UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th January 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Gandhi Smarak Bhawan

Context
Recently the former in-charge of the Gandhi Smarak Bhawan in Punjab was arrested and remanded him in three days of police custody.
About Gandhi Smarak Bhavan:
- Gandhi Smarak Nidhi (GSN) was established by the Indian National Congress after the martyrdom of Mahatma Gandhi in 1948.
- It was inaugurated by Dr. Zakir Hussain then Vice-President of India.
- It is being run by GANDHI SMARAK NIDHI PUNJAB, HARYANA and HIMACHAL PRADESH and since its inception is contributing its share in spreading Gandhian thought and Ideology through Seminar, Meetings, Discussions and personal contacts.
- The ad hoc committee constituted as per the decision taken in February 1948 included great national leaders – Dr. Rajendra Prasad, Pt. Jawahar Lal Nehru, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Chakravarty Rajagopalachari, Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad and Shri Jagjivan Ram amongst many others.
- In December 1948 the GSN was constituted as a public charitable Trust having a 24 member Board of Trustees including the above national leaders along with other equally eminent national leaders.
- The main purposes of the fund was to further the manifold constrictive activities in which Gandhiji was interested, and to preserve and propagate his teachings.
- When in 1966 the Punjab State divided into three states then Trust renamed as Gandhi Smarak Nidhi Punjab, Haryana and Himachal Pradesh.
- The Nidhi’s headquarter is situated in Swadhyay Ashram, Village Pattikalyana, Tehsil Samalkha, District Panipat, Haryana (India).
Source: Indian Express
Avalanches: Authorities warn of avalanches in 11 districts of Jammu and Kashmir
Context
A day after two workers were killed in an avalanche near the Zojila tunnel in Sonamarg, Jammu and Kashmir, the area was struck by twin avalanches.
- The State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA) issued a warning regarding avalanches above 2,000 meters over Anantnag, Bandipora, Baramula, Doda, Poonch, etc., in the next 24 hours.
What is an Avalanche?
- When a mass of snow, rock, ice, soil, and other material slides rapidly down a mountainside it leads to an Avalanche.
- Avalanches of rocks or soil are often called landslides, while snow slides are the most common kind of avalanche.
- A snow avalanche begins when an unstable mass of snow breaks away from a slope and picks up speed and more snow as it moves downhill, producing a river of snow and a cloud of icy particles that rises high into the air.
- A large, fully developed avalanche can weigh as much as a million tons and can travel faster than 320 kms per hour and may lead to loss of life or property.
What are the Main Types of Snow Avalanches?
- Sluff Avalanches is a small slide of dry, powdery snow that occurs when the weak layer of a snowpack is on the top.
- Slab Avalanches occur when the weak layer lies lower down in a snowpack and when it breaks off it pulls all the layers on top of it down the slope.
What are the Factors that Destabilise the Snowpack?
- Snow avalanches are most likely to occur after a fresh snowfall adds a new layer to a snowpack.
- Avalanches can be triggered by natural forces, such as the pull of gravity on a steep slope, earthquakes, warming temperatures (weakening the bonds between the layers), wind, terrain, vegetation and general snowpack conditions.
- They can also be caused by human activity, such as the load of a skier, construction/development activities or by use of explosives (to set off hazardous slopes) as part of avalanche control.
What are the Avalanches Prone Areas in India?
- The Himalayas are well known for the occurrence of snow Avalanches particularly Western Himalayas - the snowy regions of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Western Uttar Pradesh.
- There are three types of snow avalanche zones –
- Red Zone: The most dangerous zone that have an impact pressure of more than 3 tonnes per square metre.
- Blue Zone: Where the avalanche force is less than 3 tonnes per square metre and where living and other activities may be permitted.
- Yellow Zone: Where snow avalanche occurs only occasionally.
What are the Measures to Control Avalanches?
- Currently, scientists are not able to predict with certainty when and where avalanches will happen.
- However, they can estimate hazard levels and designate vulnerable zones by checking on the snowpack, temperature and wind conditions.
- By building large, sturdy structures to anchor snowpacks and ban unsustainable developmental and tourism activities in Avalanche hazardous zones.
