UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 6th February 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Who was Sant Guru Ravidas?

Context
The President of India has greeted fellow citizens on the eve of the birth anniversary of Sant Guru Ravidas.
Guru Ravidas
- Ravidas was an Indian mystic poet-saint of the Bhakti movement and founder of the Ravidassia religion during the 15th to 16th century CE.
- Venerated as a guru (teacher) in the region of Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and mainly Punjab and Haryana. He was a poet-saint, social reformer and spiritual figure.
- The life details of Ravidas are uncertain and contested. Scholars believe he was born in 1450 CE, in the cobbler caste.
- Ravidas’s devotional verses were included in the Sikh scriptures known as Guru Granth Sahib.
- The Panch Vani text of the Dadupanthi tradition within Hinduism also includes numerous poems of Ravidas.
- He taught the removal of social divisions of caste and gender and promoted unity in the pursuit of personal spiritual freedoms.
Why his preaching is important?
- Philosophy and values of Sant Ravidas like social justice, equality and fraternity have been imbued in our constitutional values.
- He had envisaged a society that is based on equality and free from any kind of discrimination.
- He gave it the name ‘Be-gampura’ (a city near Lahore) where there is no place for any kind of grief or fear.
- Such an ideal city would be bereft of fear, vulnerability or scarcity. Rule of law based on the right ideas like equality and welfare of all would be the principle for governance.
Source: Indian Express
What is Dhamaal?

Context
The story of Dhamaal performance traditions reveals the rich and complex mixing of cultures in a world shaped by human movement and history
About Dhamaal:
- Dhamaal is a mix of Sufi and African (mostly East African) musical and dance
- It refers particularly to the spiritual practices of the Siddis of Gujarat.
- Usually, Dhamaal songs and dances are performed to celebrate the anniversary of the birth and death of spiritual leaders.
- They are performed in two ways
- Dance Dhamaal: It is performed in both sitting and dance positions and the focus is more on the sounds of the instruments.
- Baithaaki Dhamaal: is performed in the sitting position and the focus is more on the lyrics and less on the musical instruments.
- The spiritual songs that are sung during the Dhamaals are known as zikrs.
Key facts about Siddis
- The term Siddi refers to Afro-Indians— Africans who mixed with Indians through marriage and relationships.
- They crossed the Indian Ocean and arrived in India during the 12th, 13th and 14th century
- They were transported by Islamic invaders and Portuguese colonisers as enslaved people, palace guards, army chiefs, harem keepers, spiritual leaders, Sufi singers, dancers and treasurers.
- In the present day, the majority of them are found in the west and southwest of India, in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Telangana states.
GS-II
73rd establishment day of Supreme Court

Context
This year’s event is being aired on social media platforms and will witness Singapore’s Chief Justice Sundaresh Menon, who is of Indian origin, as the chief guest.
When was the Supreme Court founded?
- On January 28, 1950, two days after India became a sovereign democratic republic, the Supreme Court of India came into being.
- The first CJI of India was H. J. Kania.
- The inauguration took place in the Chamber of Princes in the Parliament building which was the home to the Federal Court of India for 12 years preceding the Supreme Court’s establishment.
- The Parliament House was to be the home of the Supreme Court for years that were to follow until the court acquired its own present building with lofty domes and its signature spacious colonnaded verandas in 1958.
History of established
- In 1861, the Indian High Courts Act 1861 was enacted to create high courts for various provinces and abolished Supreme Courts at Calcutta, Madras and Bombay and also the sadar adalats in presidency towns in their respective regions.
- These new high courts had the distinction of being the highest courts for all cases till the creation of the Federal Court of India under the Government of India Act 1935.
- The Federal Court had jurisdiction to solve disputes between provinces and federal states and hear appeals against judgment of the high courts.
Premise of the Supreme Court
- In 1958, when the court shifted its premises, the building was shaped to project the image of scales of justice, in the central wing.
- In 1979, two new wings – the East wing and the West wing – were added to the complex. In all, there are 19 Courtrooms in the various wings of the building.
- The Chief Justice’s Court is the largest of the Courts located at the Centre of the Central Wing.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Startup India Seed Fund Scheme

