UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 13th January 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Gangasagar Mela

Context
Lakhs of pilgrims are descending on Sagar Island in the southernmost tip of West Bengal for the annual Gangasagar Mela, being held between January 12 and 14, to celebrate Makar Sankranti.
What is Gangasagar Mela?
- Every year during Gangasagar mela, devotees from all over the country gather at the confluence of the Ganga and the Bay of Bengal to take a sacred dip during Makar Sankranti (mid-January).
- The mela is said to be India’s second largest pilgrimage gathering after the Kumbh Mela.
- Gangasagar, the largest and the oldest living tradition in Bengal, has been mentioned in Indian epics such as the Ramayana and Mahabharata, putting its existence as early as 400 BCE.
- Legends suggest that the first Kapil Muni’s temple was constructed by Queen Satyabhama in 430 AD, and the present idol was established by Swami Ramanand in 1437, marking the beginning of a pilgrimage that remains timeless till today.
About Sagar Island
- Sagar Island is an island in the Ganges delta, lying on the Continental Shelf of Bay of Bengal about 100 km (54 nautical miles) south of Kolkata.
- This island forms the Sagar CD Block in the Kakdwip subdivision of South 24 Parganas district in the Indian State of West Bengal.
- Although Sagar Island is a part of the Sundarbans, it does not have any tiger habitation or mangrove forests or small river tributaries as is characteristic of the overall Sundarban delta.
- This island is a place of Hindu pilgrimage.
- Every year on the day of Makar Sankranti (14 January), hundreds of thousands of Hindus gather to take a holy dip at the confluence of river Ganges and Bay of Bengal and offer prayers (puja) in the Kapil Muni Temple.
Source: Indian Express
Discretionary Haj Quota in India

Context
The Union Minister for Minority Affairs has done away with the discretionary Haj quota for pilgrims, in keeping with Prime Minister’s resolve to end VIP culture in the country.
About Haj Pilgrimage
- The holy Haj is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims.
- It is considered to be a mandatory religious duty for all adult Muslims physically and financially capable of doing so.
- The rites of pilgrimage are performed over five to six days, in Dhu al-Hijjah, the last month of the Islamic calendar.
How is it managed?
- For the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the pilgrimage poses a massive logistical challenge.
- Housing, feeding and facilitating safe pilgrimages for millions of pilgrims who descend upon Mecca from across the world during a brief period of time is difficult, to say the least.
- Thus, Saudi Arabia allots country-wise quotas which determine the total number of pilgrims who can make a journey from a particular country.
- These quotas are broadly allotted on the basis of the number of Muslims a country houses. However, the quotas are also major diplomatic issues.
- Every year, countries lobby Saudi Arabia for more slots. After a Covid-19-related lull, the pilgrimage will resume at its full scale in 2023.
How India manages this?
- India signed the Haj 2023 bilateral agreement with Saudi Arabia.
- According to the agreement, a total of 1,75,025 Indian Haj pilgrims will be able to perform Haj, reportedly the highest in history.
- This quota allotted to India is then further distributed by the Ministry of Minority Affairs and the Haj Committee of India (HCoI) to various stakeholders.
- According to the 2018-22 policy document, 70 per cent of India’s total quota goes to the HCoI and 30 per cent goes to private operators.
Distribution of Quotas
- Out of the total number of slots with the HCoI, 500 are held under the Government discretionary quota whereas the rest are distributed to different states on the basis of their Muslim population.
- A draw of lots is conducted in each state to determine who makes the journey in case the number of applicants exceed the number of slots available.
What are the haj discretionary quotas?
- The “Government discretionary quota” is further divided in two, 200 seats are with the Haj Committee itself and 300 are with people holding important offices at the Centre. These include,
- 100 with the President
- 75 with the Prime Minister
- 75 with the Vice President
- 50 with the Minister of Minority Affairs
- As per the old policy, these seats could be allocated to individuals who applied for the pilgrimage through normal means but were unsuccessful in getting a slot for the pilgrimage.
- This quota has now been abolished with these seats being added back to the general pool.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
United Nations Institute for Water, Environment and Health (UNU-INWEH)
Context
A report was recently released by United Nations Institute for Water, Environment and Health (UNU-INWEH) that stated that world will lose 26% storage by 2050 to trapped sediment.
About UNU-INWEH:
- UNU-INWEH was established in 1996 as subsidiary body of the United Nations University (UNU) institutes and an academic arm of the UN.