Source: Mint
GS-II
Regulation of Hate speech

Context
Recently, the Supreme Court reprimanded the government for its failure to stop hate speech and hate crimes in the country.
About Hate Speech:
- Hate speech is defined as any speech, gesture, conduct, writing, or display that may incite violence or prejudicial action against or by any individual or group, or because it disparages or intimidates a particular individual or group.
Significance of Curbing Hate Speech:
- It is used to provoke individuals or society to commit acts of terrorism, genocides, ethnic cleansing etc.
- It undermines social equality as it reaffirms historical marginalization, oppression & discrimination.
- It is enacted to cause psychological and physical harm to its victims as it incites violence.
- It is a tool to create panic through rumour mongering against targeted people. For example, the Northeast exodus.
Laws and regulations on hate speech in India: In India, hate speech is regulated by several laws and acts, including the Indian Penal Code (IPC), the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), and the Indian Information Technology (IT) Act.
- Indian Penal Code (IPC): It contains provisions that prohibit hate speech, such as :
- Section 153A: It deals with actions promoting enmity between different groups on grounds of religion, race, place of birth, residence, language, etc., and doing acts prejudicial to maintenance of harmony.
- Section 295A: It deals with deliberate and malicious acts, intended to outrage religious feelings of any class by insulting its religion or religious beliefs.
- Section 505: It pertains to statements creating or promoting enmity, hatred or ill-will between classes)
- Indian Information Technology (IT) Act: It regulates online speech, including hate speech. Under the act, intermediaries such as social media platforms are required to remove content that is in violation of the law within 36 hours of being notified.
- Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC): It provides for the arrest of individuals who have committed a cognizable offense, such as hate speech.
- Representation of People’s Act(1951):
- Section 8: It prevents a person convicted of the illegal use of the freedom of speech from contesting an election.
- Sections 123(3A) and 125 of the RPA: It bars the promotion of animosity on the grounds of race, religion, community, caste, or language in reference to elections and includes it under corrupt electoral practices.
- Court Judgements: In the past, The Supreme court of India has issued several judgments on hate speech.
- Shreya Singhal v. Union of India (2015): The court struck down Section 66A of the IT Act, which had criminalized online speech, stating that it violated the right to freedom of speech and expression.
- Sukumar v. State of Tamil Nadu (2019): The court held that hate speech on social media platforms is not protected by the right to freedom of speech and expression.
- Freedom of speech: The right to freedom of speech is protected under Article 19 of the Constitution but it is not absolute and can be limited in certain circumstances, such as when it incites violence or discrimination.
- Online Hate speech: The internet has made it easier for hate speech to spread, and many social media platforms have policies in place to address hate speech on their platforms.
- However, the effectiveness of these policies can be limited, and more needs to be done to combat online hate speech.
- Prevention: It begins with education, raising awareness about the harmful effects of hate speech and promoting tolerance and inclusivity.
- In this regard, the government, civil society organizations and communities at large can play a role in preventing hate speech.
Challenges before curbing Hate speech:
- Defining hate speech: There is no universally accepted definition of hate speech, and different countries and cultures have different norms and expectations in this area.
- This makes it difficult to establish clear guidelines for what constitutes hate speech and what does not.
- Addressing hate speech by public figures and politicians: Expression of hate is not limited to anonymous internet users, public figures and politicians also contribute to spreading hate speech.
- However, due to their public platform, it may be challenging to hold them accountable for their statements.
- Identifying and removing hate speech online: The vast majority of hate speech takes place online, and it can be difficult to identify and remove this content.
- Platforms like Facebook and Twitter have struggled to effectively moderate hate speech, and there is no consensus on how to approach this problem.
- Balancing free speech and hate speech: Hate speech laws are often viewed as a restriction on free speech. This can lead to legal challenges and pushback from civil liberties groups.
- Addressing hate speech in non-English languages: Hate speech is not limited to English-speaking countries, and it can be difficult to identify and remove hate speech in other languages. Additionally, cultural and linguistic nuances may not be well understood by those trying to moderate content.
