would, should, ought)
The form of the verb is the same as that of a verb in the Simple Future Tense, i.e., modal auxiliary + be + III form.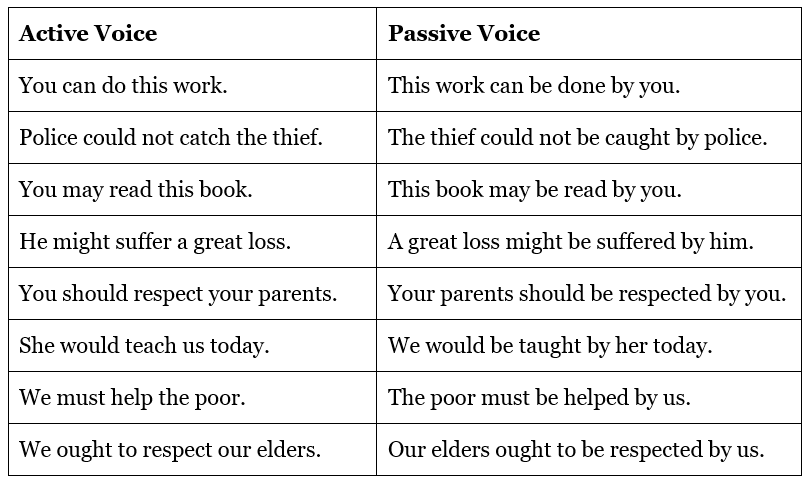
Imperative Sentences
A sentence that expresses a command, or a request or an advice, or an entreaty is called an Imperative Sentence or Desire.
Characteristics of Imperative Sentences
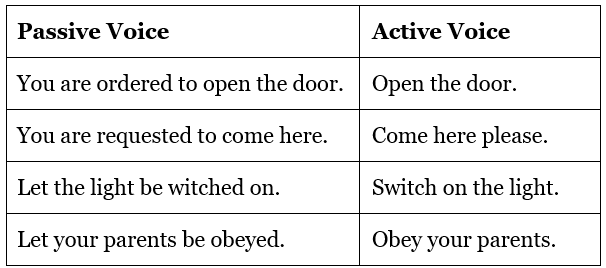
1. The object you is generally missing in Imperative Sentences. The structure of such sentences in Passive Voice is: Let + object + be/not be + V3
2. In sentences which express request, advice and order, such phrases as, You are requested to/advised to /ordered to are used.
3. Word kindly/please are dropped.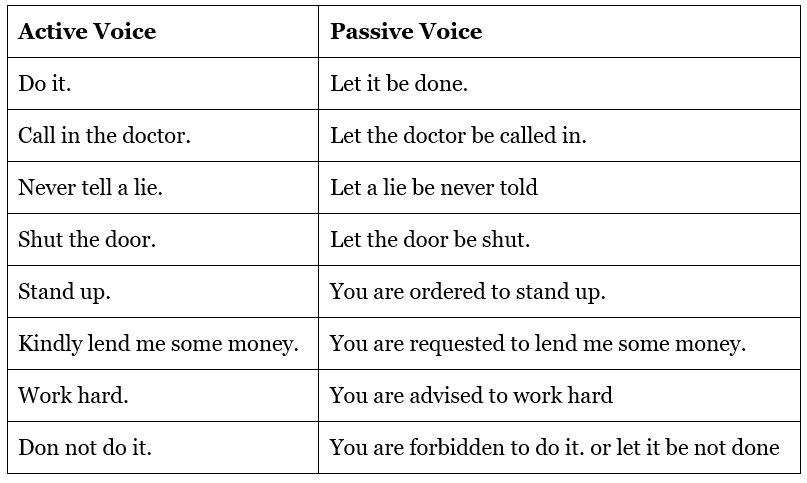
Change of Voice in the Infinitive Verbs

Verbs/phrases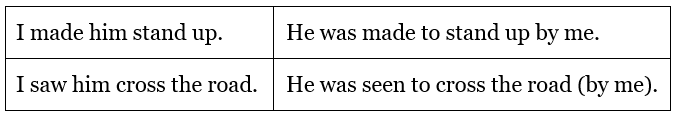
It is time to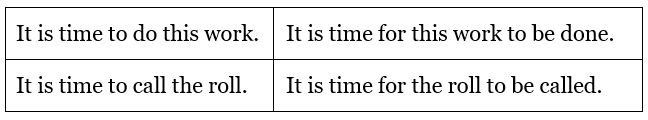
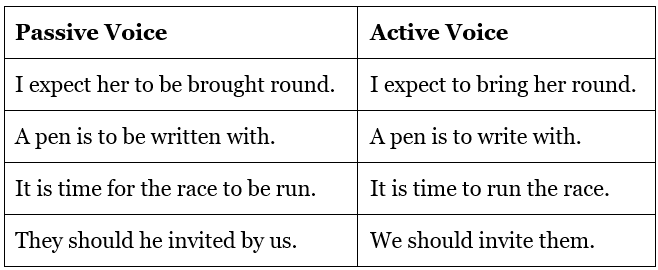
Sentences which cannot be changed into passive voice
Transitive and intransitive verb
A verb can be either transitive or intransitive. A transitive verb needs an object (in sentence) to give complete meaning while intransitive verb does need an object (in sentence) to give complete meaning.
For example:
Transitive verb: He sent a letter. (Send is a transitive verb and it needs an object i.e. letter to express full meaning.)
Intransitive Verb: He laughs. (Laugh is an intransitive verb and it does not need object for expressing full meaning.)
e.g. Sleep, go, reach, sit, die, are examples of intransitive verbs.
Intransitive verb cannot be changed into passive voice
The sentences having intransitive verbs (belonging to any tense) cannot be changed into passive voice. The reason is that there is not any object in such sentences and without object of sentence passive voice is not possible.
A sentence can be changed into passive voice if it has subject and object. Sometimes subject may not be written in passive voice but it does not mean that it has no subject. Such sentences have subject but the subject is so common or familiar or known that if even it is not written in passive voice, it gives full meaning.
For example: Cloth is sold in yards.
|
70 videos|84 docs|90 tests
|




