- Its operations are secured through long-term host-country and core-funding agreements with the Government of Canada.
- The Institute is located in Hamilton, Canada; its facilities are supported by McMaster University.
- It specializes on water for development, working, primarily with countries in the Global South, and addressing water issues of global significance.
- It is the UN Think Tank on Water created by the UNU Governing Council.
- UNU-INWEH is the only Institute in UNU that focuses entirely and solely on water issues.
- It is also the only entirely water-focused UN entity in Canada.
- UNU-INWEH is linked to key processes in the UN system, and represents the entire UNU in UN-Water – a cross-agency group in the UN and international partners working on water and sanitation issues globally.
Important findings of the report:
- About 50,000 large dams across the world will lose 24-28 % water storage capacity by 2050 due to sediment trapped in them.
- These water reservoirs have already lost about 13-19 % capacity to sedimentation.
- Sedimentation is caused when a river carrying eroded soil is blocked by a dam at its watershed.
- Sediment helps to maintain the aquatic ecosystem.
- Poor management Sedimentation can lead to nutritional disbalances causing eutrophication, damages in habitations downstream, choke of dam and turbine system.
- Shallow water formed due to sedimentation also reduces the recreational value of the reservoirs.
- United Kingdom, Panama, Ireland, Japan and Seychelles will experience highest water storage losses by 2050 losing between 35% and 50% of their original capacities.
- Bhutan, Cambodia, Ethiopia, Guinea and Niger will be five least-affected countries losing less than 15 % by 2050.
- Dredging can be costly and only temporary.
- Dredging- to clear the mud from the bottom of a river, canal, etc. using a special machine.
Major highlights of the report in the Asia-Pacific region:
- Asia has 35,252 large dams, making it the world’s most heavily dammed region.
- Region has 60% of the world’s population and water storage is crucial for sustaining water and food security.
- In 2022, region will lose 13% of its initial dam storage capacity.
- It will lose nearly a quarter (23%) of initial storage capacity by 2050.
- Loss of storage capacity of Japan’s 3,052 dams is most acute in the region.
- India’s Central Water Commission reported in 2015 that-
- Among 141 large reservoirs that are over 50 years old, one-quarter had already lost at least 30% of their initial storage capacity.
- UNU-INWEH estimates that India’s 3,700 large dams will have lost on average 26% of their initial total storage by 2050.
- China, world’s most heavily dammed nation has lost about 10% of its storage and will lose a further 10% by 2050.
Source: DownToEarth
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights
Context
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights is celebrating its 18th Foundation Day.
- A Quiz was launched by the Commission on the occasion of National Youth Day (Swami Vivekananda Jayanti) to create awareness among children about child rights.
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights
- The Commission is a statutory body constituted under Section 3 of the Commission for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005
- It aims to protect the child rights and other related matters in the country.
- The Commission is further mandated to monitor the proper and effective implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012; Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 and Right to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009.
- In one of the functions laid down under Section 13 of the CPCR Act, 2005, the Commission has been assigned with the function to examine and review the safeguards provided by or under any law for the time being in force for the protection of child rights and recommend measures for their effective implementation.
- The Commission also has the powers of Civil Court trying a suit under Section 14 of CPCR Act, 2005 and Code of Civil Procedure, 1908.
- It works under the aegis of Ministry of Women and Child Development
Source: PIB
Mental Health Problem and effective policy
Context
The fifth Global Mental Health Summit, co-sponsored by over half a dozen organisations engaged with mental health, was held in Chennai to discuss mental health in the context of human rights, ethics and justice. Highlighting the importance of mental health, it gave a call for action against the continued neglect by society at large and the governments at central and state levels, in particular.
Findings of national mental health survey
- The National Mental Health Survey (NMHS): The latest National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) conducted by National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS) in collaboration with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and WHO, was published in 2016.
- Prevalence of mental disorder: According to the survey, the prevalence of mental disorders among adults in India is around 10.6%. The most common disorders were anxiety disorders (7.3%) and mood disorders (4.5%).
- Higher among women than men: The survey also found that the prevalence of mental disorders was higher among women than men, and that the majority of people with mental disorders did not receive any treatment.
- Prevalence of mental disorders is higher in urban areas: It also found that the prevalence of mental disorders was higher in urban areas than in rural areas, and that there was a higher prevalence of mental disorders among people with lower levels of education and income.
- Gap in treatment coverage for people with mental disorder : The survey highlighted that there is a significant gap in treatment coverage for people with mental disorders, and that the majority of people with mental disorders do not receive any treatment.