Context
Recently, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has approved Rs. 477.25 crore under the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS), which is a flagship Scheme under Startup India Initiative.
- Seed Funding is an early stage of investment in a start-up or a new business idea. The goal of seed funding is to help the company reach a point where it can secure additional rounds of funding or generate revenue to become self-sustaining.
What is the Startup India Initiative?
- The Startup India initiative envisages building a robust Start-up ecosystem in the country for nurturing innovation and providing opportunities to budding entrepreneurs.
- Under the Initiative, an Action Plan of 19 Action Points was unveiled by the Prime Minister in January, 2016.
- This Action Plan laid down a roadmap for the creation of a conducive ecosystem for Startups in India.
- The flagship schemes under Startup India initiative namely, Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS), SISFS and Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS) extend support to startups at various stages of their business cycle.
What is SISFS?
- About:
- The scheme was announced at Startup India International Summit on 16th January 2021.
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) approved an outlay of Rs. 945 Crore for the period of 4 years starting from 2021-22 to provide financial assistance to startups for Proof of Concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry, and commercialization.
- Execution and Monitoring:
- An Experts Advisory Committee (EAC) has been constituted by DPIIT, which will be responsible for the overall execution and monitoring of the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme.
- The EAC will evaluate and select incubators for allotment of Seed Funds, monitor progress, and take all necessary measures for efficient utilization of funds towards fulfilment of objectives of Startup India Seed Fund Scheme.
- Eligibility:
- A startup, recognized by DPIIT (Ministry of Commerce and Industry), incorporated not more than 2 years ago at the time of application.
- Startups should not have received more than Rs. 10 lakhs of monetary support under any other Central or State Government scheme.
- Preference would be given to startups creating innovative solutions in sectors such as social impact, waste management, water management, financial inclusion, education, agriculture, food processing, biotechnology, healthcare, energy, mobility, defence, space, railways, oil and gas, textiles, etc.
- Grants and Support:
- It will support an estimated 3,600 entrepreneurs through 300 incubators in the next 4 years.
- Grants of upto Rs. 5 crores will be provided to the eligible incubators selected by the committee.
- The selected incubators will provide grants of up to Rs. 20 lakhs for validation of proof of concept, or prototype development, or product trials to startups.
- Investments of up to Rs. 50 lakhs will be provided to the startups for market entry, commercialization, or scaling up through convertible debentures or debt-linked instruments.
What is the Need for Seed Fund?
- Easy availability of capital is essential for entrepreneurs at the early stages of growth of an enterprise.
- The Indian startup ecosystem suffers from capital inadequacy in the seed and ‘Proof of Concept’ development stage.
- The capital required at this stage often presents a make-or-break situation for startups with good business ideas.
- Many innovative business ideas fail to take off due to the absence of this critical capital required at an early stage for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry and commercialization.
- Seed Fund offered to such promising cases can have a multiplier effect in validation of business ideas of many startups, leading to employment generation.
Source: PIB
What is the North Star?
Context
Vice President said Parliament is the “North Star” of democracy, “a place of discussion and deliberation to realize the aspirations and dreams of the people”.
What is North Star?
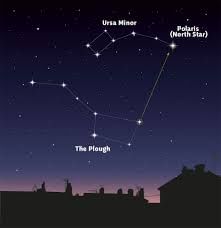
- North Star is a metaphor to refer to something constant/permanent that leads and provides direction.
- Polaris, also known as the North Star or the Pole Star, is a very bright star (around 2500 times more luminous than our sun) placed less than 1° away from the north celestial pole.
- Its position and brightness have made humans use it for navigation since late antiquity.
- It is a part of the constellation Ursa Minor and is around 323 light-years away from Earth.
How it helps navigation?
- It stands almost motionless in the night sky, with all the stars of the northern sky appearing to rotate around it.
- This makes it an excellent fixed point from which to draw measurements for celestial navigation.
- Simply the elevation of the star above the horizon gives the approximate latitude of the observer and in the northern hemisphere, if you can see Polaris you can always tell which way is north.
- Upon crossing the equator to the South, the North Star is lost over the horizon and hence stops being a useful navigational aid.
When the North Star was first used to navigate?
- Polaris seems to have been first charted by the Roman mathematician and astronomer Ptolemy, who lived from about 85 to 165 B.C.
- While there does exist some evidence pointing at how the star was used for navigation in late antiquity, it is during the ‘Age of Exploration’ that it becomes such a central part of human history.
- Christopher Columbus, on his first trans-Atlantic voyage of 1492, “had to correct (his ship’s bearings) for the circle described by the pole star about the pole”, wrote his son in his biography.
- As European colonizers set sail for exotic locations across the world, the North Star became an ever-so-important feature.
Source: Indian Express
Surveillance Balloon
Context
The United States (US) shot down a Chinese surveillance balloon that has been spotted over US airspace for a couple of days.
What is a Surveillance Balloon?
- About:
- These cheap, quiet and hard-to-reach balloons have been used for reconnaissance purposes, including in conflicts like the American Civil War.
- The practice became widespread during World War I and was used extensively during the Cold War when the US launched hundreds of balloons to gather intelligence on the Soviet Union and China.
- While their use has declined with the rise of unmanned drones and satellites, many countries still employ spy balloons.
- The Purpose of Sending the Balloon:
- China has for decades complained about US surveillance by ships and spy planes near its own territory, leading to occasional confrontations over the years. According to China, the balloon was for research but got off track.
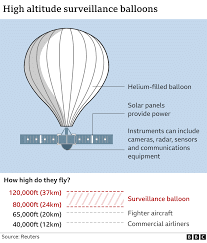
- Close-range Monitoring: In the age of satellites, surveillance balloons which are typically advanced balloons equipped with high-tech, downward-pointing imaging gear offer close-range monitoring.
- Image Quality: The lower-flying balloons, which hover at about the same height as commercial airlines fly, can typically take clearer images than the lowest orbiting satellites.
- Satellites that rotate in sync with Earth capture continuous but hazier images due to farther orbit.
- Intercepting Communication: Surveillance balloons can also be capable of “gathering electronic signals” and intercepting communications.
- Electronic Surveillance: It can be used in intercepting communication signals, tapping phone calls, and monitoring emails and other forms of digital communication.
- Human Intelligence (HUMINT): It is one of the main components used in surveillance by recruiting individuals with access to sensitive information, such as embassy staff, military personnel, or government officials.
- Cyber Espionage: It is a form of cyber-attack that steals classified, sensitive data or intellectual property to gain an advantage over a competitive company or government entity.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites are sometimes used to gather information about foreign countries.
- Drone Technology: Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can be used for surveillance and espionage purposes. Drones equipped with cameras, listening devices, and other sensors can fly over foreign territories and gather intelligence.
- About:
- Air space, in international law, is the space above a particular national territory, treated as belonging to the government controlling the territory.
- It does not include outer space, which, under the Outer Space Treaty of 1967 is declared to be free and not subject to national appropriation.
- The treaty, however, did not define the altitude at which outer space begins and air space ends.
- Air Sovereignty:
- It is the fundamental right of a sovereign state to regulate the use of its air space and enforce its own aviation law.
- The State controls the entry of foreign aircraft into its territory and that persons within its territory are subject to its laws.
- The principle of air space sovereignty is established through the Paris Convention on the Regulation of Aerial Navigation (1919) and subsequently by other multilateral treaties.
- Under the 1944 Chicago Convention, contracting states agree to permit aircraft registered in the other contracting states and engaged in commercial non-scheduled flights to fly into their territory without prior diplomatic permission and, moreover, to pick up and discharge passengers, cargo, and mail.
- This provision, in practice, has become a dead letter.
- Prohibited Air Space:
- It refers to an area of air space within which flight of aircraft is not allowed, usually due to security concerns. It is one of many types of special use airspace designations and is depicted on aeronautical charts with the letter "P" followed by a serial number.
- Restricted Air Space:
- Different from prohibited air space, in this space, entry is typically forbidden for all aircraft and is not subjected to clearance from ATC (Air Traffic Control) or the air space's controlling body.
Source: Indian Express
What is Wolf 1069 b?