- Lack of resources and legal framework: Many countries lack the resources and legal framework to effectively address hate speech.
- This can make it difficult to enforce laws and regulations, and it can also create a sense of impunity for those who engage in hate speech.
Way Forward:
India has a diverse population with different languages, religions, and cultures, thus there is a need to curb incidents of hate speech and crimes that can have a detrimental impact on individuals and communities. It is a complex and multifaceted issue that poses significant challenges for regulators and policymakers which will require a multifaceted approach that includes education, technology, and legal enforcement.
Thus, it becomes important for governments, civil society organizations, and individuals to work together to combat hate speech and promote a more inclusive and tolerant society.
Source: The Hindu
Who are the Wagner Group of mercenaries?

Context
The leader of the Wagner Group of mercenaries is using the Russian assault on the Donetsk town of Soledar to "elevate his political stature and indirectly criticize the conventional Russian military," according to an update published by the Institute for the Study of War (ISW).
About Wagner Group:
- What is it? The Wagner Group also known as PMC Wagner is a Russian paramilitary organization.
- Origin: The group is believed to have been founded in 2014 by a Russian veteran of the Chechen war who so admired Hitler he named the group after Richard Wagner, the führer's favorite composer.
- The skull is the symbol of the Wagner Group.
- The organization first came to the world's attention in 2014, fighting alongside Russian-backed separatists in the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine.
- The organization has also been active across Africa in recent years — Libya, Sudan, Mozambique, Mali and the Central African Republic.
- Today there are thought to be some 10,000 Wagner Group members.
- The U.S. government has called Wagner a "proxy force" of Russia's defense ministry.
What does the term ‘führer’ mean?
- Führer, also spelled Fuehrer means leader.
- It is a title used by Adolf Hitler to define his role of absolute authority.
- As early as July 1921 he had declared the Führerprinzip (“leader principle”) to be the law of the Nazi Party.
Source: Indian Express
Competition Commission of India
Context
Google has said that the order passed by India’s competition regulator — the Competition Commission of India (CCI) — against Android’s operating system policies will result in devices getting expensive in India and lead to proliferation of unchecked apps that will pose threats for individual and national security.
About Competition Commission of India:
- The Competition Commission of India has been established to enforce the competition law under the Competition Act, 2002.
- It comes under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- It should be noted that on the recommendations of Raghavan committee, the Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 (MRTP Act) was repealed and replaced by the Competition Act, 2002.
- The Commission consists of a Chairperson and not more than 6 Members appointed by the Central Government.
- It is the statutory duty of the Commission to eliminate practices having an adverse effect on competition, promote and sustain competition, protect the interests of consumers and ensure freedom of trade carried on by other participants, in markets in India as provided in the Preamble as well as Section 18 of the Act.
- The Commission is also mandated to give its opinion on competition issues to government or statutory authority and to undertake competition advocacy for creating awareness of competition law.
- Advocacy is at the core of effective competition regulation.
- Competition Commission of India (CCI), which has been entrusted with implementation of law, has always believed in complementing robust enforcement with facilitative advocacy.
- It is a quasi-judicial body.
- CCI also approves combination under the act so that two merging entities do not overtake the market.
The Competition Act
- The Competition Act, 2002, as amended by the Competition (Amendment) Act, 2007, follows the philosophy of modern competition laws.
- The Act prohibits anti-competitive agreements, abuse of dominant position by enterprises and regulates combinations (acquisition, acquiring of control and M&A), which causes or likely to cause an appreciable adverse effect on competition within India.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
Trend in Investments

Context
A sharp 61.2% sequential rise in capital spending by the Central and State governments lifted fresh investment plans announced in the third quarter (Q3) of 2022-23 to ₹7.1 lakh crore, even though private sector investments dropped 41% from ₹6.31 lakh crore in Q2 to ₹3.71 lakh crore between October and December 2022.
- Rising input costs, hardening interest rates and the slowdown expected in developed economies are the headwinds making mid-size Indian companies go slow on their investment plans
- However, all other major sectors posted positive growth in terms of fresh investments during the first nine months of 2022-23.