- Plan for mental health: The survey has provided an important information for Indian government and mental health professional to plan and implement mental health programs and policies in the country.
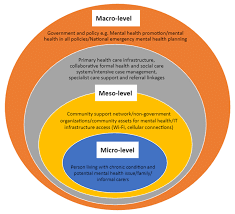
What constitutes good policy making on mental health?
- Policy should be based on research and findings: Policies should be based on sound research and evidence from scientific studies. This helps to ensure that policies are effective in addressing mental health issues and are not based on assumptions or stereotypes.
- Active engagement of stakeholders: Policy making should involve a wide range of stakeholders, including people with lived experience of mental health issues, mental health professionals, and representatives from relevant government departments and non-governmental organizations.
- A comprehensive and integrated approach: Mental health policies should be comprehensive and address a wide range of issues, including prevention, early intervention, treatment, and recovery. They should also be integrated with other policies, such as those related to education, housing, and employment.
- Ensure easy access to mental health care: policies should ensure that people have access to appropriate and affordable mental health care, including both medication and psychosocial therapies.
- Public awareness and Sensitization : policies should ensure that people with mental health issues are treated with dignity and respect, and that their human rights are protected.
Case study: How India tackled HIV/AIDS?
- Active surveillance system: The need for crafting strategic interventions based on epidemiological evidence from an active surveillance system.
- Modelling different options: The importance of modelling different options of addressing the wide array of interventions required in different geographies, among different target groups, to provide the data related to cost effectiveness as well as efficacy of the interventions required for scaling up.
- Proactive advocacy of systemic issues among all influencers: The proactive advocacy of systemic issues among all influencers the media, judiciary, politicians, police and other intersectoral departments whose programmes and activities have had a direct bearing on the key populations being worked on.
- Community engagement: The use of peer leaders and civil society that was allocated over 25 per cent of the budget. Though a central sector programme was fully funded by the central government, every intervention was formulated with active participation and dialogue among the states and constituencies of local leaders.
Strategy for better implementation of mental health policy
- Clear goals and objectives: Having clear and measurable goals and objectives can help to ensure that policies are implemented effectively and that progress can be tracked.
- Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity building for mental health professionals, as well as for other relevant stakeholders such as community leaders, can help to ensure that policies are implemented effectively.
- Community engagement: Involving communities in the planning and implementation of mental health policies can help to ensure that policies are responsive to the specific needs and priorities of local populations.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Regularly monitoring and evaluating the implementation of policies can help to identify any barriers or challenges, and make adjustments as necessary.
- Multi-sectoral approach: Adopting a multi-sectoral approach that involves collaboration between different sectors, such as health, education, social welfare, housing, and employment can help to ensure that policies are implemented in a coordinated and effective manner.
- Policy flexibility: Policies should be flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances, and be responsive to feedback and suggestions from the community and stakeholders.
latest research in mental health domain
- The growing recognition of the importance of early intervention in mental health: Research has shown that early intervention can prevent mental health issues from becoming more severe, and can help individuals to recover more quickly.
- The use of technology in mental health: There has been an increase in the use of technology, such as mobile apps, virtual reality, and teletherapy, to deliver mental health care. Studies have shown that these technologies can be effective in improving mental health outcomes.
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health: The pandemic has had a significant impact on mental health, and research has been conducted to understand the extent of the impact and to develop strategies to mitigate it.
- Advancements in brain imaging and genetics: Researchers are using brain imaging techniques and genetic studies to gain a better understanding of the underlying causes of mental disorders and to develop more effective treatments.
- The use of personalized medicine in mental health: There is growing interest in the use of personalized medicine, which involves using genetic and other information to tailor treatment to the individual patient, to improve mental health outcomes.
- The benefits of nature-based interventions for mental health: Studies have shown that spending time in nature can have a positive impact on mental health, including reducing symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression.
- The importance of social determinants of mental health: Research has highlighted the importance of social determinants such as poverty, education, and social support in mental health.
- The importance of addressing mental health in the workplace: Studies have highlighted the impact of workplace stress and burnout on mental health and the importance of workplace interventions to promote mental well-being.
Conclusion
Mental health problems and not related to age of persons. From children to old age all can suffer from this menace. Government of the must formulated, implement the effective, resulted oriented mental health policy as earliest as possible
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
CII Bio-Energy Summit

Context
The Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas & Housing and Urban Affairs was addressing the 11th edition of CII Bio-Energy Summit.