Astronomers have recently discovered Wolf 1069 b, an Earth-mass exoplanet that could potentially be habitable.
About Wolf 1069 b:
- It is a potentially habitable exoplanet 31 light-years away from Earth.
- It orbits a red dwarf star, Wolf 1069.
- Wolf 1069 b lies within its star’s habitable zone.
- Wolf 1069 b receives approximately 65% of the solar radiance that Earth receives.
- Wolf 1069 b is potentially a rocky world, at about 26 the mass of Earth and 1.08 the size.
- Its surface is cool, which makes it appear orange.
- Wolf 1069 b is tidally locked to its parent star, meaning one side is always in daylight, and the opposite side is always in darkness.
- It orbits the star within 15.6 days at a distance equivalent to one-15th of the separation between the Earth and the sun.
What is a dwarf star?
- A dwarf star is any star of average or low luminosity, mass, and size.
- The colour of dwarf stars can range from blue to red, the corresponding temperature varying from high (above 10,000 K) to low (a few thousand K).
Source: PIB
What is Dearness Allowance (DA)?

Context
The Central government is likely to increase the dearness allowance (DA) for its over one crore employees and pensioners by four percentage points to 42% from the existing 38%.
About Dearness Allowance (DA):
- What is it? DA is a cost of living adjustment that the Government pays to public sector employees and pensioners.
- Why is DA paid? To curb the effect of inflation.
- How is DA calculated?
- It is calculated as a percentage of the basic salary.
- DA for Central Government employees is calculated differently than that of public sector employees.
- The formula to calculate the DA was changed in 2006 by the Government.
- DA % for Central Govt Employees = {(All-India Consumer Price Index average (Base year 2001 =100) for the last 12 months -115.76)/115.76} x 100
- DA % for Public Sector Employees = {(All-India Consumer Price Index Average (Base year 2001 =100) for the last 3 months - 126.33)/126.33} x 100
- Since DA is based on the cost of living, this salary component is not fixed. DA varies from employee to employee based on their presence in the urban, semi-urban, or rural sectors.
- Taxability:
- DA is fully taxable for individuals who are salaried employees.
- It is compulsory to declare the tax liability concerning DA when filing an ITR.
- Types of DA:
- Variable Dearness Allowance (VDA):
- VDA applies to Central government employees.
- It undergoes revision every six months based on the changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- Industrial Dearness Allowance (IDA):
- IDA applies to the Public sector employees of the Central Government.
- IDA is revised every quarter based on the changes in CPI.
- Variable Dearness Allowance (VDA):
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5254 docs|1109 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 6th February 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the GS-I exam? |  |
| 2. What are the subjects covered in GS-II? |  |
| 3. When is the UPSC Civil Services Examination conducted? |  |
| 4. How can I prepare for the GS-III exam? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of daily current affairs for UPSC preparation? |  |
