Capital Expenditure:
- Capital expenditure is the money spent by the government on the development of long term assets such as machinery, equipment, building, health facilities, education, etc.
- It also includes the expenditure incurred on acquiring fixed assets like land and investment by the government that gives profits or dividend in future.
- Capital spending is associated with investment or development spending, where expenditure has benefits extending years into the future.
- It includes – Acquiring fixed and intangible assets, Upgrading an existing asset, Repairing an existing asset, Repayment of loan
Significance of capital expenditure:
- It allows the economy to generate revenue for many years by adding or improving production facilities and boosting operational efficiency.
- It also increases labour participation, takes stock of the economy and raises its capacity to produce more in future.
- Repayment of loan is also capital expenditure, as it reduces liability.
Revenue expenditure:
- Unlike capital expenditure, which creates assets for the future, revenue expenditure is one that neither creates assets nor reduces any liability of the government.
- Salaries of employees, interest payment on past debt, subsidies, pension, etc, fall under the category of revenue expenditure. It is recurring in nature.
Source: The hindu
Alternate Investment Fund and Credit Default Swap
Context
The Securities and exchange board of India has allowed alternative investment funds) to participate in credit default swaps (CDS) as protection for both buyers and sellers.
- Category I and Category II AIFs may buy CDS on underlying investment in debt securities, only for the purpose of hedging.
- Category III AIFs may buy CDS for hedging or otherwise, within permissible leverage
- Credit default swap market is very illiquid at present.
Alternate Investment Fund(AIFs):
- In India, AIFs are defined in Regulation 2(1) (b) of Securities and Exchange Board of India (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
- Meaning – It refers to any privately pooled investment fund, (whether from Indian or foreign sources), in the form of a trust or a company or a body corporate or a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP).
- They include angel funds, commodities, real estate, venture capital, private equity, etc.
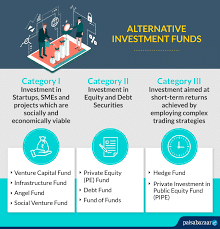
- Categories of AIFs
- Category I: Mainly invests in start- ups, SME’s or any other sector which Govt. considers economically and socially viable
- Category II: private equity funds or debt funds for which no specific incentives or concessions are given by the government or any other Regulator
- Category III : hedge funds or funds which trade with a view to make short term returns or such other funds which are open ended and for which no specific incentives or concessions are given by the government
Benefits of AIF:
- Security against volatility – These schemes do not put their funds in investment options that trade publicly. Hence, they are not related to the broader markets and do not fluctuate with their ups and downs.
- Excellent portfolio diversification to a wide array of assets
- Profitable returns – as these funds have numerous investment options, They are a better source of passive income. Further, returns are less prone to fluctuations as these schemes are not linked to the stock market.
Credit Default Swap (CDS)
- They are a type of insurance, introduced by JP Morgan
- It is used for hedging counter-party concentration risk and credit risks
- It is a contract between two parties, called protection buyer and protection seller against default risk by a particular company.
- The company is called the reference entity and the default is called credit event.
- Under the contract, the protection buyer is compensated for any loss emanating from a credit event in a reference instrument. In return, the protection buyer makes periodic payments to the protection seller.
- In the credit event, the buyer receives the face value of the bond or loan from the protection seller.
- From the seller’s perspective, CDS provides a source of easy money if there is no credit event.
- If the credit event does not occur before the maturity of the loan, the protection seller does not make any payment to the buyer.
- The settlement of the CDS takes place either through cash settlement or physical settlement.
- There are different varieties of CDS, like binary CDS, basket CDS, contingent CDS and dynamic CDS.
- There are different types of credit events such as bankruptcy, failure to pay, and restructuring.
- Asset-backed securities (ABS) is the most common type of CDS.
- CDS can be structured either for the event of shortfall in principal or shortfall in interest. There are three options for calculating the size of payment by the seller to the buyer.
- Fixed cap: The maximum amount paid by the protection seller is the fixed rate.
- Variable cap: The protection seller compensates the buyer for any interest shortfall and the limit set is Libor plus fixed pay.
- No cap: In this case, the protection seller has to compensate for shortfall in interest without any limit.