- India has increased the ethanol blending in petrol from 1.53% in 2013-14 to 10.17% in 2022.
- setting up 2G refineries to make ethanol from Parali (Panipat) and Bamboo (Numaligarh) with the twin objective of reducing pollution along with achieving energy security goals is another milestone in this direction.
- Green Hydrogen Policy with a production target of 5 million tonnes by 2030 and aims to produce 4 MT Green Hydrogen annually & accrue Rs. 1 lakh crore of cumulative fossil fuel import savings by 2030.
The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII)
- CII is a non-government, not-for-profit, industry-led and industry-managed organization
- It was founded in 1895
- It has 9000 members from the private as well as public sectors, including SMEs and MNCs, and an indirect membership of over 300,000 enterprises from 286 national and regional sectoral industry bodies.
- With 62 offices, including 10 Centres of Excellence, in India, and 8 overseas offices in Australia, Egypt, Germany, Indonesia, Singapore, UAE, UK, and USA, as well as institutional partnerships with 350 counterpart organizations in 133 countries, CII serves as a reference point for Indian industry and the international business community.
Aim:
- It works to create and sustain an environment conducive to the development of India, partnering Industry, Government and civil society, through advisory and consultative processes.
Functions:
- CII charts change by working closely with Government on policy issues, interfacing with thought leaders, and enhancing efficiency, competitiveness and business opportunities for industry through a range of specialized services and strategic global linkages.
- It also provides a platform for consensus-building and networking on key issues.
- CII assists industry to identify and execute corporate citizenship programmes.
- Partnerships with civil society organizations carry forward corporate initiatives for integrated and inclusive development across diverse domains including affirmative action, livelihoods, diversity management, skill development, empowerment of women, and sustainable development, to name a few.
Source: PIB
Local Bubble
Context
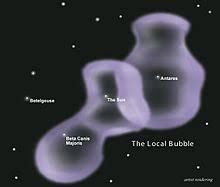
Researchers from the Center for Astrophysics (CfA) | Harvard & Smithsonian have generated a 3D magnetic map of the cavity called Local Bubble.
Local Bubble:
- It is a 1,000-light-year-wide cavity or a superbubble.
- Local Bubble is thought to have originated from supernovae roughly 14 million years ago. (Supernova is a cosmic explosion occurring when stars meet their end)
- Other superbubbles also exist in the Milky Way –
- Superbubbles are comparable to holes in Swiss cheese – Supernova explosions blow holes in the cheese and new stars form around these holes
Significance:
- Superbubbles trigger the formation of new stars and planets and influence the overall shapes of galaxies
- Star-forming regions occur along the bubble’s surface.
About the study:
- Mechanisms powering the formation and expansion of the Local Bubble are not well-understood
- Further, there is little information on how magnetic fields likely impact the bubble and local star formation.
- To generate a magnetic map of the Local Bubble, Gaia and Planck were used — space-based observatories launched by the European Space Agency (ESA)
- Gaia was used to identify the location and local concentration of cosmic dust. This helped them trace the boundaries of the Local Bubble.
- Planck provided information on the magnetic alignment of cosmic dust. This alignment can indicate the orientation of the magnetic field acting on the dust particles, allowing the researchers to generate a 3D magnetic field orientation on the surface of the Local Bubble
- It is expected to improve the 3-D map’s accuracy with technology and a clearer understanding of the Local Bubble
Source: DTE
White Tufted Royal Butterfly
Context
A team of butterfly observers have recently found White Tufted Royal Butterfly, a rare butterfly species at Kalliyad in Kannur.
- The species had earlier been spotted in Agasthyakoodam in 2017 and the Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuary in 2018.
About White Tufted Royal Butterfly:
- It is protected under Schedule 2 of the Wildlife Protection Act 1972.
- Its wingspan is just 32-40 mm.
- Its larvae feed on Scurrula parasitica, a plant belonging to the Loranthaceae family.
- It is also known as Pratapa deva.
- It is found in Indomalayan realm.
- There are eight species of this butterfly where 2 are common and others rare.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5275 docs|1115 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 13th January 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the subjects covered in GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III for UPSC exams? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III for UPSC exams? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of daily current affairs in the UPSC exam preparation? |  |
| 4. How can I stay updated with daily current affairs for UPSC exams? |  |
| 5. What is the level of complexity expected in the UPSC exam questions related to GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III? |  |