Calculation:
- The modelling of the CDS price is based on modelling the probability of default and recovery rate in the event of a credit event.
- The value of CDS for the protection buyer = Expected present value of the contingent leg – Expected present value of fixed leg
- In the real world, modelling of the CDS price is difficult because of the problem in computing default probabilities and default correlation.
Uses:
- Although used for hedging credit risks, credit default swap (CDS) has been held culpable for vitiating financial stability of an economy.
- This is particularly attributable to the capital inadequacy of the protection sellers.
- When big protection sellers are inadequately capitalised, the over-the-counter (OTC) CDS market raises its ugly head.
Source: Financialexpress
Doppler Weather Radar Network

Context
Union Minister of State Science & Technology; Minister of State Earth Sciences; MoS PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy and Space said, Entire Country will be covered by Doppler Weather Radar Network by 2025
- According to the Annual Statement on Climate of India 2022 issued by the India Meteorological Department (IMD), 2,227 extreme weather-related deaths in India.
Doppler Weather Radar Network:
- Aim – to predict extreme weather events more accurately.
- Doppler radar is a specialized tracking system that uses the Doppler effect to track weather conditions and calculate information about the location and velocity of a storm or other forms of extreme weather events.
- Forecasting with the help of doppler radar is more timely and accurate which can be critical during safe evacuations in the likelihood of extreme weather events.
- IMD has augmented Doppler Weather Radar network in HP, Uttarakhand, Ladakh and J&K which will help further to predict extreme weather events more accurately.
- Accuracy has increased by about 20-40% for different severe weather events forecast during last five years by making best use of Space based observation of INSAT-3D and 3DR, OceanSat satellites for prediction
Benefits:
- Warning and advisory services are helping farmers and fishermen to improve their economy as found from a latest survey by National Centre for Applied Economic Research. For example, the investment in monsoon mission programme has resulted in return of 50 rupees for investment of each one rupee.
- Farmers below the poverty line specially have benefited immensely as Agromet Advisories at District and Block Levels are used effectively by crores of farmers during various stages of farming and the service is being expanded.
- Climate Services are very important for short and long term planning and strategy development
- Soon a National Framework will be created on priority to provide climate products and information for Sectoral applications.
Other initiatives:
- Flash Flood Guidance in 2021 has been augmented further by increasing the number of watersheds from 30,000 to 1,00,000 of the country in 2022.
- It is being provided every 6 hours to Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka apart from our national use.
- The web GIS services launched by IMD in 2021 have been augmented further with addition of hazard and vulnerability element in collaboration with other state and central agencies is helping the public, disaster managers and stakeholders to initiate timely response action to mitigate the disasters further
Doppler effect
- Doppler Effect refers to the change in Wave Frequency during the relative motion between a wave source and its observer.
- It was discovered by Christian Johann Doppler who described it as the process of increase or decrease of starlight that depends on the relative movement of the star.
- Doppler Effect works on both light and sound objects.
- For instance, when a sound object moves towards you, the frequency of the sound waves increases, leading to a higher pitch.
- Conversely, if it moves away from you, the frequency of the sound waves decreases and the pitch comes down.
- The drop in pitch of ambulance sirens as they pass by and the shift in red light are common examples of the Doppler Effect.
- Edwin Hubble made the discovery that the universe expands as a consequence of the Doppler Effect. It has important applications in the fields of astronomy and space technology.
- The use of Doppler Effect in astronomy in relation to light waves depends on the fact that the spectra of stars are not constant.
- Different stars exhibit different absorption lines at defined frequencies, but Doppler Effect is identifiable only when these absorption lines are away from these defined frequencies.
- There are various applications of Doppler Effect. It is used in:
- Sirens
- Astronomy
- Radar
- Medical imaging and blood flow managemen
- Flow management
- Velocity profile management
- Satellite communication
- Audio
- Vibration measurement
Source: PIB
|
38 videos|5264 docs|1112 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th January 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What are the key topics covered in GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific strategies to answer questions in GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. How much weightage do GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III carry in the UPSC exam? |  |























